Blount’s disease (BD) is an orthopedic childhood disorder characterized by outward bowing of the leg Leg The lower leg, or just "leg" in anatomical terms, is the part of the lower limb between the knee and the ankle joint. The bony structure is composed of the tibia and fibula bones, and the muscles of the leg are grouped into the anterior, lateral, and posterior compartments by extensions of fascia. Leg: Anatomy due to abnormal ossification Ossification The process of bone formation. Histogenesis of bone including ossification. Bones: Development and Ossification of the medial aspect of the tibial epiphysis Epiphysis The head of a long bone that is separated from the shaft by the epiphyseal plate until bone growth stops. At that time, the plate disappears and the head and shaft are united. Bones: Structure and Types. Blount’s disease mostly affects children of African descent and tends to debut at approximately 1–3 years of age. Diagnosis is made by clinical findings and is confirmed by imaging. The goal of treatment is to correct the anatomy through bracing or surgical repair, according to the severity and age of the patient at diagnosis. The prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas is excellent if treatment is promptly started.
Last updated: Jan 13, 2025
Blount’s disease (BD) is the progressive bowing of the legs produced by abnormal ossification Ossification The process of bone formation. Histogenesis of bone including ossification. Bones: Development and Ossification at the medial aspect of the tibial epiphysis Epiphysis The head of a long bone that is separated from the shaft by the epiphyseal plate until bone growth stops. At that time, the plate disappears and the head and shaft are united. Bones: Structure and Types.
The exact cause of BD is not known and is believed to be multifactorial or due to a combination of hereditary and developmental factors:
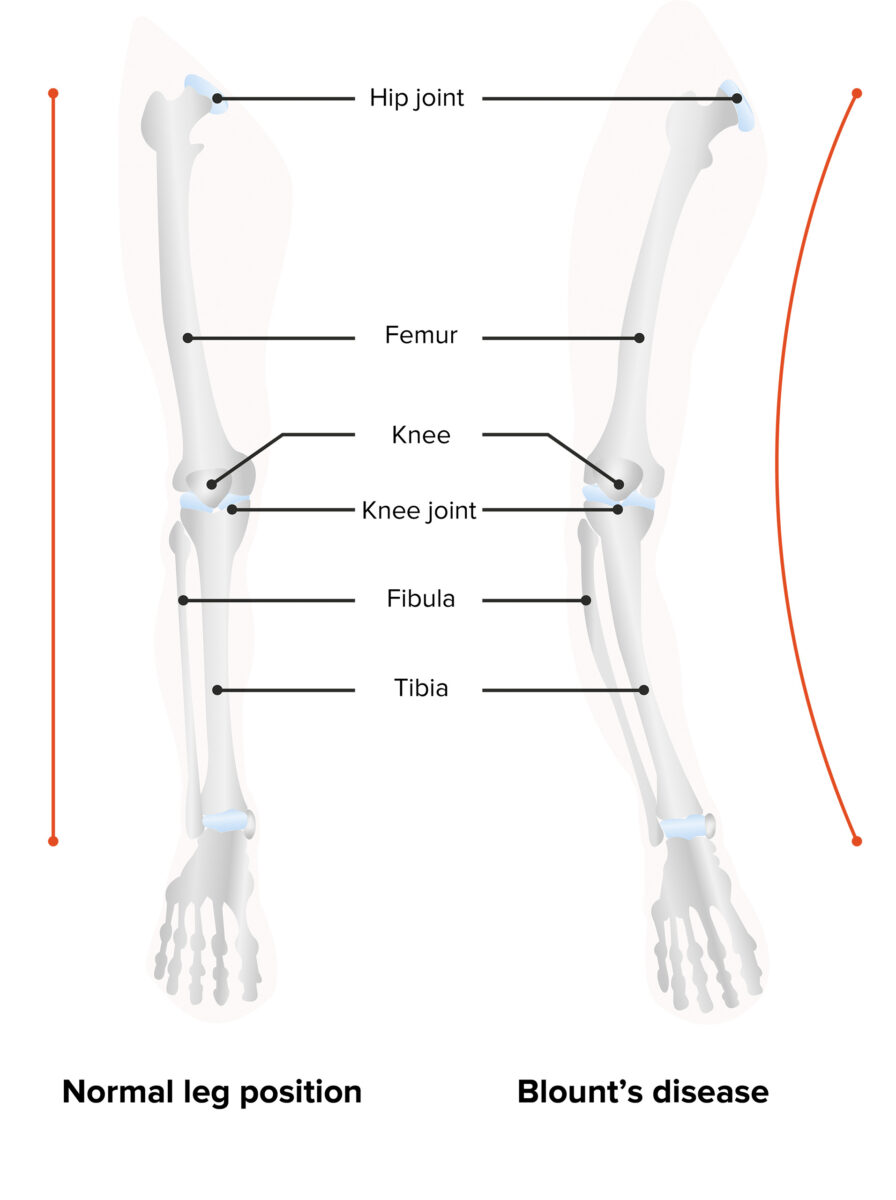
Blount’s disease: varus deformity and backward bending of the leg
Image by Lecturio.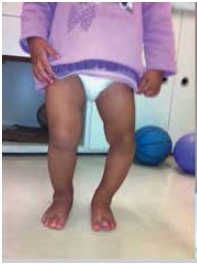
Left leg with varus deformity
Image: “Blount’s disease” by Universidade de São Paulo, Faculdade de Medicina, Hospital das Clínicas, Instituto de Ortopedia e Traumatologia, São Paulo, SP, Brazil. License: CC BY 4.0, edited by Lecturio.| Early BD | Late BD |
|---|---|
| No pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways | Pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways in the tibial area |
| Bilateral | Unilateral |
| Significant deformity Deformity Examination of the Upper Limbs | Mild deformity Deformity Examination of the Upper Limbs |
| Associated with early ambulation | Associated with obesity Obesity Obesity is a condition associated with excess body weight, specifically with the deposition of excessive adipose tissue. Obesity is considered a global epidemic. Major influences come from the western diet and sedentary lifestyles, but the exact mechanisms likely include a mixture of genetic and environmental factors. Obesity |
The diagnosis of BD is achieved through medical history, physical examination, and confirmation via imaging studies.
Severity is based on the metaphyseal-diaphyseal angle (MDA):
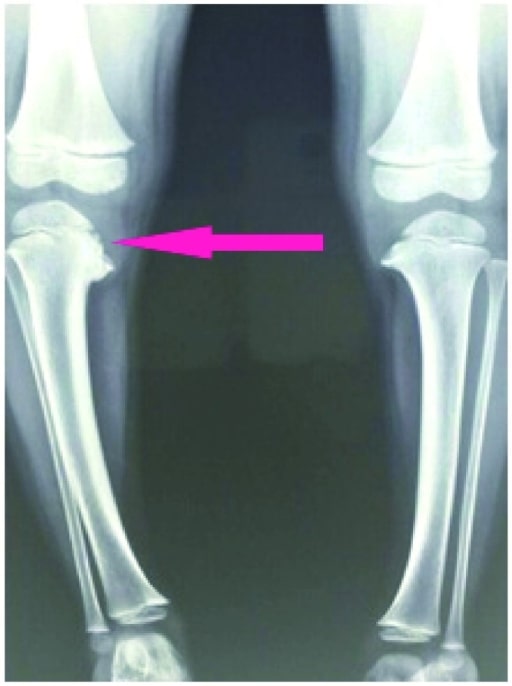
Knee X-ray shows depression of the medial tibial plateau with beaking of the posteromedial tibial physis (pink arrow).
Image: “X-ray” by US National Library of Medicine. License: CC BY 4.0The age of the patient and the severity of the deformity Deformity Examination of the Upper Limbs determine the type of management.
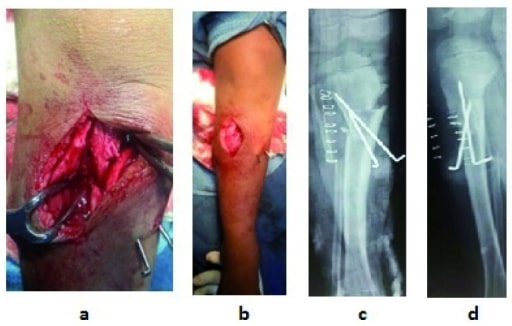
Osteotomy: intraoperative (a) and postoperative (b) with X-rays; post-surgery (c, d)
Image: “f5” by US National Library of Medicine. License: CC BY 4.0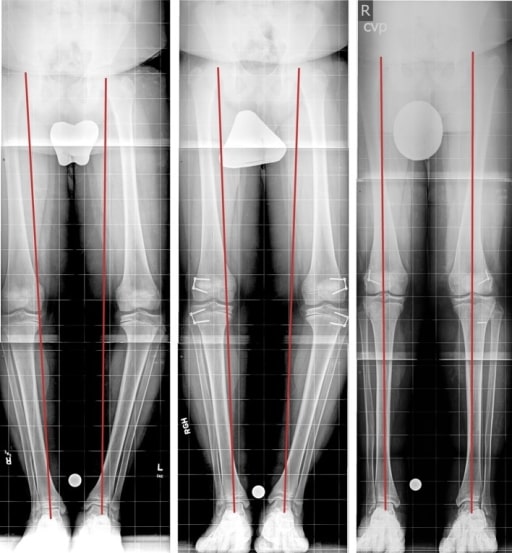
Late bilateral BD treated by hemiepiphysiodesis: The right-most image is diagnostic, the center image is after 3 months of treatment, and the left image is the last follow-up with correction.
Image: “Fig3” by Rubin Institute for Advanced Orthopedics, Sinai Hospital of Baltimore, 2401 West Belvedere Avenue, Baltimore, MD, 21215, USA. License: CC BY 4.0