Blotting techniques involve the separation (via electrophoresis) and transfer of DNA, RNA, or proteins onto a blotting membrane. The target DNA is then attached to a molecule in order to aid detection. Southern blotting is used to evaluate for specific DNA sequences and may be used in identification of genetic mutations and in forensics. Northern blotting focuses on RNA sequences and is helpful in assessing gene expression. Western blotting identifies proteins and antibodies and has applications in diagnosing infectious diseases, protein abnormalities (such as prion disease), and autoimmune conditions. Although these tests have good specificity, they have significant disadvantages owing to their expense, labor-intensiveness, and slow turnaround time.
Last updated: Apr 27, 2025
Blotting is an investigative technique used to detect and identify macromolecules, such as nucleic acids Acids Chemical compounds which yield hydrogen ions or protons when dissolved in water, whose hydrogen can be replaced by metals or basic radicals, or which react with bases to form salts and water (neutralization). An extension of the term includes substances dissolved in media other than water. Acid-Base Balance and proteins Proteins Linear polypeptides that are synthesized on ribosomes and may be further modified, crosslinked, cleaved, or assembled into complex proteins with several subunits. The specific sequence of amino acids determines the shape the polypeptide will take, during protein folding, and the function of the protein. Energy Homeostasis. This technique is accomplished by:
The 4 basic types of blotting are
| Technique | Southern blot | Northern blot | Western blot |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target | DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure sequences | RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure sequences | Protein |
| Separation | Electrophoresis | Electrophoresis | Electrophoresis |
| Blotting method | Capillary transfer | Capillary transfer | Electrophoretic transfer |
| Probe Probe A device placed on the patient’s body to visualize a target Ultrasound (Sonography) | Oligonucleotides | Oligonucleotides | Antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions |
| Common detection methods |
|
|
|
All blotting techniques use electrophoresis, which involves using an electrical field to separate molecules.
Blotting techniques follow a general procedure:
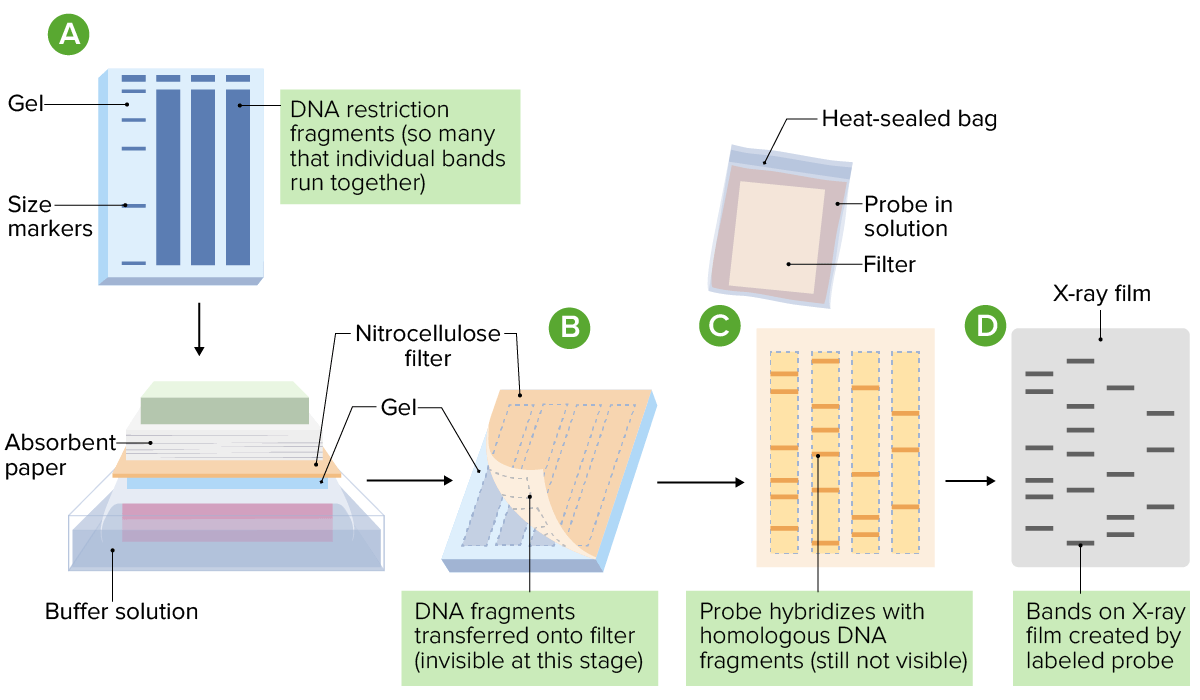
Procedure for Southern blotting:
A: DNA is cleaved with restriction enzymes and separated via electrophoresis.
B: DNA fragments are blotted onto a nitrocellulose filter.
C: The filter is exposed to a solution containing a radiolabeled probe, allowing for hybridization with target DNA sequences.
D: Bands on the filter are then exposed to X-ray film for visualization.
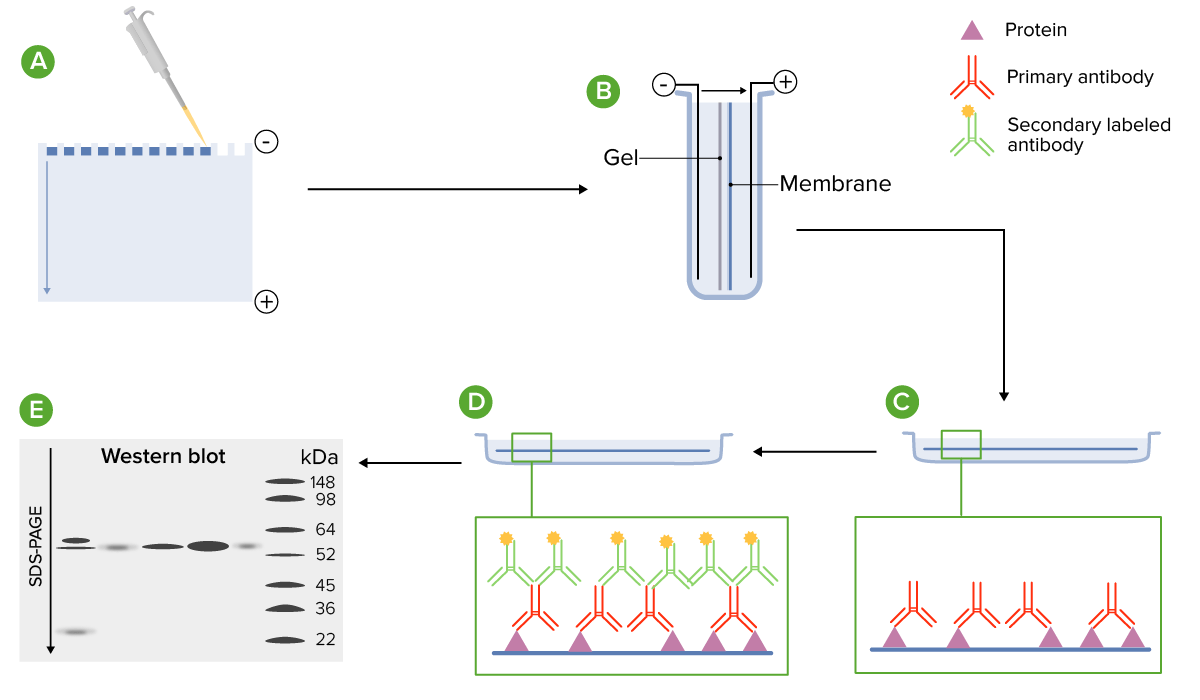
Procedure for Western blotting:
A: Protein samples are loaded onto a gel and separated via electrophoresis.
B: The separated proteins are electrophoretically transferred onto a membrane.
C: The membrane is incubated with a primary antibody that is specific to the target protein, which allows formation of antibody–antigen complexes.
D: The membrane is incubated again with labeled secondary antibodies, which bind to the primary antibodies.
E: In this case, a substrate is added that interacts with the labels, allowing for detection via chemiluminescence.
SDS-PAGE: sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
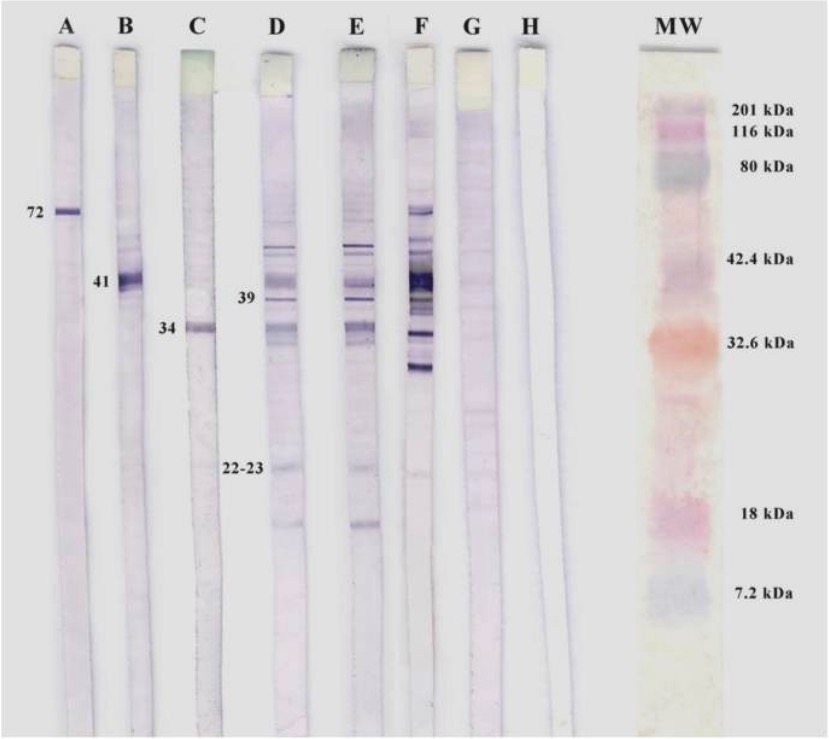
Western blotting of Borrelia burgdorferi:
A, B, and C: Positive controls for specific monoclonal antibodies
D and E: Individuals seropositive for IgM
F: Positive control
G: Negative control
H: White control (phosphate-buffered saline)
MW: molecular weight
Northern blotting can be used to assess RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure levels and gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics expression.
Identification Identification Defense Mechanisms of antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions: