There are 47 blood group systems, among which the ABO group is the most important. Blood groups are determined by antigens that are surface markers on red blood cells Red blood cells Erythrocytes, or red blood cells (RBCs), are the most abundant cells in the blood. While erythrocytes in the fetus are initially produced in the yolk sac then the liver, the bone marrow eventually becomes the main site of production. Erythrocytes: Histology ( RBCs RBCs Erythrocytes, or red blood cells (RBCs), are the most abundant cells in the blood. While erythrocytes in the fetus are initially produced in the yolk sac then the liver, the bone marrow eventually becomes the main site of production. Erythrocytes: Histology) and composed of proteins Proteins Linear polypeptides that are synthesized on ribosomes and may be further modified, crosslinked, cleaved, or assembled into complex proteins with several subunits. The specific sequence of amino acids determines the shape the polypeptide will take, during protein folding, and the function of the protein. Energy Homeostasis and carbohydrates Carbohydrates A class of organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of cn(H2O)n. The largest class of organic compounds, including starch; glycogen; cellulose; polysaccharides; and simple monosaccharides. Basics of Carbohydrates. Antigens are also found on platelets Platelets Platelets are small cell fragments involved in hemostasis. Thrombopoiesis takes place primarily in the bone marrow through a series of cell differentiation and is influenced by several cytokines. Platelets are formed after fragmentation of the megakaryocyte cytoplasm. Platelets: Histology, leukocytes Leukocytes White blood cells. These include granular leukocytes (basophils; eosinophils; and neutrophils) as well as non-granular leukocytes (lymphocytes and monocytes). White Myeloid Cells: Histology, and tissue cells as well as in soluble form in body secretions such as breast milk, seminal fluid, saliva Saliva The clear, viscous fluid secreted by the salivary glands and mucous glands of the mouth. It contains mucins, water, organic salts, and ptyalin. Salivary Glands: Anatomy, sweat, gastric secretions Gastric secretions Gastrointestinal Secretions, urine, and amniotic fluid Amniotic fluid A clear, yellowish liquid that envelopes the fetus inside the sac of amnion. In the first trimester, it is likely a transudate of maternal or fetal plasma. In the second trimester, amniotic fluid derives primarily from fetal lung and kidney. Cells or substances in this fluid can be removed for prenatal diagnostic tests (amniocentesis). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity. Individuals will naturally develop antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions (Abs) against the ABO antigens they do not have. For this reason, determining an individual’s blood group is important prior to any blood product transfusion and prior to donating or receiving an organ transplant. If appropriate matching does not happen, a massive activation of the immune system Immune system The body's defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs and coagulation cascade Coagulation cascade The coagulation cascade is a series of reactions that ultimately generates a strong, cross-linked fibrin clot. Hemostasis will ensue, leading to shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock, organ failure, and even death.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
There are 4 common blood groups in the ABO system: A, B, AB, and O.
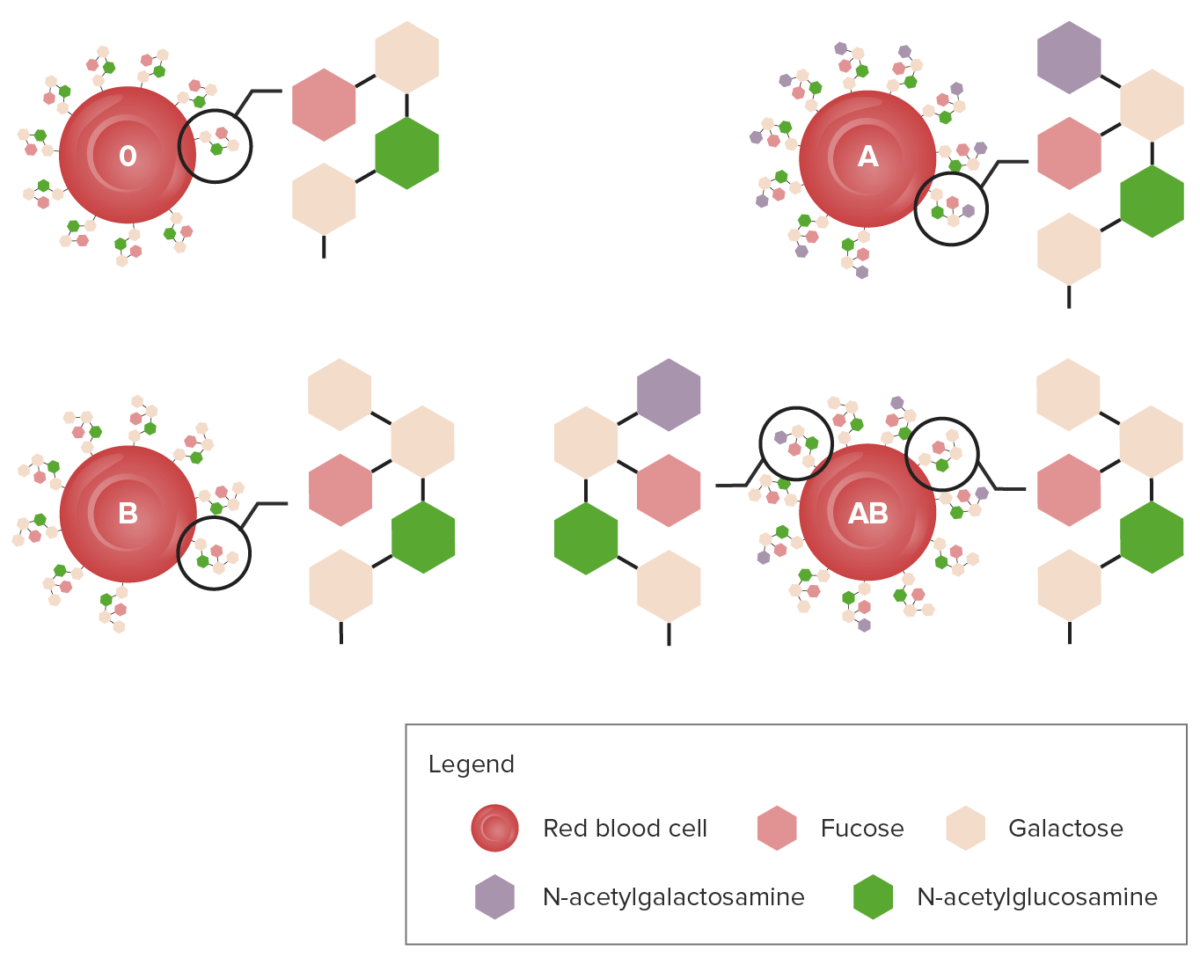
Diagram showing the carbohydrate chains that determine the ABO blood group
Image by Lecturio.Blood-type frequencies vary in different racial/ethnic groups. The ABO blood type is inherited in an autosomal codominant fashion:
| Mother A | Mother B | Mother O | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Father A | AA AA Amyloidosis | AB | AO |
| Father B | BA | BB | BO |
| Father O | OA OA Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis, and is due to cartilage destruction and changes of the subchondral bone. The risk of developing this disorder increases with age, obesity, and repetitive joint use or trauma. Patients develop gradual joint pain, stiffness lasting < 30 minutes, and decreased range of motion. Osteoarthritis | OB | OO |
| Alleles | Blood type |
|---|---|
| A + A | A |
| A + O | A |
| A + B | AB |
| B + B | B |
| B + O | B |
| O + O | O |
Individuals will naturally develop antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions (Abs) against the ABO antigens they do not have:
These Abs can elicit a hemolytic response upon encountering their respective antigen Antigen Substances that are recognized by the immune system and induce an immune reaction. Vaccination:
Blood groups are associated with differential risk to certain diseases. Blood group O may have ↓ risk for:
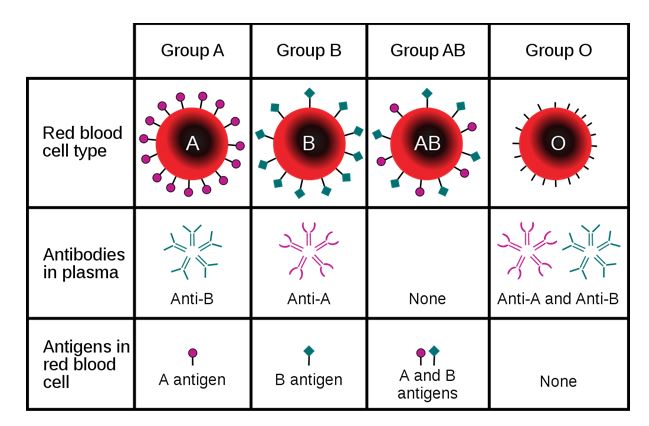
Diagram showing that a person may express A, B, AB, or no antigen at all:
The diagram also describes the type of antibody produced by the carrier.
Rh factor (Rhesus factor) is an RBC surface antigen Antigen Substances that are recognized by the immune system and induce an immune reaction. Vaccination.
Anti-Rh Abs occur when:
If fetus is Rh+ and the mother Rh–, serial monitoring during pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care is needed and is accomplished by:
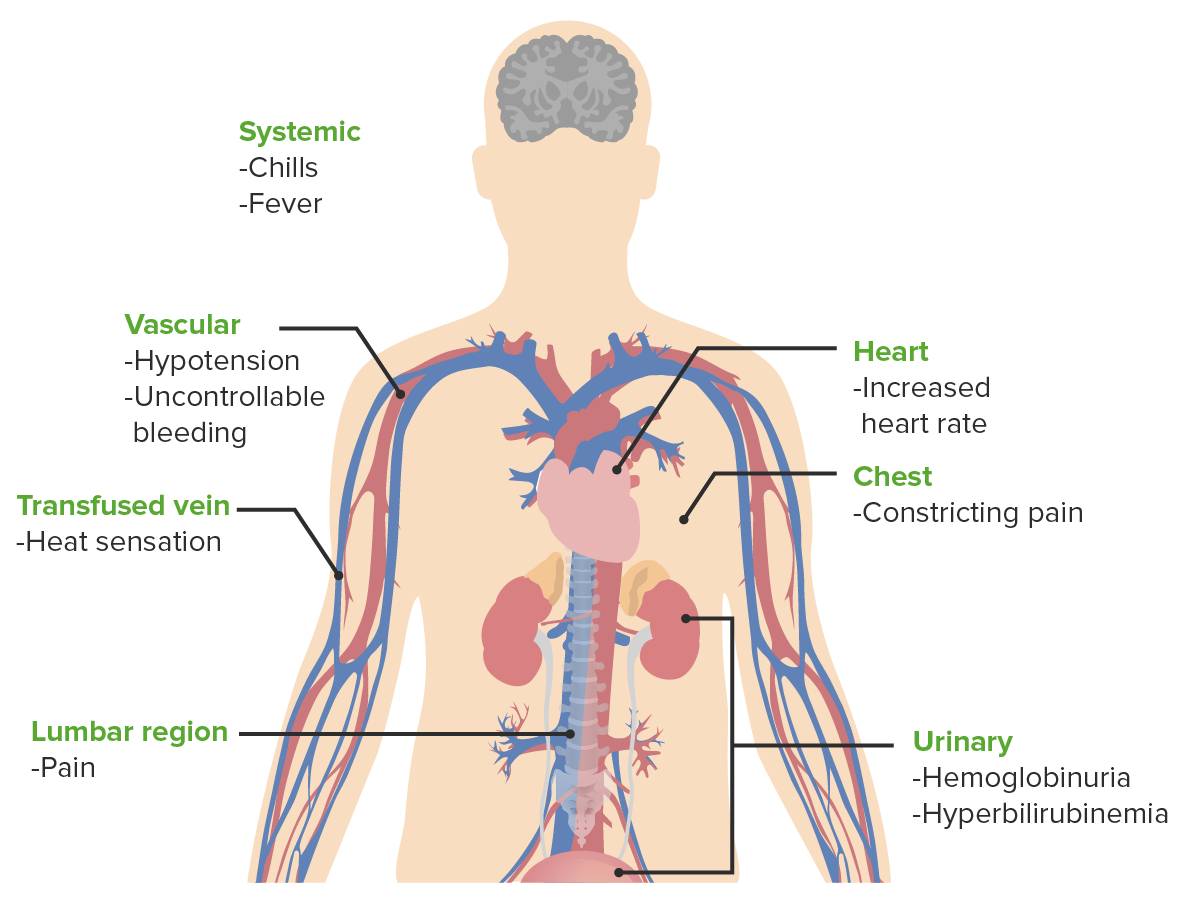
Signs and symptoms of acute hemolytic transfusion reactions
Image by Lecturio.Complications of blood transfusion can be acute (minutes to hours) or delayed (days to months).
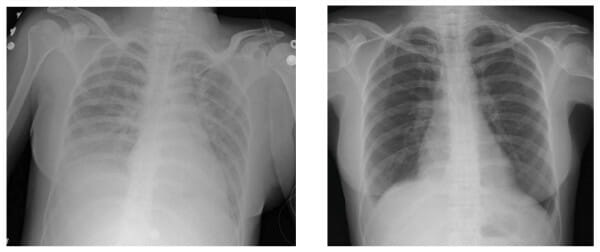
Transfusion-related acute lung injury:
Left: Chest X-ray finding during acute symptoms
Right: Chest X-ray finding after weaning individual from ventilator