Benzodiazepines work on the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A ( GABA GABA The most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNSA) receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors to produce inhibitory effects on the CNS. Benzodiazepines do not mimic GABA GABA The most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS, the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in humans, but instead potentiate GABA GABA The most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS activity. The drug class of benzodiazepines has anxiolytic, muscle-relaxant, hypnotic, sedative, and anticonvulsant Anticonvulsant Anticonvulsant drugs are pharmacological agents used to achieve seizure control and/or prevent seizure episodes. Anticonvulsants encompass various drugs with different mechanisms of action including ion-channel (Na+ and Ca+2) blocking and GABA reuptake inhibition. First-Generation Anticonvulsant Drugs properties. These agents are not generally recommended for long-term use, as patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship can develop physiological and psychological dependence. Side effects may include cognitive impairment, somnolence, and respiratory depression.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
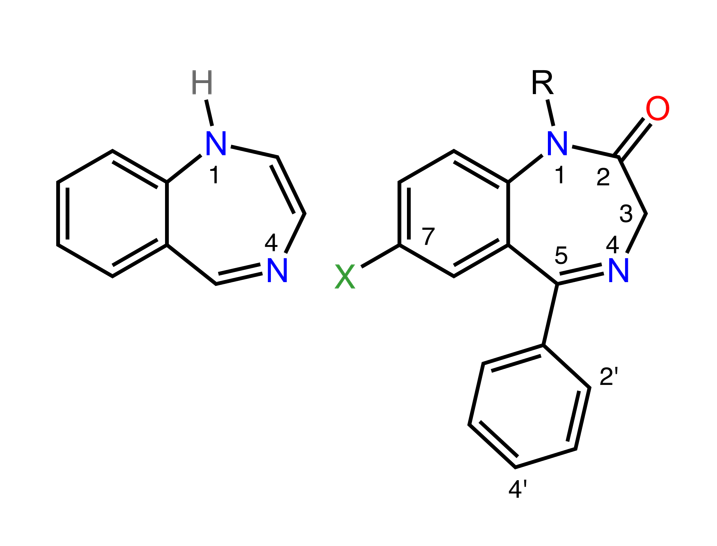
Structure of benzodiazepines:
The image on the left shows the classic 1,4-benzodiazepine ring. The image on the right shows the most common benzodiazepine ring system.
GABA GABA The most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS:
GABA GABA The most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors:
Benzodiazepine therapeutic effects:
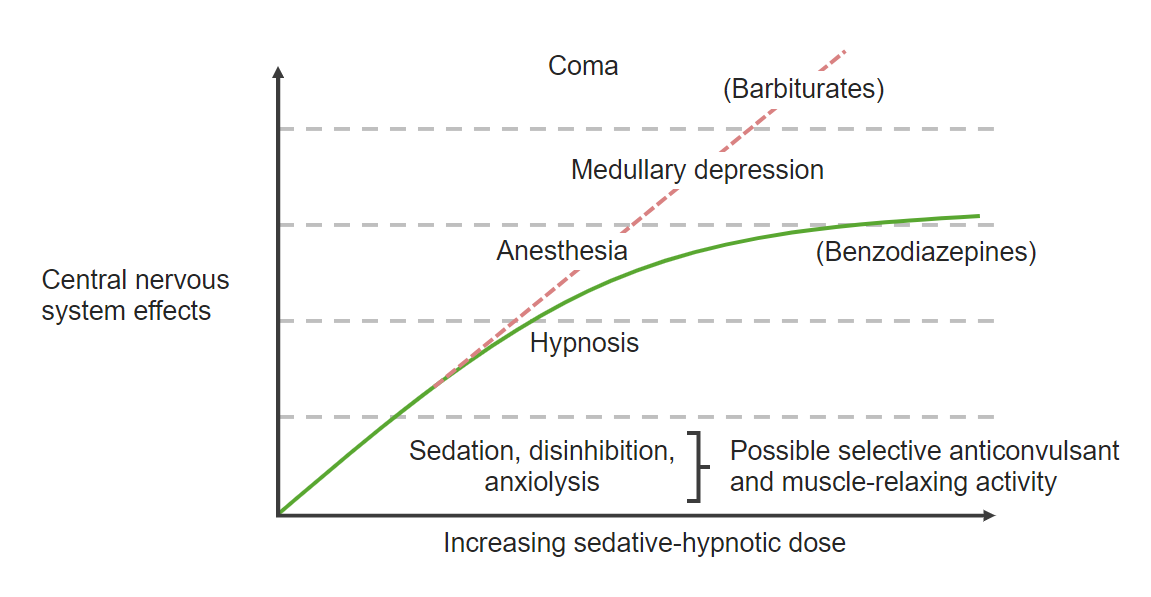
Benzodiazepine dose-response curve:
The dose-response curve for benzodiazepines is shown above. Benzodiazepines exert anxiolytic properties at low doses and have a ceiling effect, in which increasing doses peak at anesthetic effects.
Lipophilic benzodiazepines have a more rapid absorption Absorption Absorption involves the uptake of nutrient molecules and their transfer from the lumen of the GI tract across the enterocytes and into the interstitial space, where they can be taken up in the venous or lymphatic circulation. Digestion and Absorption.
Elimination Elimination The initial damage and destruction of tumor cells by innate and adaptive immunity. Completion of the phase means no cancer growth. Cancer Immunotherapy occurs through the kidney (glucuronides are excreted in the urine).
The table below highlights important benzodiazepine medications and addresses the properties of each. With respect to pharmacokinetics Pharmacokinetics Pharmacokinetics is the science that analyzes how the human body interacts with a drug. Pharmacokinetics examines how the drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted by the body. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics, it is important to pay attention Attention Focusing on certain aspects of current experience to the exclusion of others. It is the act of heeding or taking notice or concentrating. Psychiatric Assessment to the onset of action, metabolism, and elimination Elimination The initial damage and destruction of tumor cells by innate and adaptive immunity. Completion of the phase means no cancer growth. Cancer Immunotherapy.
| Drug | Onset of action | Duration | Metabolism | Major active metabolites |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alprazolam | Intermediate | Intermediate | CYP3A4 CYP3A4 Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers) | No |
| Chlordiazepoxide | Intermediate | Long | CYP3A4 CYP3A4 Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers) | Yes |
| Clonazepam | Intermediate | Intermediate | CYP3A4 CYP3A4 Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers) | No |
| Clorazepate | Rapid | Long | Yes | |
| Diazepam | Rapid | Long |
|
Yes |
| Flurazepam | Rapid | Long | CYP3A4 CYP3A4 Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers) | Yes |
| Lorazepam | Intermediate | Intermediate | Glucuronidation | No |
| Midazolam | Rapid | Short | CYP3A4 CYP3A4 Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers) | Yes |
| Oxazepam | Slow | Short | Glucuronidation | No |
| Temazepam | Slow | Intermediate | Glucuronidation | No |
| Triazolam | Rapid | Short | CYP3A4 CYP3A4 Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers) | No |
Benzodiazepines are CNS depressants. Therefore, they are clinically useful for situations when a sedating agent may be needed. The table below addresses individual agents and their indications. Here are general indications for benzodiazepines:
| Medication | Formulation | Indications |
|---|---|---|
| Alprazolam | Oral |
|
| Chlordiazepoxide | Oral |
|
| Clonazepam | Oral |
|
| Clorazepate | Oral |
|
| Diazepam |
|
|
| Flurazepam | Oral | Insomnia Insomnia Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty in the initiation, maintenance, and consolidation of sleep, leading to impairment of function. Patients may exhibit symptoms such as difficulty falling asleep, disrupted sleep, trouble going back to sleep, early awakenings, and feeling tired upon waking. Insomnia |
| Lorazepam (Ativan®) |
|
|
| Midazolam (Versed®) |
|
|
| Oxazepam | Oral |
|
| Temazepam (Restoril®) | Oral | Insomnia Insomnia Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty in the initiation, maintenance, and consolidation of sleep, leading to impairment of function. Patients may exhibit symptoms such as difficulty falling asleep, disrupted sleep, trouble going back to sleep, early awakenings, and feeling tired upon waking. Insomnia |
| Triazolam (Halcion®) | Oral | Insomnia Insomnia Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty in the initiation, maintenance, and consolidation of sleep, leading to impairment of function. Patients may exhibit symptoms such as difficulty falling asleep, disrupted sleep, trouble going back to sleep, early awakenings, and feeling tired upon waking. Insomnia |
There are some high-yield points to pay attention Attention Focusing on certain aspects of current experience to the exclusion of others. It is the act of heeding or taking notice or concentrating. Psychiatric Assessment to when considering benzodiazepines:
These drugs rarely lead to overdose in isolation. When combined with other classes of drugs, such as alcohol and opiates Opiates Opiates are drugs that are derived from the sap of the opium poppy. Opiates have been used since antiquity for the relief of acute severe pain. Opioids are synthetic opiates with properties that are substantially similar to those of opiates. Opioid Analgesics, there is a much higher risk for toxicity Toxicity Dosage Calculation.
The following are therapeutic uses of benzodiazepines: