Amino acids Acids Chemical compounds which yield hydrogen ions or protons when dissolved in water, whose hydrogen can be replaced by metals or basic radicals, or which react with bases to form salts and water (neutralization). An extension of the term includes substances dissolved in media other than water. Acid-Base Balance (AAs) are composed of a central carbon atom attached to a carboxyl group, an amino group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (R group). There are hundreds of AAs found in nature, but only 20 are predominantly used as the building blocks of proteins Proteins Linear polypeptides that are synthesized on ribosomes and may be further modified, crosslinked, cleaved, or assembled into complex proteins with several subunits. The specific sequence of amino acids determines the shape the polypeptide will take, during protein folding, and the function of the protein. Energy Homeostasis in humans (proteinogenic). Nine of these 20 are “essential,” as they cannot be synthesized. In addition to the 20 standard AAs, 2 rare proteinogenic amino acids Acids Chemical compounds which yield hydrogen ions or protons when dissolved in water, whose hydrogen can be replaced by metals or basic radicals, or which react with bases to form salts and water (neutralization). An extension of the term includes substances dissolved in media other than water. Acid-Base Balance are also recognized, selenocysteine and pyrrolysine. Amino acids Acids Chemical compounds which yield hydrogen ions or protons when dissolved in water, whose hydrogen can be replaced by metals or basic radicals, or which react with bases to form salts and water (neutralization). An extension of the term includes substances dissolved in media other than water. Acid-Base Balance differ from one another only in the chemical nature of the R group. They are most commonly classified according to their interaction with water as hydrophobic, hydrophilic Hydrophilic Aminoglycosides, or ionic.
Last updated: Apr 24, 2025
Each amino acid ( AA AA Amyloidosis) is composed of one alpha, or central, carbon bonded to:
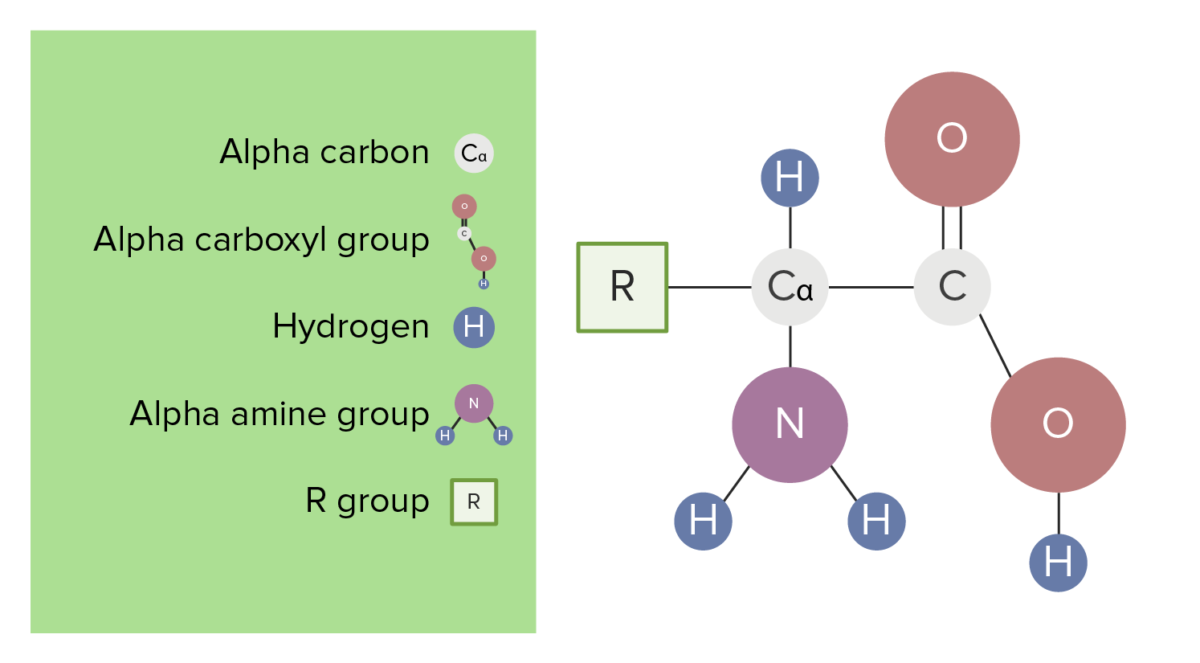
The basic structure of amino acids
Image by Lecturio.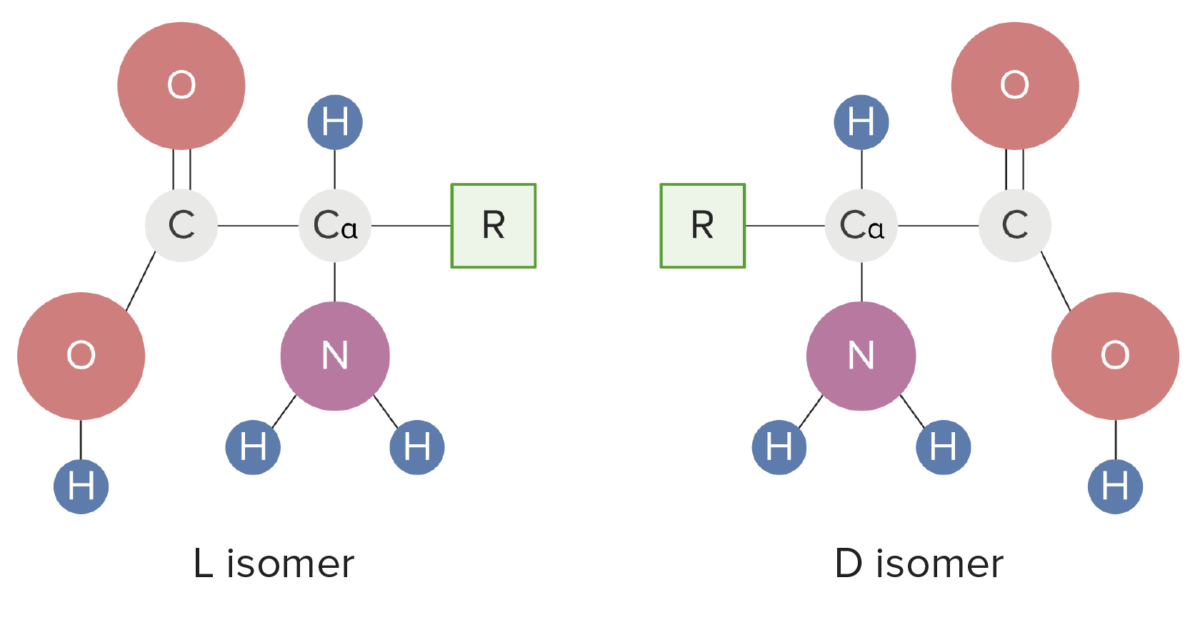
Isomeric forms of amino acids
Image by Lecturio.R groups determine the differences in structure, function, and biological interactions of AAs.
R groups can be classified in 2 ways:
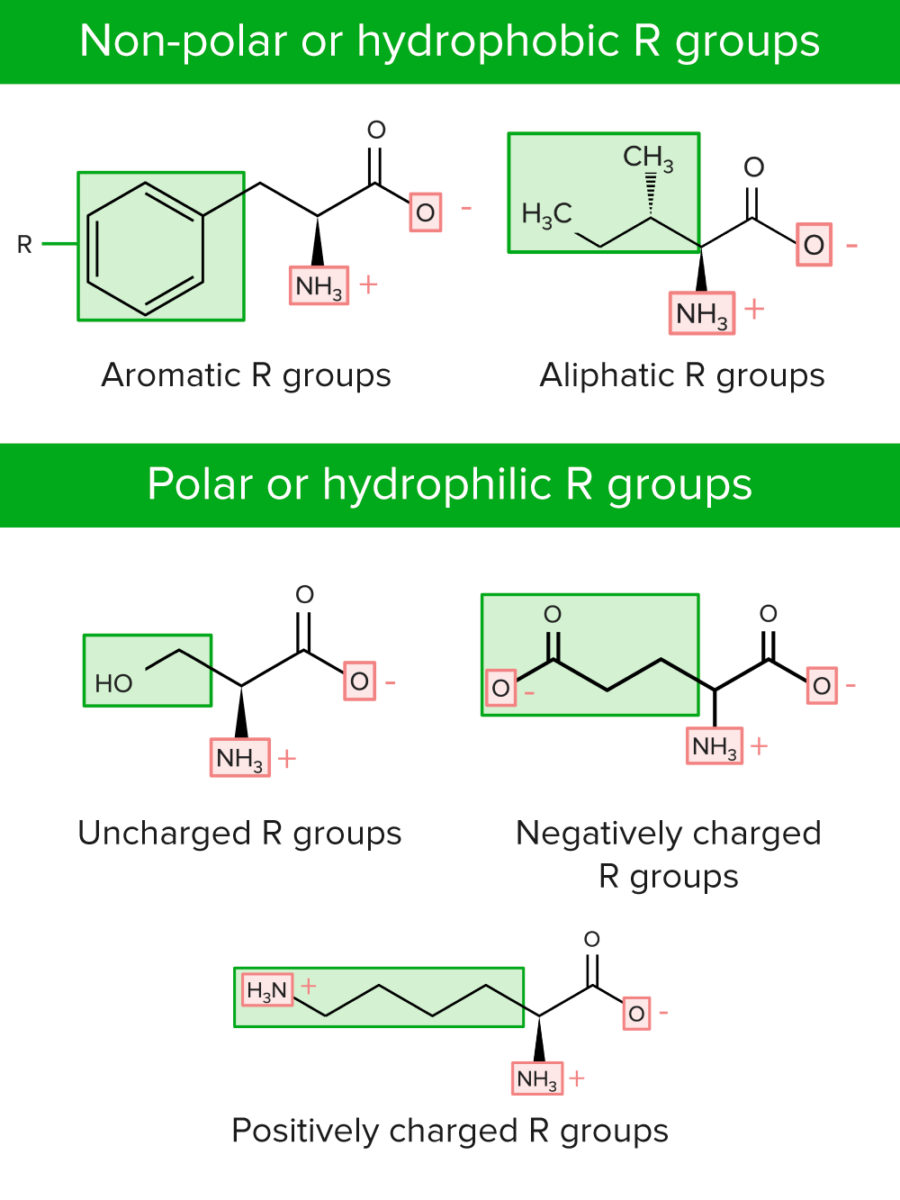
Categories of R groups or side chains of amino acids
Image by Lecturio.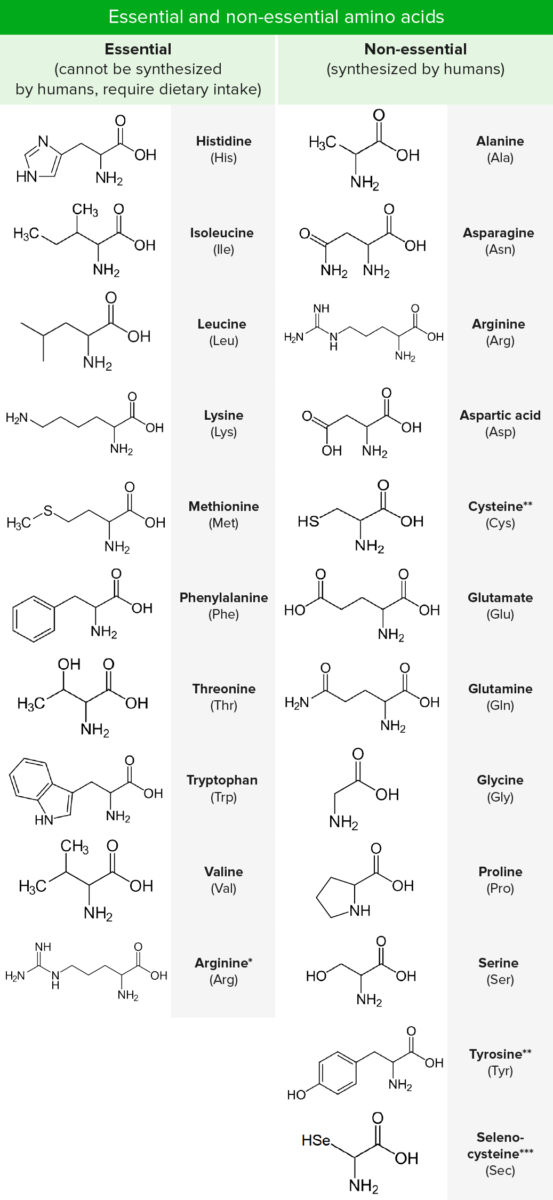
*Required only during periods of growth or positive nitrogen balance.
**Synthesized from essential AAs.
***Cysteine analogue with selenium instead of the usual sulfur. Not directly encoded in the genetic code
| Non-polar or hydrophobic | Polar or hydrophilic Hydrophilic Aminoglycosides | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Aromatic |
|
Positively charged or basic |
|
| Aliphatic |
|
Uncharged |
|
| Negatively charged or acidic |
|
||
In addition to the 20 standard AAs, 2 rare proteinogenic amino acids Acids Chemical compounds which yield hydrogen ions or protons when dissolved in water, whose hydrogen can be replaced by metals or basic radicals, or which react with bases to form salts and water (neutralization). An extension of the term includes substances dissolved in media other than water. Acid-Base Balance are also recognized:

Zwitterion form
Image by Lecturio.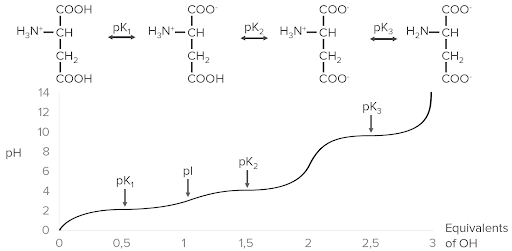
Example of ionization using aspartic acid. At the top are the 4 different forms that can exist with ionization. Notice how as equivalents of hydroxyl (OH), plotted on the x-axis, are added, the pH (y-axis) increases. As pH increases, the pK points are reached and progressively more hydrogen ions (protons) are released from the aspartic acid, lowering its charge.
Image by Lecturio.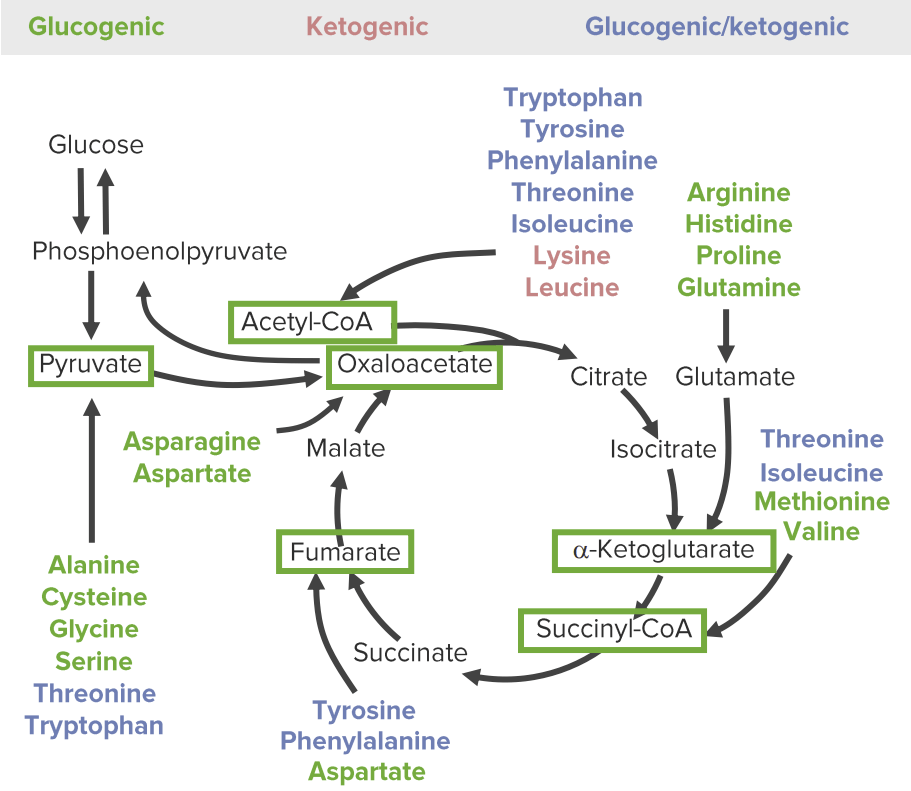
The 3 categories of catabolic products of amino acids: glucogenic (green), ketogenic (red), and both glucogenic and ketogenic (blue). The glucose-pyruvate pathway on the left represents glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. The cyclic pathway on the right represents the citric acid cycle. All amino acids are broken down into 1 of 6 intermediates (green boxes): pyruvate, acetyl-CoA, oxaloacetate, alpha-ketoglutarate, succinyl-CoA, and fumarate.
Image by Lecturio.The catabolism of AAs involves anaplerotic reactions (chemical reactions that form intermediates of metabolic pathways).
Amino acids Acids Chemical compounds which yield hydrogen ions or protons when dissolved in water, whose hydrogen can be replaced by metals or basic radicals, or which react with bases to form salts and water (neutralization). An extension of the term includes substances dissolved in media other than water. Acid-Base Balance can be classified by the catabolic products and into which metabolic pathways they will serve as intermediates: