Basal ganglia are a group of subcortical nuclear agglomerations involved in movement, and are located deep to the cerebral hemispheres. Basal ganglia include the striatum (caudate nucleus Nucleus Within a eukaryotic cell, a membrane-limited body which contains chromosomes and one or more nucleoli (cell nucleolus). The nuclear membrane consists of a double unit-type membrane which is perforated by a number of pores; the outermost membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum. A cell may contain more than one nucleus. The Cell: Organelles and putamen), globus pallidus, substantia nigra, and subthalamic nucleus Nucleus Within a eukaryotic cell, a membrane-limited body which contains chromosomes and one or more nucleoli (cell nucleolus). The nuclear membrane consists of a double unit-type membrane which is perforated by a number of pores; the outermost membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum. A cell may contain more than one nucleus. The Cell: Organelles. The components intricately synapse Synapse The junction between 2 neurons is called a synapse. The synapse allows a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or target effector cell. Synapses and Neurotransmission onto each other to promote or antagonize movement.
Last updated: Mar 3, 2025
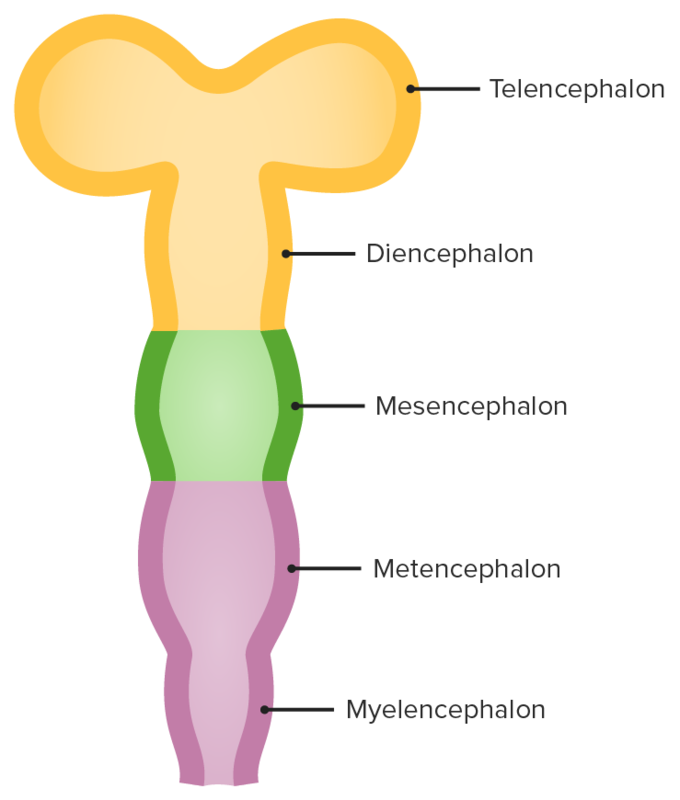
Secondary brain vesicles: The telencephalon develops from the prosencephalon and will go on to form several important structures of the brain, including the cerebral cortex and basal ganglia.
Image by Lecturio.The basal ganglia are a cluster of subcortical nuclei deep to cerebral hemispheres and are involved in the initiation, maintenance, and inhibition of movement.
The striatum (neostriatum) is composed of:
The lenticular nucleus Nucleus Within a eukaryotic cell, a membrane-limited body which contains chromosomes and one or more nucleoli (cell nucleolus). The nuclear membrane consists of a double unit-type membrane which is perforated by a number of pores; the outermost membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum. A cell may contain more than one nucleus. The Cell: Organelles is made up of:
Substantia nigra:
Subthalamic nucleus Nucleus Within a eukaryotic cell, a membrane-limited body which contains chromosomes and one or more nucleoli (cell nucleolus). The nuclear membrane consists of a double unit-type membrane which is perforated by a number of pores; the outermost membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum. A cell may contain more than one nucleus. The Cell: Organelles:
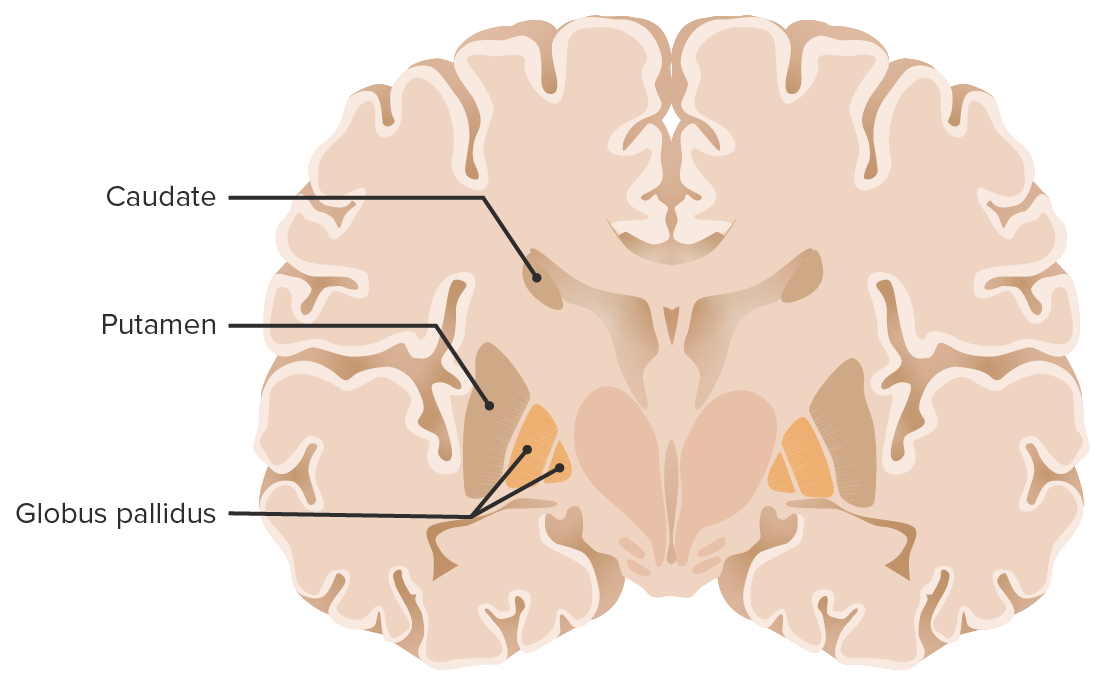
Coronal section of the brain showcasing the basal ganglia
Image by Lecturio.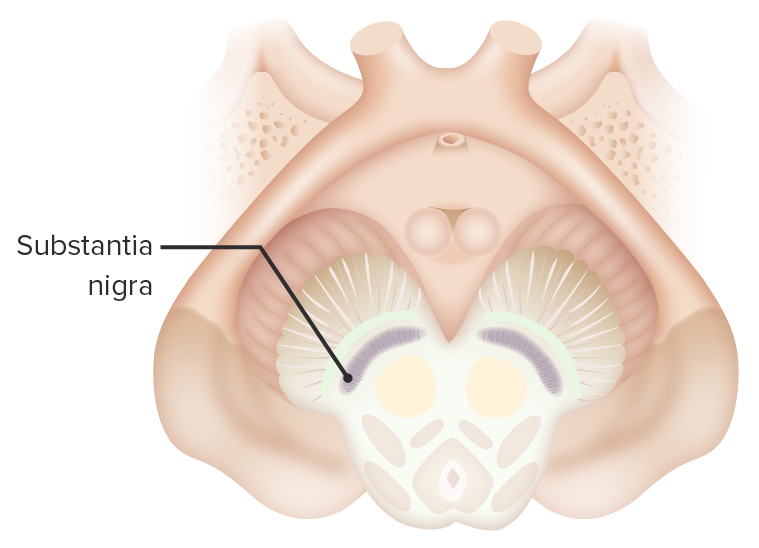
Transverse section of the midbrain showcasing the substantia nigra, 1 of the basal ganglia.
Image by Lecturio.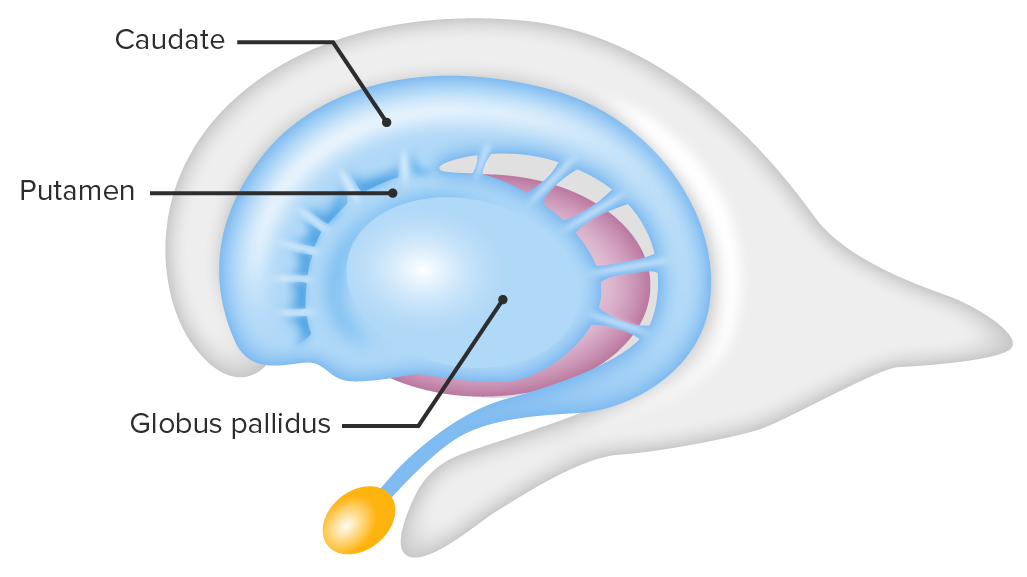
Lateral view showcasing the striatum and globus pallidus, 2 of the basal ganglia structures: Note how the caudate nucleus, a part of the striatum, holds an anatomical relation to the lateral ventricle.
Image by Lecturio.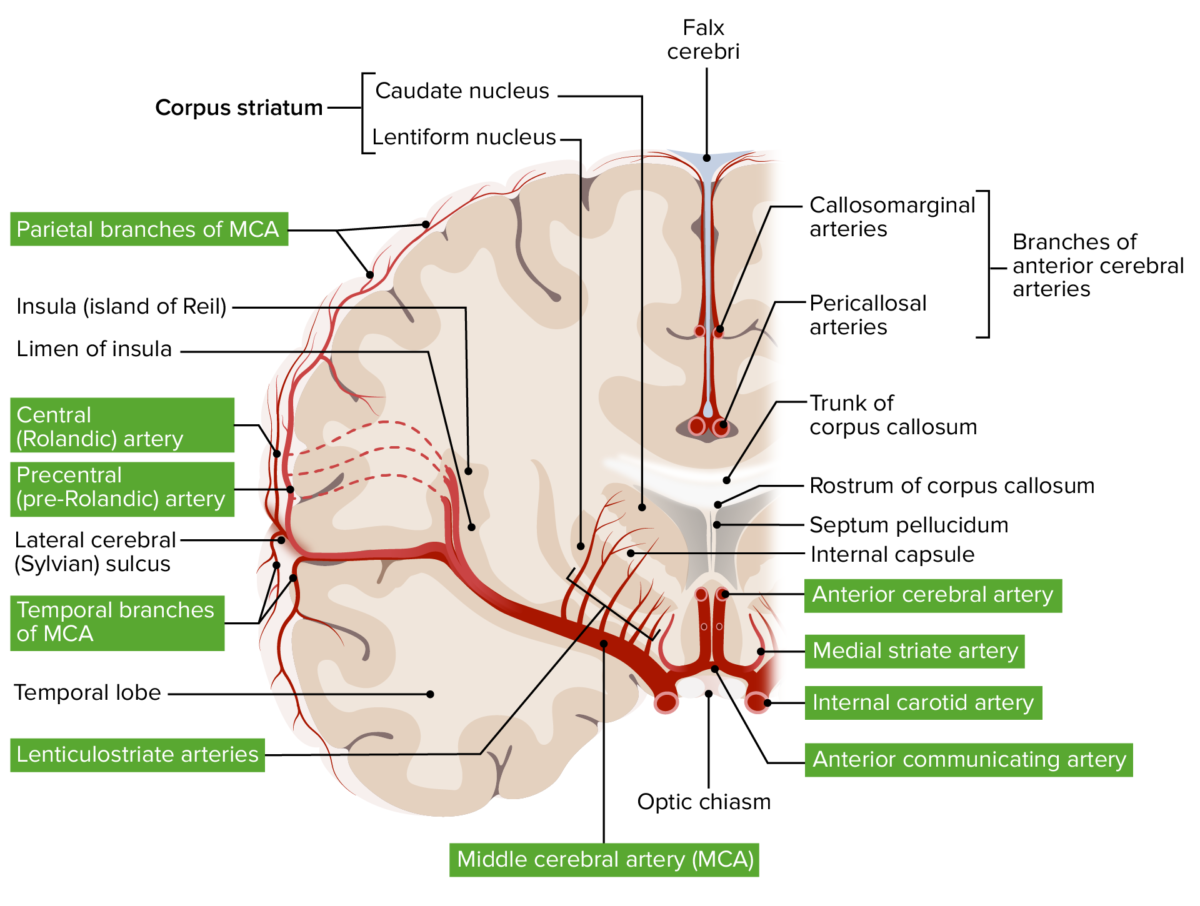
Arterial supply of the basal ganglia by the perforating branches of the middle cerebral artery
Image by Lecturio.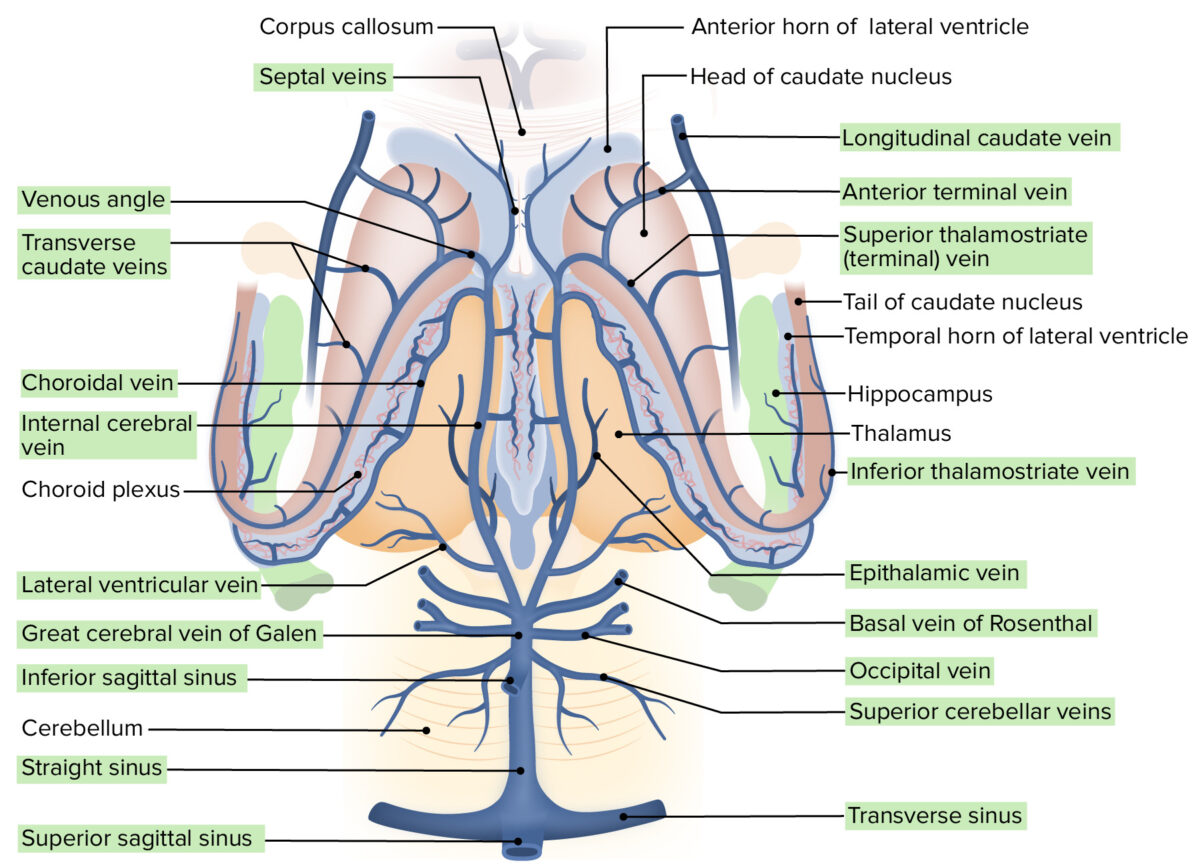
Venous drainage of the inferior aspect of the encephalon: See the internal cerebral and basal veins charged with drainage of the basal ganglia.
Image by Lecturio.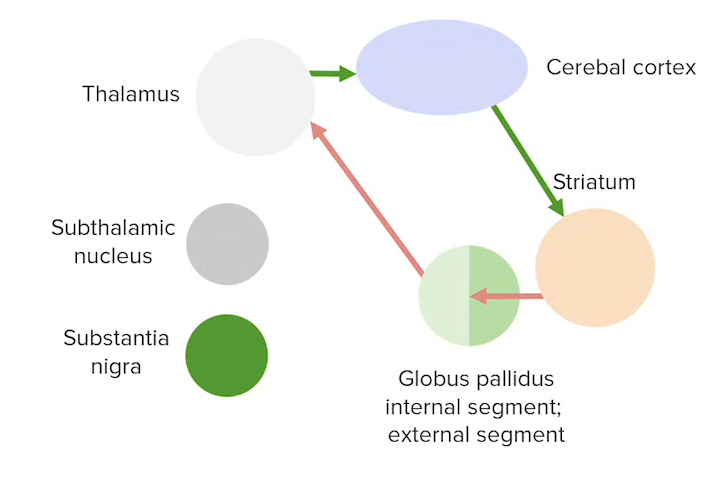
Direct pathway (excitatory) between the basal ganglia and the cerebral cortex
Image by Lecturio.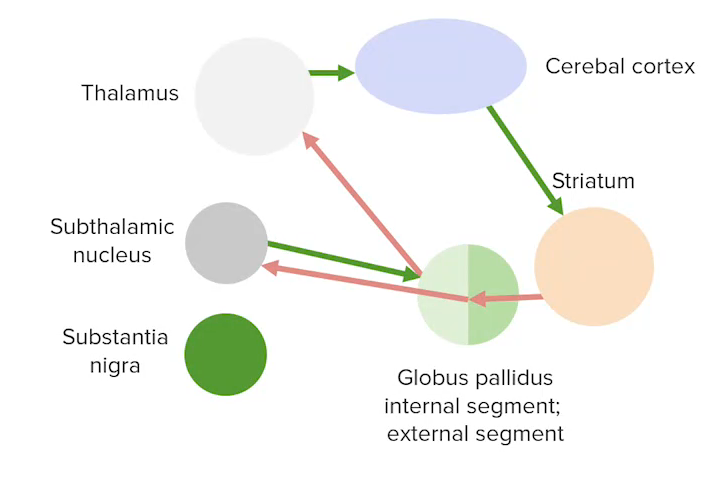
Indirect (inhibitory) pathway between the basal ganglia and the cerebral cortex
Image by Lecturio.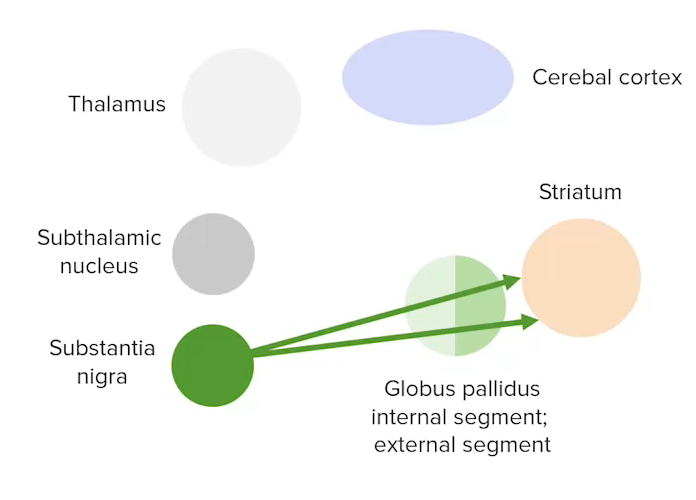
Nigrostriatal pathway between the substantia nigra and the striatum
Image by Lecturio.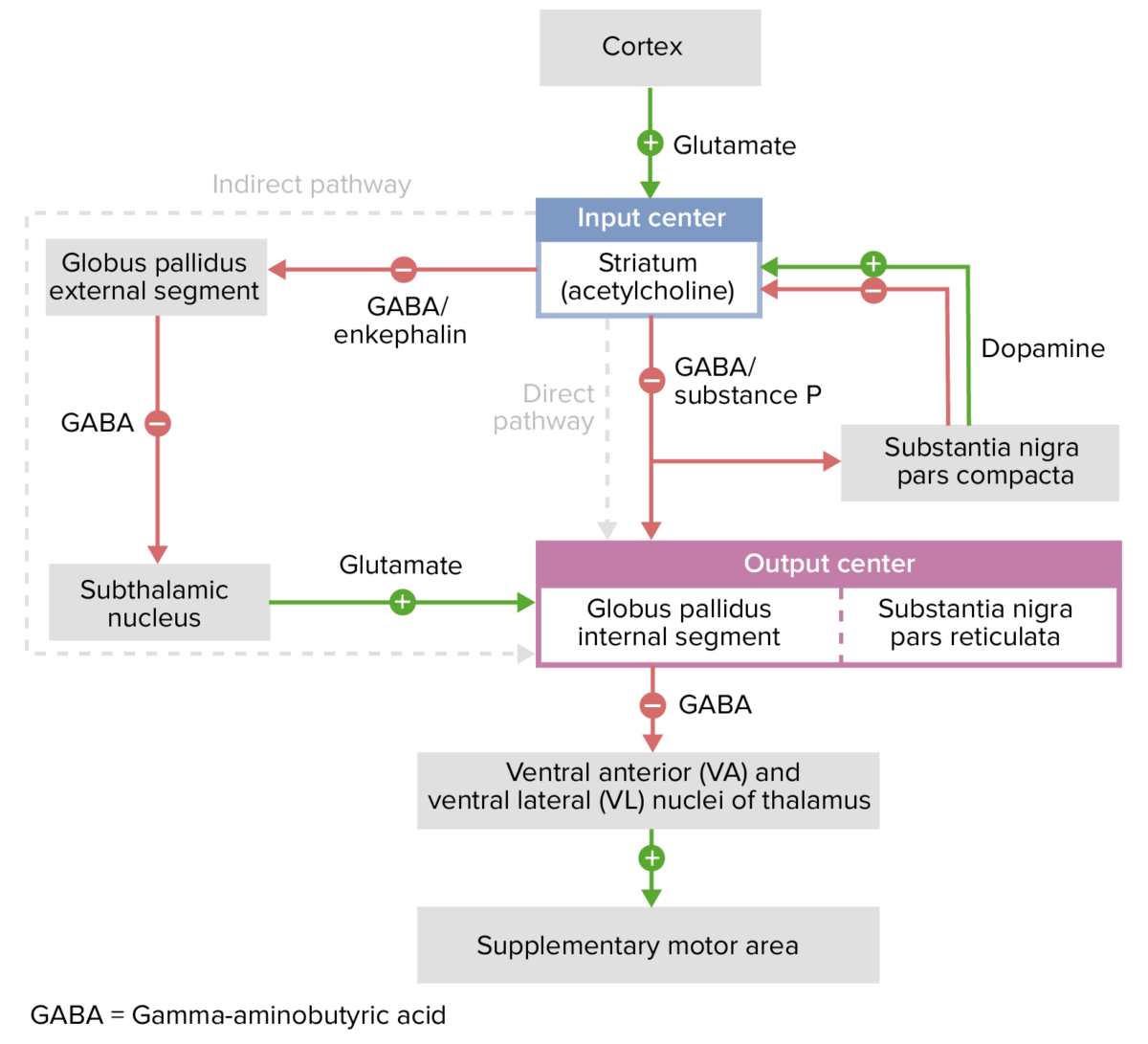
Excitatory and inhibitory pathways of the basal ganglia
Image by Lecturio.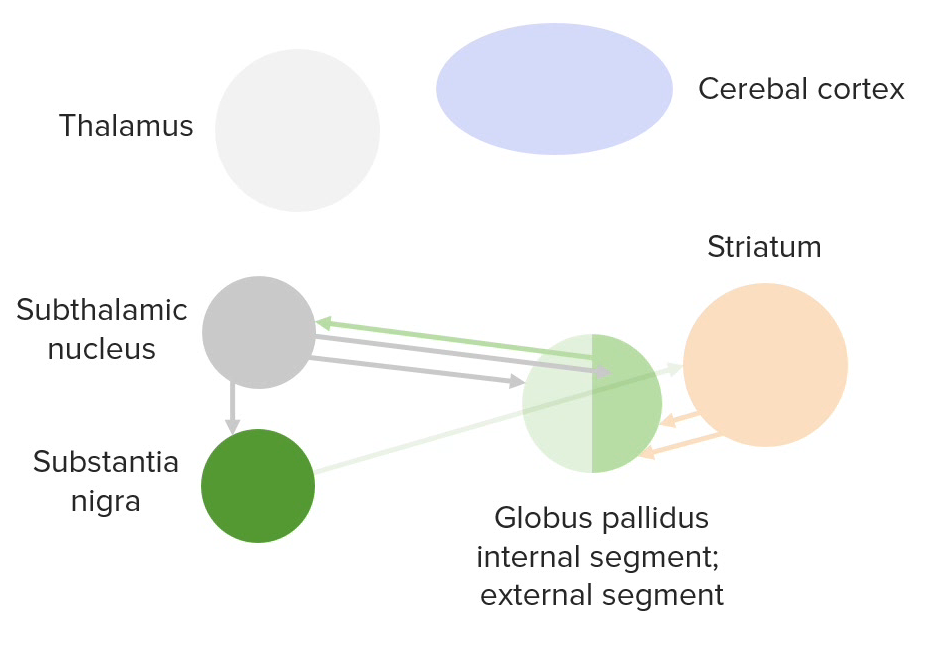
Diagram of the intrinsic connections between the basal ganglia
Image by Lecturio.