Bartonella is a genus of gram-negative bacteria gram-negative bacteria Bacteria which lose crystal violet stain but are stained pink when treated by gram's method. Bacteriology in the family Bartonellaceae. As a facultative intracellular Facultative intracellular Yersinia spp./Yersiniosis parasite, Bartonella can infect healthy people as well as act as an opportunistic pathogen Opportunistic pathogen Moraxella. Bartonella species are transmitted by vectors such as ticks Ticks Blood-sucking acarid parasites of the order ixodida comprising two families: the softbacked ticks (argasidae) and hardbacked ticks (ixodidae). Ticks are larger than their relatives, the mites. They penetrate the skin of their host by means of highly specialized, hooked mouth parts and feed on its blood. Ticks attack all groups of terrestrial vertebrates. In humans they are responsible for many tick-borne diseases, including the transmission of rocky mountain spotted fever; tularemia; babesiosis; african swine fever; and relapsing fever. Coxiella/Q Fever, fleas, sandflies, and mosquitoes. B. henselae is the most common of the 3 species known to cause human disease; it is a zoonosis that causes cat-scratch disease and bacillary angiomatosis Bacillary Angiomatosis A reactive vascular proliferation that is characterized by the multiple tumor-like lesions in skin, bone, brain, and other organs. Bacillary angiomatosis is caused by infection with gram-negative Bartonella bacilli (such as Bartonella henselae), and is often seen in AIDS patients and other immunocompromised hosts. AIDS-defining Conditions (BA). The other 2 species are human-specific: B. bacilliformis causes trench fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever and BA, and B. quintana causes Oroya fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, verruga peruana, and Carrion’s disease.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
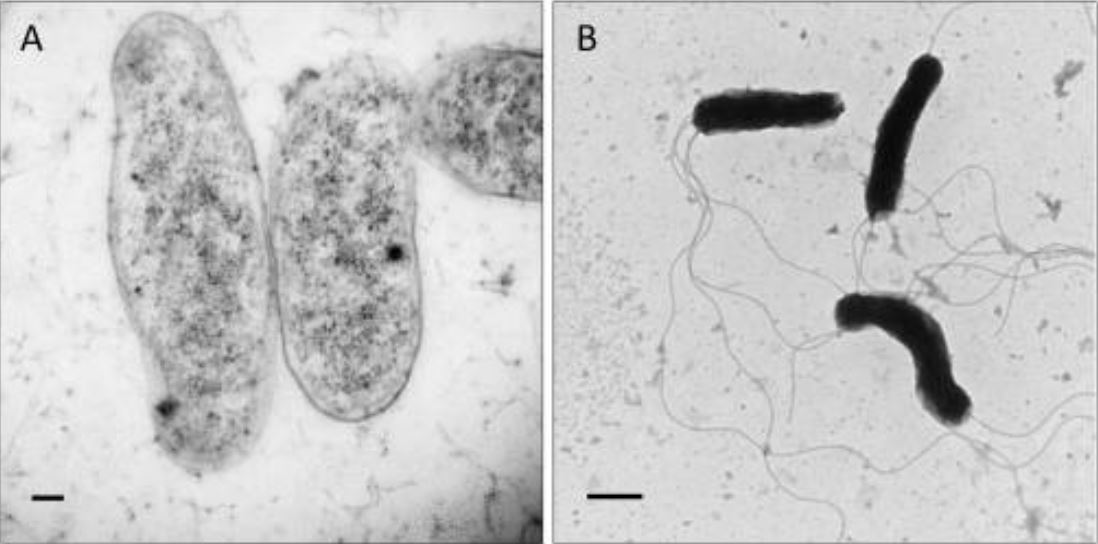
Transmission electron micrographs showing morphology of Bartonella bacilliformis:
Scale bars represent 100 nm in panel A and 500 nm in panel B.
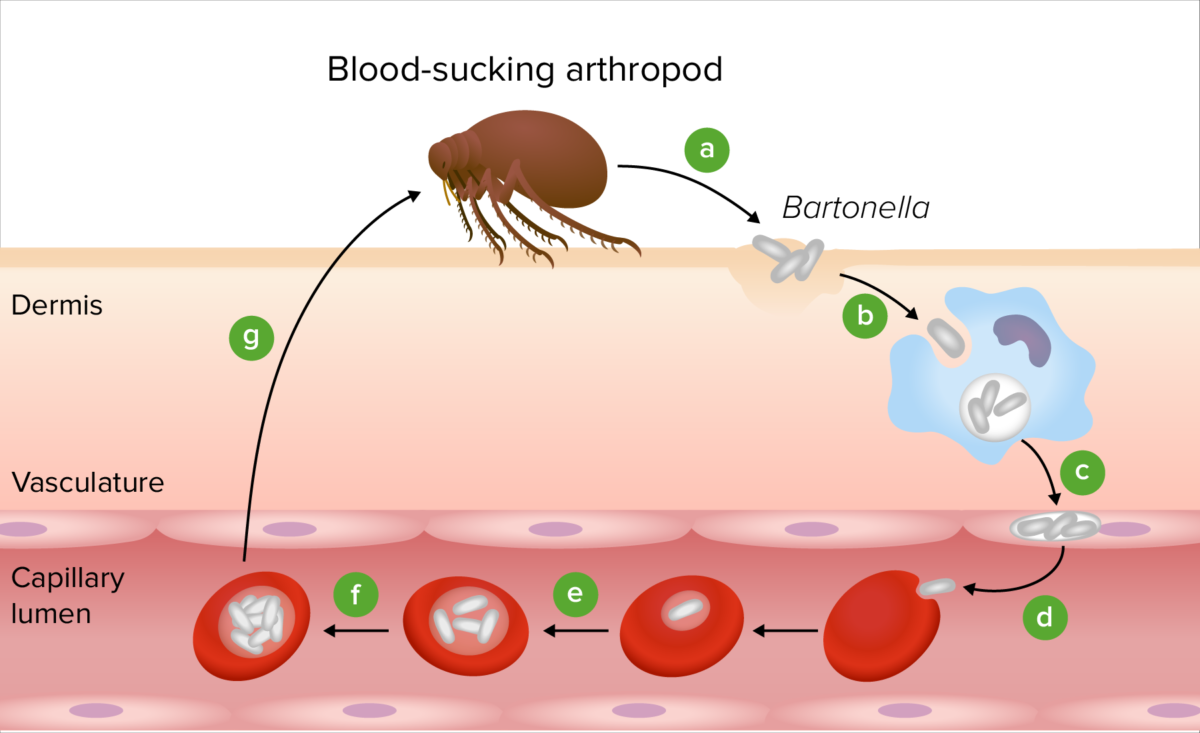
Pathogenesis of Bartonella:
Following transmission by an arthropod vector (a), the Bartonella bacteria colonize the skin (b). The bacteria are then transported to the vascular endothelium (c) and are seeded into the bloodstream to invade erythrocytes (d). After replication inside the RBC (e), the bacteria persist in the intraerythrocytic niche (f), making them competent for transmission by another bloodsucking arthropod (g).
Bartonellosis in humans is caused by 3 main species of Bartonella bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology and produces a wide range of symptoms and diseases depending on the species and the immune state of the infected individual.
| Species | Disease |
|---|---|
| B. bacilliformis |
Carrion’s disease, also known as:
|
| B. quintana |
|
| B. henselae |
|
Transmission:
Clinical presentation:
Transmission:
Clinical presentation:
Transmission:
Clinical presentation:
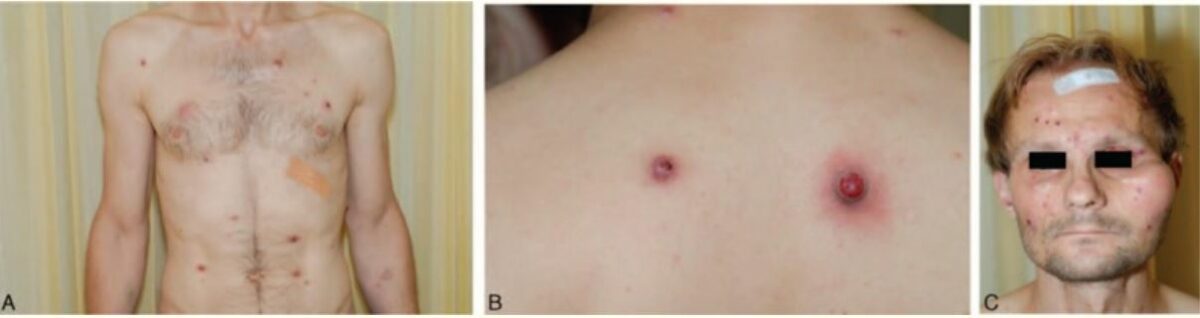
Clinical presentation of a patient with bacillary angiomatosis:
A: Multiple red papules on the chest and abdomen
B: 2 nodules on the back
C: Papules on the face with a subcutaneous mass lesion over the left zygomatic arch
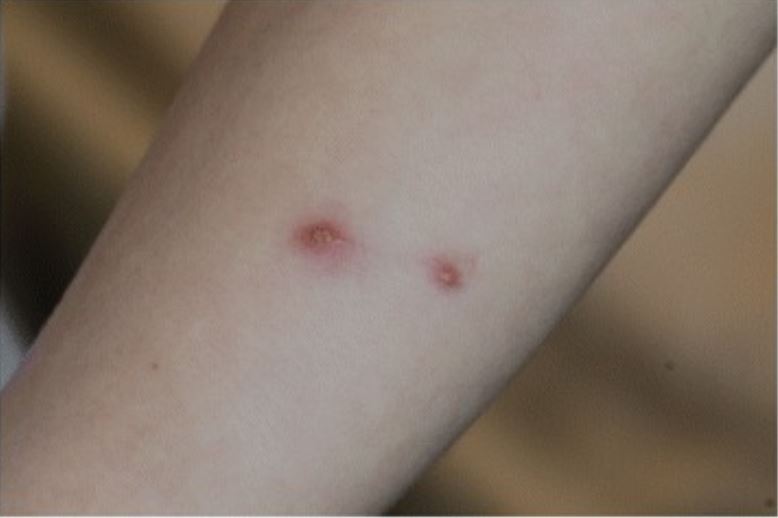
Cat-scratch disease:
Active skin lesions, typically painless, are seen a few days to 2 weeks after inoculation in ⅓ to ⅔ of patients. Painful regional lymphadenopathy usually develops 1–3 weeks after inoculation.
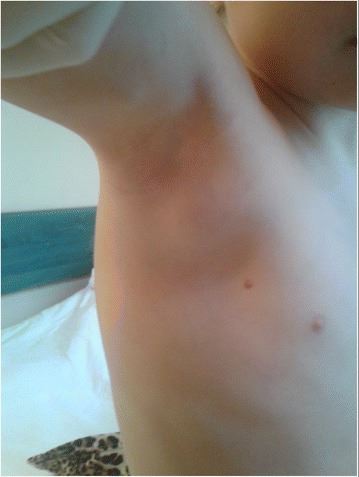
Peripheral axillary lymphadenopathy in a 5-year-old child with cat-scratch disease
Image: “The significance of Bartonella henselae bacterias for oncological diagnosis in children” by Mazur-Melewska K, Jończyk-Potoczna K, Mania A, Kemnitz P, Szydłowski J, Służewski W, Figlerowicz M. License: CC BY 4.0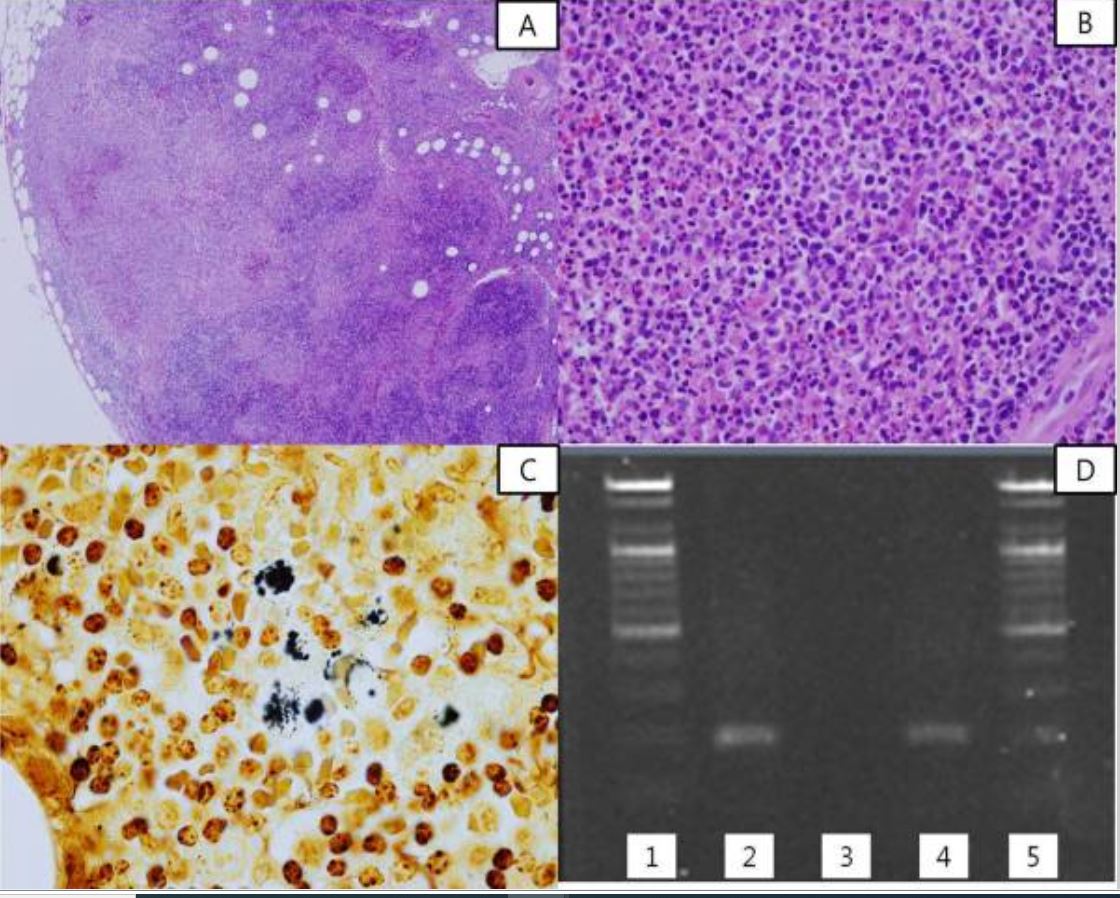
Histopathology, silver stain, and PCR of cat scratch disease:
A: The affected lymph node shows reactive follicular hyperplasia and multiple geographic microabscesses.
B: Numerous neutrophils are seen in the necrotic foci of the lymph node.
C: Some clumps of bacteria are found in the lymph node (black silver stain).
D: Results of semi-nested PCR for Bartonella henselae. Lanes 1 and 5 show the DNA ladder marker; lane 2 shows a positive control, lane 3 a negative control, and lane 4 lymph node tissue from the patient.
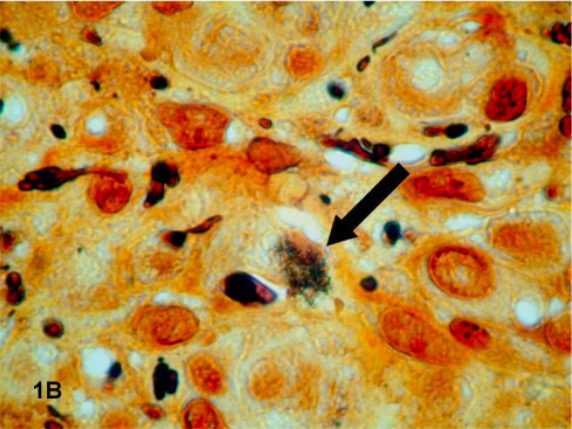
Histopathology specimen from a patient with bacillary angiomatosis:
A dark-staining cluster of Bartonella quintana (indicated by an arrow) is revealed with Warthin-Starry staining of a tissue specimen.
Most cases of bartonellosis can be diagnosed through the detection of characteristic symptoms and physical findings and a complete medical history. Specialized laboratory tests are used to confirm the diagnosis.
Aside from supportive care, management is dependent on the specific species of Bartonella contracted and the severity of each case.