Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts Cysts Any fluid-filled closed cavity or sac that is lined by an epithelium. Cysts can be of normal, abnormal, non-neoplastic, or neoplastic tissues. Fibrocystic Change in the kidneys Kidneys The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs located retroperitoneally against the posterior wall of the abdomen on either side of the spine. As part of the urinary tract, the kidneys are responsible for blood filtration and excretion of water-soluble waste in the urine. Kidneys: Anatomy. The 2 main types of PKD are autosomal recessive Autosomal recessive Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal recessive diseases are only expressed when 2 copies of the recessive allele are inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), which is often diagnosed antenatally or shortly after birth, and autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. The 2 main types of PKD are autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), which is often diagnosed in adulthood, and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), which is often diagnosed antenatally or shortly after birth. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) ( ADPKD ADPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. The 2 main types of PKD are autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), which is often diagnosed in adulthood, and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), which is often diagnosed antenatally or shortly after birth. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)), which is often diagnosed in adulthood. Autosomal recessive Autosomal recessive Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal recessive diseases are only expressed when 2 copies of the recessive allele are inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance polycystic kidney disease is primarily characterized by cystic Cystic Fibrocystic Change dilatations of the renal collecting ducts and intrahepatic bile Bile An emulsifying agent produced in the liver and secreted into the duodenum. Its composition includes bile acids and salts; cholesterol; and electrolytes. It aids digestion of fats in the duodenum. Gallbladder and Biliary Tract: Anatomy duct dilatation with hepatic fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans. Diagnosis is through physical exam and ultrasonography. Management requires a multidisciplinary approach to slow the progression of renal disease by controlling hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension, proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children, and symptoms. The prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas of ARPKD depends on the age at presentation, along with the degree of hepatic and renal involvement. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship progressing to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) will need renal replacement therapy.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) affects about 500,000 people in the United States. Autosomal recessive Autosomal recessive Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal recessive diseases are only expressed when 2 copies of the recessive allele are inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) (formerly known as infantile PKD), is 1 of the 2 main types of PKD.
Manifestations vary by age and affect the following:
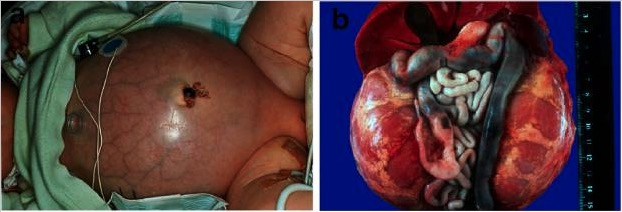
Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD):
a) Baby with a distended abdomen due to voluminous kidneys, leading to respiratory problems and early demise
b) Abdominal situs of a perinatally demised ARPKD patient with symmetrically enlarged kidneys in their reniform configuration
In the 1st 3 years, survivors of the neonatal period experience a temporary improvement of renal function, followed by a decline.
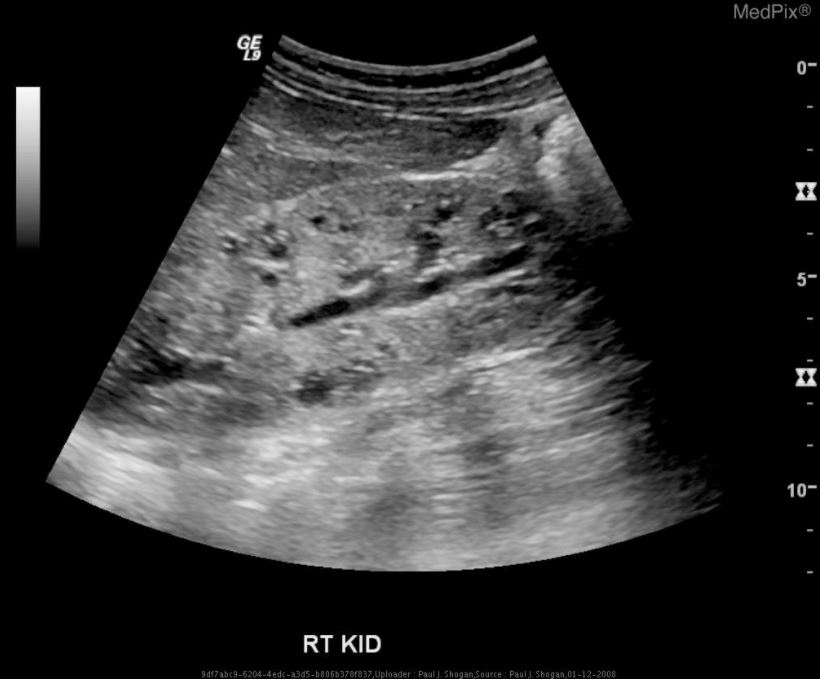
Ultrasonography of the right kidney demonstrating autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD):
diffusely increased echogenicity, loss of corticomedullary differentiation, and multiple microcysts within the renal parenchyma
Antenatal management (if detected early):
Neonatal management:
Infancy and childhood management:
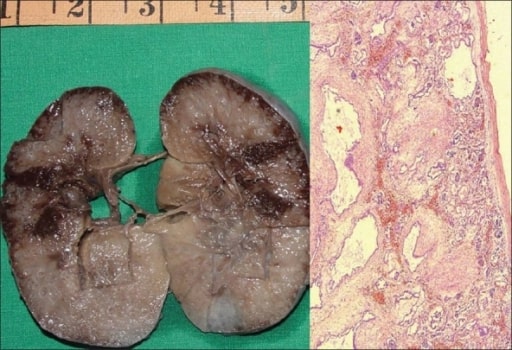
Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) in a fetus:
On the left, a gross specimen is shown of a right kidney measuring 10 × 7 × 4 cm. The cut surface is spongy with poor corticomedullary differentiation. There are multiple, tiny cysts with some at right angles to the cortical surface.
On the right, a photomicrograph is showing numerous cysts lined by a single layer of low cuboidal epithelial cells with thick, peritubular mesenchyme. The glomeruli are normal (H&E, 40x).
The 2 main types of PKD are autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. The 2 main types of PKD are autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), which is often diagnosed in adulthood, and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), which is often diagnosed antenatally or shortly after birth. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) ( ADPKD ADPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. The 2 main types of PKD are autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), which is often diagnosed in adulthood, and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), which is often diagnosed antenatally or shortly after birth. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)) and ARPKD.
| ADPKD ADPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. The 2 main types of PKD are autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), which is often diagnosed in adulthood, and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), which is often diagnosed antenatally or shortly after birth. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) | ARPKD | |
|---|---|---|
| Inheritance | Autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance | Autosomal recessive Autosomal recessive Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal recessive diseases are only expressed when 2 copies of the recessive allele are inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance |
| Genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure involved | PKD1, PKD2 PKD1, PKD2 Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) | PKHD1 |
| Associated proteins Proteins Linear polypeptides that are synthesized on ribosomes and may be further modified, crosslinked, cleaved, or assembled into complex proteins with several subunits. The specific sequence of amino acids determines the shape the polypeptide will take, during protein folding, and the function of the protein. Energy Homeostasis | Polycystin-1, polycystin-2 | Fibrocystin |
| Age of presentation | Adulthood | Antenatal, neonatal, infant |
| Clinical features |
|
|
| Gross and pathologic morphology |
|
|
| Ultrasound findings |
Multiple
cysts
Cysts
Any fluid-filled closed cavity or sac that is lined by an epithelium. Cysts can be of normal, abnormal, non-neoplastic, or neoplastic tissues.
Fibrocystic Change (based on age):
|
|