Mendelian inheritance is defined as a pattern of segregation of genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure, originating from any 1 of the parents, into gametes. Autosomal inheritance is a key component of Mendelian inheritance. Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure from the 22 autosomal chromosomes Chromosomes In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. DNA Types and Structure. As such, autosomal diseases are inherited at equal rates among both genders. Autosomal recessive diseases are only expressed when 2 copies of the recessive allele Allele Variant forms of the same gene, occupying the same locus on homologous chromosomes, and governing the variants in production of the same gene product. Basic Terms of Genetics are inherited, whereas autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele Allele Variant forms of the same gene, occupying the same locus on homologous chromosomes, and governing the variants in production of the same gene product. Basic Terms of Genetics is inherited. Inborn errors of metabolism are classically autosomal recessive, whereas inherited structural abnormalities are classically inherited in an autosomal-dominant manner.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Recessive alleles are only manifested when they are homozygous, which means that the individual inherited a recessive allele Allele Variant forms of the same gene, occupying the same locus on homologous chromosomes, and governing the variants in production of the same gene product. Basic Terms of Genetics from each parent.
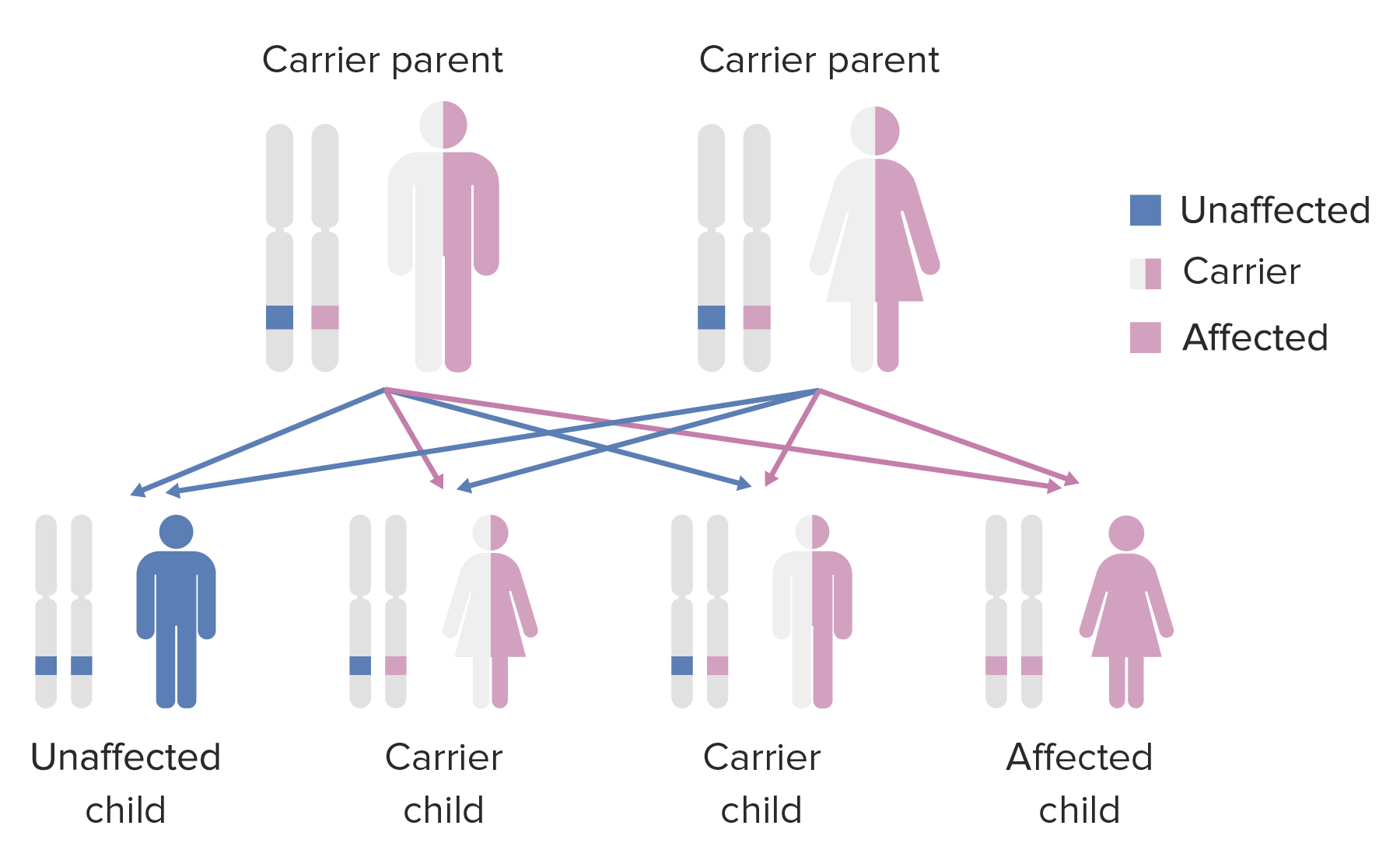
Autosomal recessive inheritance: Affected offspring will have unaffected parents who are carriers.
Image by Lecturio.Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics Genetics Genetics is the study of genes and their functions and behaviors. Basic Terms of Genetics. Often, the dominant allele Allele Variant forms of the same gene, occupying the same locus on homologous chromosomes, and governing the variants in production of the same gene product. Basic Terms of Genetics codes for a functional protein, whereas the recessive allele Allele Variant forms of the same gene, occupying the same locus on homologous chromosomes, and governing the variants in production of the same gene product. Basic Terms of Genetics does not. If there is a dominant and recessive allele Allele Variant forms of the same gene, occupying the same locus on homologous chromosomes, and governing the variants in production of the same gene product. Basic Terms of Genetics in a heterozygous genotype Genotype The genetic constitution of the individual, comprising the alleles present at each genetic locus. Basic Terms of Genetics, only the dominant allele Allele Variant forms of the same gene, occupying the same locus on homologous chromosomes, and governing the variants in production of the same gene product. Basic Terms of Genetics manifests.
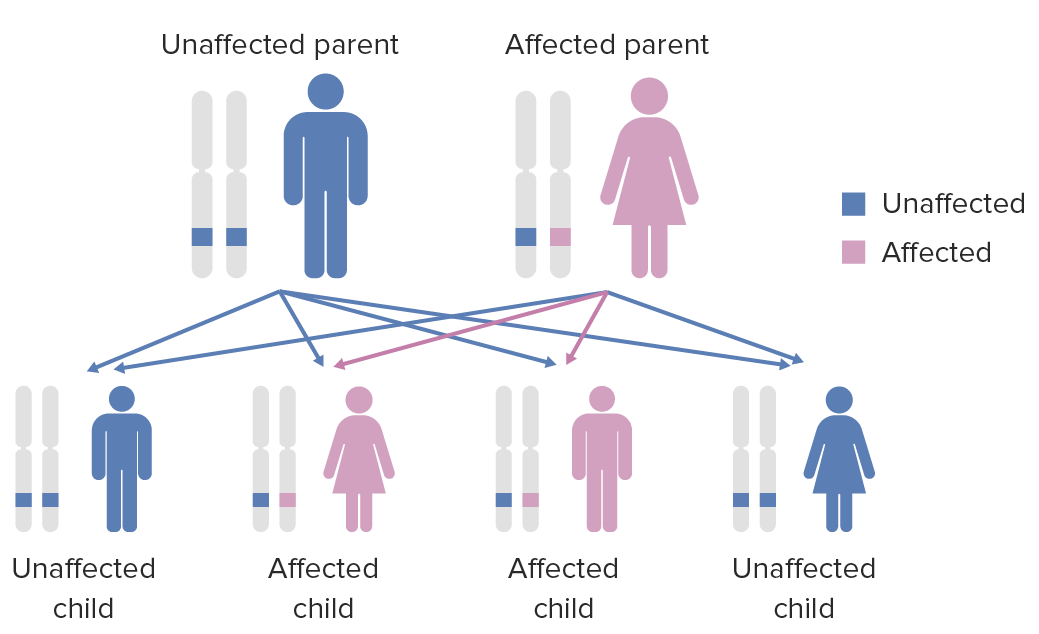
Diagram of the inheritance pattern of autosomal dominant conditions
Image by Lecturio.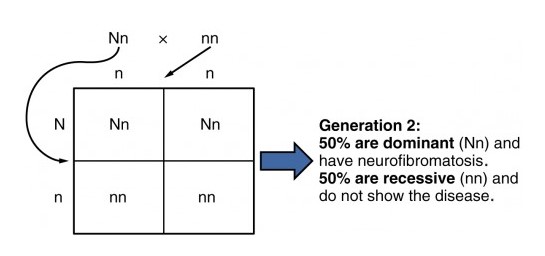
Punnett square showing the autosomal dominant inheritance of neurofibromatosis:
1 dominant allele is enough to cause the disease.
If 1 parent is homozygous and healthy and the other is heterozygous for the trait, all children will be phenotypically healthy but 50% will be carriers Carriers The Cell: Cell Membrane: Aa AA Amyloidosis x AA AA Amyloidosis = 50% AA AA Amyloidosis + 50% Aa AA Amyloidosis
| A | A | |
| A | AA AA Amyloidosis | AA AA Amyloidosis |
| a | Aa | Aa |
If both parents are heterozygous for the trait, 25% of the children will have the disease, 50% will be heterozygous carriers Carriers The Cell: Cell Membrane, and 25% will be homozygous and healthy: Aa AA Amyloidosis x Aa AA Amyloidosis = 25% AA AA Amyloidosis + 50% Aa AA Amyloidosis + 25% aa AA Amyloidosis
| A | a | |
| A | AA AA Amyloidosis | Aa |
| a | Aa | aa |
If a parent is heterozygous and the other is homozygous recessive, all children will be carriers Carriers The Cell: Cell Membrane, but 50% will have the disease: Aa AA Amyloidosis x aa AA Amyloidosis = 50% Aa AA Amyloidosis + 50% aa AA Amyloidosis
| A | a | |
| a | Aa | aa |
| a | Aa | aa |
If 1 parent is homozygous for the trait and the other is homozygous recessive, all children will be heterozygous (phenotypically affected).
| A | A | |
| a | Aa | Aa |
| a | Aa | Aa |
If both parents are heterozygous for the trait, 25% of the children will be homozygous dominant, 50% will be heterozygous, and 25% will be homozygous recessive. The phenotype Phenotype The complete genetic complement contained in the DNA of a set of chromosomes in a human. The length of the human genome is about 3 billion base pairs. Basic Terms of Genetics will be expressed by 75% of the children.
| A | a | |
| A | AA | Aa |
| a | Aa | aa AA Amyloidosis |
If 1 parent is heterozygous for the trait, 50% of the children will be heterozygous (with the disease) and the other 50% will be homozygous recessive.
| A | a | |
| a | Aa | aa AA Amyloidosis |
| a | Aa | aa AA Amyloidosis |