Autoimmunity is a pathologic immune response toward self-antigens, resulting from a combination of factors: immunologic, genetic, and environmental. The immune system Immune system The body's defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs is equipped with self-tolerance, allowing immune cells such as T cells T cells Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified - cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions and B cells B cells Lymphoid cells concerned with humoral immunity. They are short-lived cells resembling bursa-derived lymphocytes of birds in their production of immunoglobulin upon appropriate stimulation. B cells: Types and Functions to recognize self-antigens and to not mount a reaction against them. Defects in this mechanism, along with environmental triggers (such as infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease) and genetic susceptibility factors (most notable of which are the HLA genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure) can lead to autoimmune diseases Autoimmune diseases Disorders that are characterized by the production of antibodies that react with host tissues or immune effector cells that are autoreactive to endogenous peptides. Selective IgA Deficiency. These conditions are more commonly seen in women. Autoimmune diseases Autoimmune diseases Disorders that are characterized by the production of antibodies that react with host tissues or immune effector cells that are autoreactive to endogenous peptides. Selective IgA Deficiency are chronic, with clinical manifestations consistent with the associated immune response. Among these conditions are Graves’ disease Graves’ disease A common form of hyperthyroidism with a diffuse hyperplastic goiter. It is an autoimmune disorder that produces antibodies against the thyroid stimulating hormone receptor. These autoantibodies activate the TSH receptor, thereby stimulating the thyroid gland and hypersecretion of thyroid hormones. These autoantibodies can also affect the eyes (Graves ophthalmopathy) and the skin (Graves dermopathy). Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism ( autoantibodies Autoantibodies Antibodies that react with self-antigens (autoantigens) of the organism that produced them. Blotting Techniques against thyroid Thyroid The thyroid gland is one of the largest endocrine glands in the human body. The thyroid gland is a highly vascular, brownish-red gland located in the visceral compartment of the anterior region of the neck. Thyroid Gland: Anatomy hormone receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors), myasthenia gravis Myasthenia Gravis Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune neuromuscular disorder characterized by weakness and fatigability of skeletal muscles caused by dysfunction/destruction of acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction. MG presents with fatigue, ptosis, diplopia, dysphagia, respiratory difficulties, and progressive weakness in the limbs, leading to difficulty in movement. Myasthenia Gravis ( antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions against acetylcholine Acetylcholine A neurotransmitter found at neuromuscular junctions, autonomic ganglia, parasympathetic effector junctions, a subset of sympathetic effector junctions, and at many sites in the central nervous system. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors), type 1 Type 1 Spinal Muscular Atrophy diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus (pancreatic β-cell destruction by immune cells), and systemic lupus erythematosus Systemic lupus erythematosus Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune, inflammatory condition that causes immune-complex deposition in organs, resulting in systemic manifestations. Women, particularly those of African American descent, are more commonly affected. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (multiorgan damage driven by immune complexes Immune complexes The complex formed by the binding of antigen and antibody molecules. The deposition of large antigen-antibody complexes leading to tissue damage causes immune complex diseases. C3 Deficiency and autoantibodies Autoantibodies Antibodies that react with self-antigens (autoantigens) of the organism that produced them. Blotting Techniques).
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Autoimmunity is the pathologic immune response to self, or against one’s own cells, resulting in inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation, cell injury Cell injury The cell undergoes a variety of changes in response to injury, which may or may not lead to cell death. Injurious stimuli trigger the process of cellular adaptation, whereby cells respond to withstand the harmful changes in their environment. Overwhelmed adaptive mechanisms lead to cell injury. Mild stimuli produce reversible injury. If the stimulus is severe or persistent, injury becomes irreversible. Cell Injury and Death, or tissue/organ dysfunction.
The immune system Immune system The body’s defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs uses lymphocyte activation for defense against pathogens, but at the same time, maintains self-tolerance, which is unresponsiveness to one’s own antigens. Immunologic tolerance Tolerance Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics is protective and has different mechanisms (failure of which is a factor in autoimmunity).
Emergence of autoimmune disorders involves interaction of different factors (genetic, environmental, and immunologic), leading to activated immune response, with manifestations.
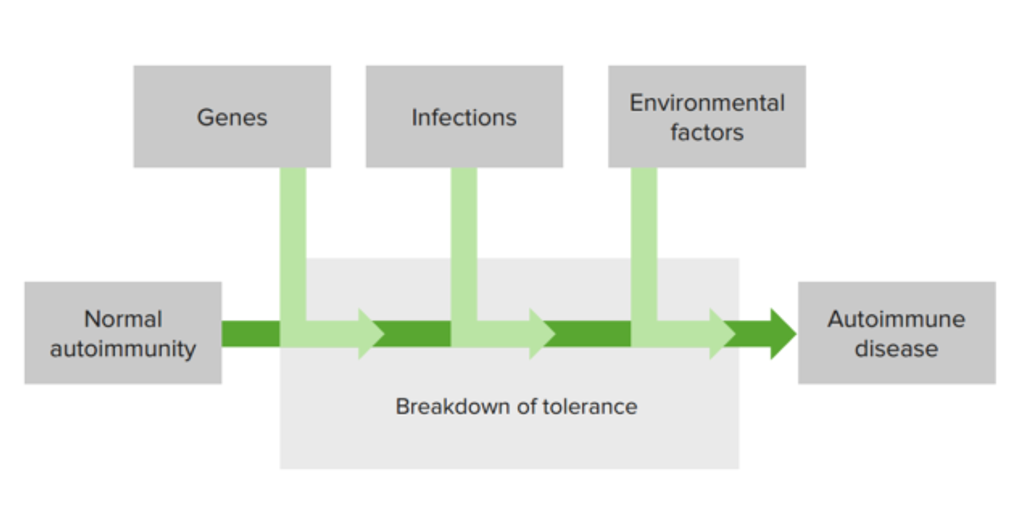
Multiple factors affect the development of autoimmune disease:
The combination of genetic susceptibility factors, the environment, and a defect in immunologic tolerance lead to activation of self-reactive lymphocytes and development of autoimmune disorders.
| Genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure | Associated autoimmune disease |
|---|---|
| MHC/HLA | Most autoimmune diseases Autoimmune diseases Disorders that are characterized by the production of antibodies that react with host tissues or immune effector cells that are autoreactive to endogenous peptides. Selective IgA Deficiency |
| PTPN22 |
|
| CTLA4 |
|
| IL2RA |
|
| IL2/IL21 |
|
| BLK |
|
The approaches used in the management of autoimmune diseases Autoimmune diseases Disorders that are characterized by the production of antibodies that react with host tissues or immune effector cells that are autoreactive to endogenous peptides. Selective IgA Deficiency are: