Atrial septal defects (ASDs) are benign Benign Fibroadenoma acyanotic Acyanotic Tetralogy of Fallot congenital heart defects characterized by an opening in the interatrial septum that causes blood to flow Flow Blood flows through the heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins in a closed, continuous circuit. Flow is the movement of volume per unit of time. Flow is affected by the pressure gradient and the resistance fluid encounters between 2 points. Vascular resistance is the opposition to flow, which is caused primarily by blood friction against vessel walls. Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure from the left atrium (LA) to the right atrium (RA) (left-to-right shunt). Atrial septal defects account for approximately 15% of all cases of congenital heart disease (CHD), making ASDs the 2nd most common CHD. There are 4 types of ASD ASD Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder marked by poor social skills, restricted interests/social interactions, and repetitive/stereotyped behaviors. The condition is termed a "spectrum" because of the wide variability in the severity of symptoms exhibited. Autism Spectrum Disorder based on the location of the defect along the atrial septum, but the most common is the ostium secundum defect. Atrial septal defects are usually detected during a routine physical examination and confirmed by an echocardiogram Echocardiogram Transposition of the Great Arteries. In infancy, most small ASDs close spontaneously by 2 years of age. Surgical closure is indicated for patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship who are symptomatic or have evidence of a hemodynamically significant shunt. In general, most patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with ASD ASD Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder marked by poor social skills, restricted interests/social interactions, and repetitive/stereotyped behaviors. The condition is termed a "spectrum" because of the wide variability in the severity of symptoms exhibited. Autism Spectrum Disorder can expect a good overall outcome.
Last updated: May 16, 2024
Atrial septal defect ( ASD ASD Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder marked by poor social skills, restricted interests/social interactions, and repetitive/stereotyped behaviors. The condition is termed a “spectrum” because of the wide variability in the severity of symptoms exhibited. Autism Spectrum Disorder) is a communication Communication The exchange or transmission of ideas, attitudes, or beliefs between individuals or groups. Decision-making Capacity and Legal Competence between the right atrium (RA) and the left atrium (LA) secondary to a defect in the development of the atrial septum during embryogenesis. Atrial septal defect is usually a benign Benign Fibroadenoma condition and is classified as an acyanotic Acyanotic Tetralogy of Fallot congenital heart disease (CHD).
Atrial septal defects are classified based on the anatomic location of the defect:
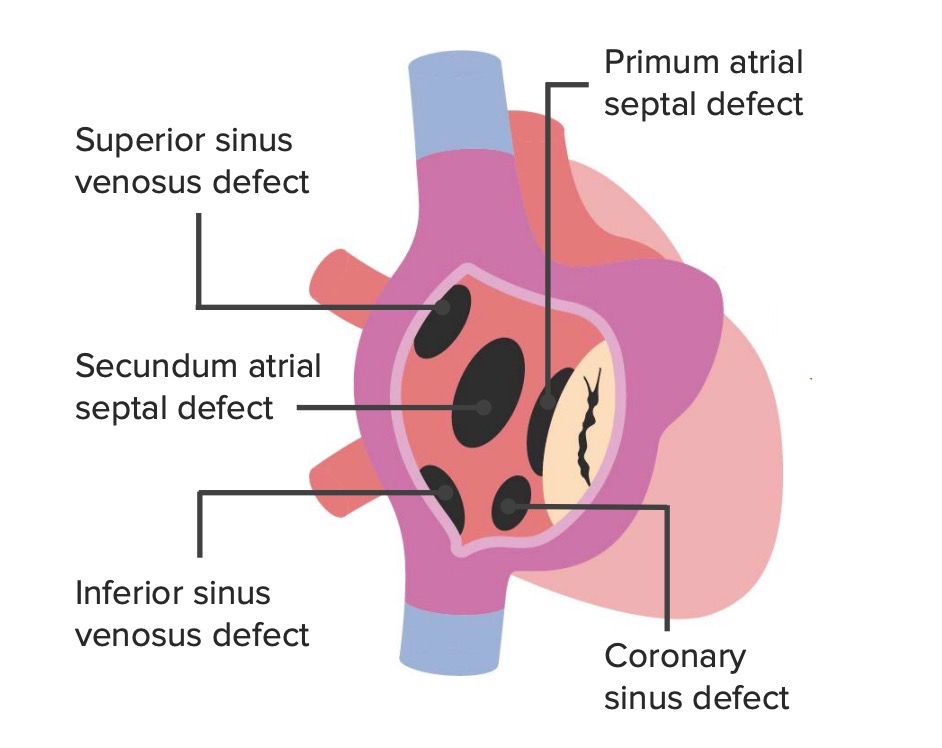
The anatomic locations of the different types of ASDs
Image by Lecturio.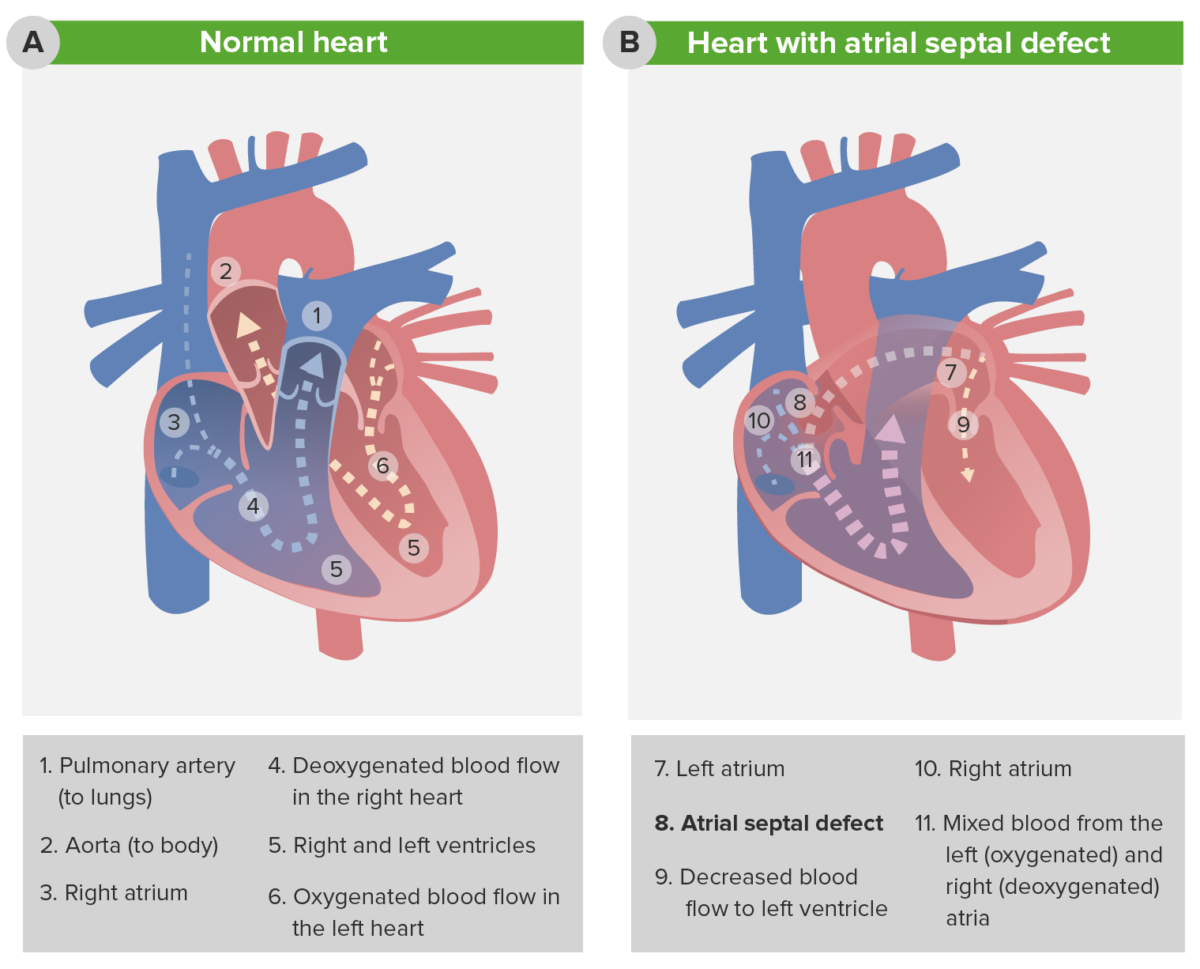
Pathophysiology of atrial septal defect
The image depicts the change in blood flow in the presence of an atrial septal defect (ASD). Note the decreased blood flow to the left ventricle (7) and the increased blood flow into the pulmonary circulation (11).
The signs and symptoms depend on the size of the defect and the severity of the shunt:
Upon physical examination, the following can be seen/detected:
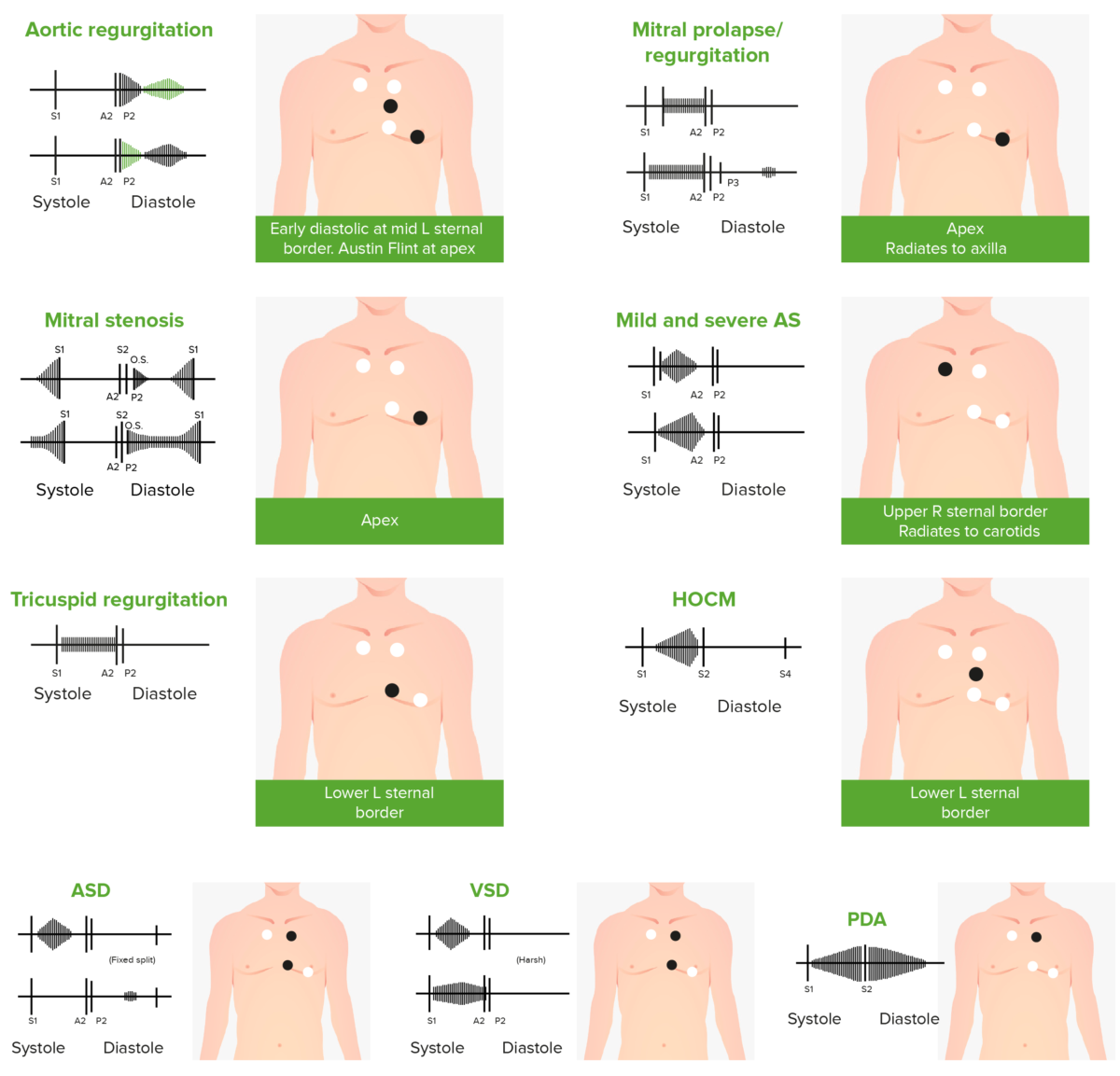
Phonocardiograms of abnormal heart sounds caused by the following cardiac defects:
aortic regurgitation, mitral valve prolapse, mitral stenosis (MS), aortic stenosis (AS), tricuspid regurgitation, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM), atrial septal defect (ASD), ventricular septal defect (VSD), and patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
Audio:
This audio file is an example of an ejection murmur and split S2 S2 Heart Sounds heard over the 2nd left intercostal space in an individual with an atrial septal defect. The crescendo-decrescendo murmur is heard between S1 S1 Heart Sounds and S2 S2 Heart Sounds, the latter of which is widely split.
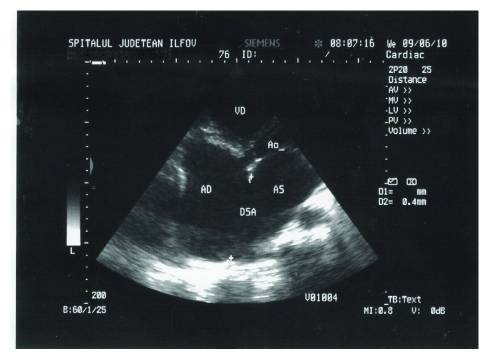
Transthoracic echocardiography of ASD, in apical 4-chamber view:
AD: right atrium
AS: left atrium
VD: right ventricle
A0: aorta
DSA: atrial septal defect
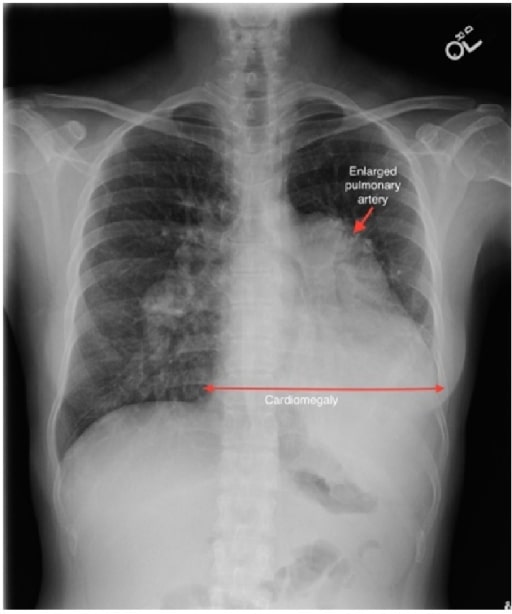
A case of sinus venosus ASD complicated by Eisenmenger’s syndrome:
A chest radiograph shows a markedly enlarged pulmonary trunk (red arrow), enlarged central pulmonary arteries, and enlargement of the cardiac silhouette.
The following conditions are associated with ASDs and can cause or modify the clinical features of ASDs: