Atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation ( AF AF Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation or Afib Afib Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia Tachyarrhythmia A tachyarrhythmia is a rapid heart rhythm, regular or irregular, with a rate > 100 beats/min. Tachyarrhythmia may or may not be accompanied by symptoms of hemodynamic change. Tachyarrhythmias and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. There are many conditions that can cause AF AF Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation, usually damage to the heart (e.g., coronary artery Coronary Artery Truncus Arteriosus disease, previous myocardial infarction Myocardial infarction MI is ischemia and death of an area of myocardial tissue due to insufficient blood flow and oxygenation, usually from thrombus formation on a ruptured atherosclerotic plaque in the epicardial arteries. Clinical presentation is most commonly with chest pain, but women and patients with diabetes may have atypical symptoms. Myocardial Infarction). Diagnosis is confirmed by an electrocardiogram Electrocardiogram An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG) that will show an “irregularly irregular” heartbeat with no distinct P waves and narrow QRS complexes. AF AF Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation increases the risk of thromboembolic events. Treatment is primarily based on ventricular rate and rhythm control, which can be achieved through drugs and/or cardioversion Cardioversion Atrial Fibrillation. Anticoagulation Anticoagulation Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs (AC) is administered if the patient is at significant risk for thromboembolic events.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
| Cardiac risk factors | Non-cardiac risk factors |
|---|---|
|
|
| P | Pulmonary diseases:
|
|---|---|
| I |
|
| R |
|
| A |
|
| T |
|
| E |
|
| S |
|
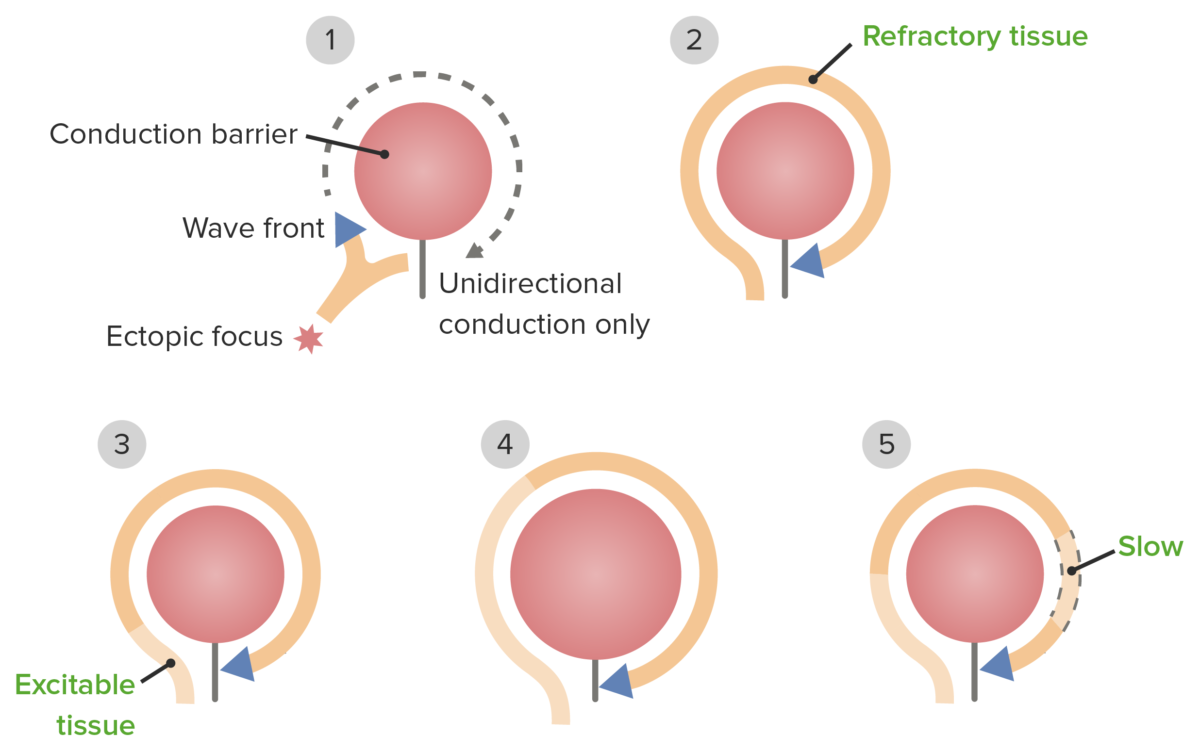
The pathophysiology of re-entrant pathways
The following list outlines the tests available in detecting and evaluating atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation (with the 1st tests being cardiac-focused). Note that presenting symptoms vary, so in some cases, noncardiac tests are performed initially.
Electrocardiogram Electrocardiogram An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG) ( ECG ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG)): confirms diagnosis[1,4,14,21]
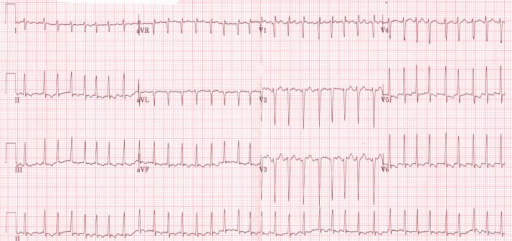
ECG shows an irregularly irregular rhythm of atrial fibrillation in a thyrotoxic patient
Image: “Initial electrocardiogram (ECG) at presentation to the emergency room” by ST4 Diabetes and Endocrinology Princess of Wales Hospital Bridgend, CF31 1RQ UK. License: CC BY 3.0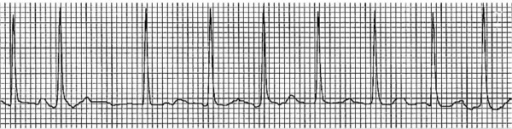
Example of an ECG tracing showing atrial fibrillation with irregularly irregular RR intervals and loss of P waves
Image: “Electrocardiogram showing atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular rate” by Division of Hematology and Oncology, Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, Miami, FL, USA. License: CC BY 2.0Ambulatory monitoring:[1,14]
Echocardiography Echocardiography Ultrasonic recording of the size, motion, and composition of the heart and surrounding tissues. The standard approach is transthoracic. Tricuspid Valve Atresia (TVA): used to identify etiology, risk stratification, structural assessment, and pre-cardioversion thrombus evaluation, not for diagnosis
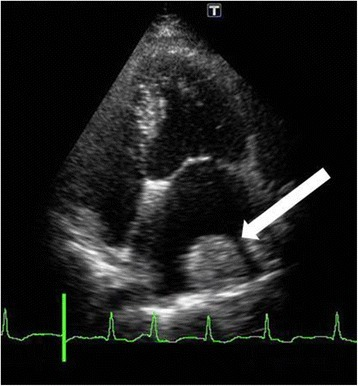
Thrombus formed on the lateral wall of the left atrium (white arrow)
Image: “Fourteen days after cardiac surgery, a thrombus had formed over the lateral left atrium wall (white arrow)” by U.S. National Library of Medicine. License: CC BY 4.0Other tests to rule out underlying and predisposing conditions.
Laboratory studies:
Imaging and procedures:
Variation in guidelines can be seen based on practice locations and availability of resources and drugs. Detailed information regarding regional recommendations is available for review (US, UK, Europe) as well as a comparison summary of the global recommendations.
Care for individuals with AF AF Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation involves addressing the acute onset of AF AF Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation (new onset or uncontrolled rate), control of chronic arrhythmia, and reduction of associated risks.
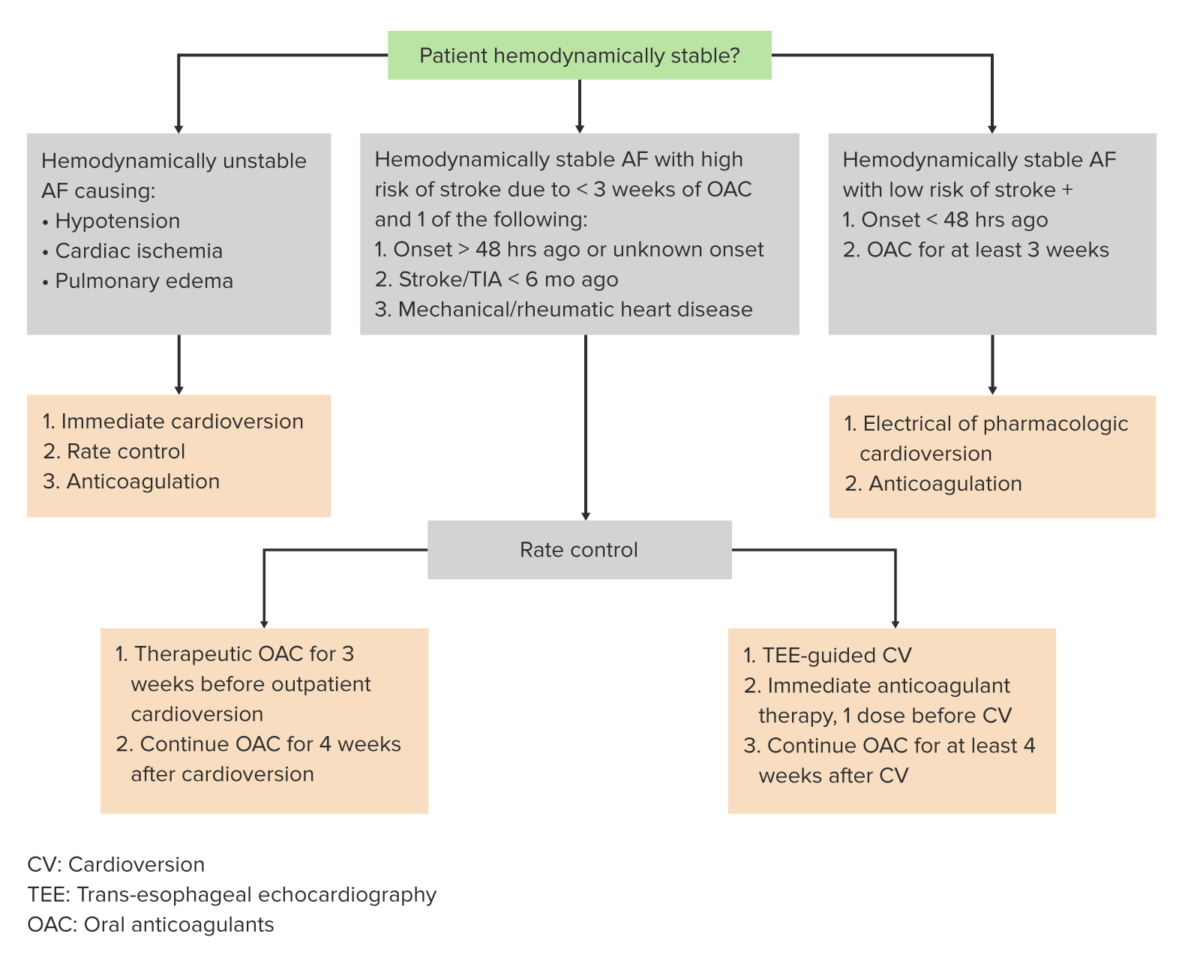
Algorithm for the management of atrial fibrillation
Image by Lecturio.AF AF Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation management consists of the following:
Special considerations:
| Management principles | Treatment options | |
|---|---|---|
| Hemodynamic status |
|
|
| Rate control vs. rhythm control | Rate control Indication:
|
|
| Rhythm control Indication:
|
|
|
| AC | Warfarin Warfarin An anticoagulant that acts by inhibiting the synthesis of vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors. Warfarin is indicated for the prophylaxis and/or treatment of venous thrombosis and its extension, pulmonary embolism, and atrial fibrillation with embolization. It is also used as an adjunct in the prophylaxis of systemic embolism after myocardial infarction. Warfarin is also used as a rodenticide. Anticoagulants, NOAC | Indication:
|
| No AC | Indication:
|
|
| Cardioversion Cardioversion Atrial Fibrillation protocol (electrical or pharmacological) | 3 weeks prior and 4 weeks post-cardioversion | |
| Treat underlying cause | Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension, coronary artery Coronary Artery Truncus Arteriosus disease, valvular heart disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Pulmonary disease Diseases involving the respiratory system. Blastomyces/Blastomycosis, thyrotoxicosis Thyrotoxicosis A hypermetabolic syndrome caused by excess thyroid hormones which may come from endogenous or exogenous sources. The endogenous source of hormone may be thyroid hyperplasia; thyroid neoplasms; or hormone-producing extrathyroidal tissue. Thyrotoxicosis is characterized by nervousness; tachycardia; fatigue; weight loss; heat intolerance; and excessive sweating. Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism, sick sinus syndrome Sick Sinus Syndrome Sick sinus syndrome (SSS), also known as sinus node dysfunction, is characterized by degeneration of the sinoatrial (SA) node, the heart’s primary pacemaker. Patients with SSS may be asymptomatic or may present with tachycardia or bradycardia. Sick Sinus Syndrome, etc ETC The electron transport chain (ETC) sends electrons through a series of proteins, which generate an electrochemical proton gradient that produces energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Electron Transport Chain (ETC). | |
Acute management has the following main components: controlling the ventricular response (VR) and determining the need for cardioversion Cardioversion Atrial Fibrillation.
Background:
Medications:
| Drug class | Medication | Typical IV dose | Typical oral dose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beta blockers | Atenolol Atenolol A cardioselective beta-1 adrenergic blocker possessing properties and potency similar to propranolol, but without a negative inotropic effect. Class 2 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Beta Blockers) | N/A | 25–100 mg daily |
| Bisoprolol Bisoprolol A cardioselective beta-1 adrenergic blocker. It is effective in the management of hypertension and angina pectoris. Class 2 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Beta Blockers) | N/A | 2.5–10 mg daily | |
| Esmolol Esmolol Antiadrenergic Drugs |
|
N/A | |
| Carvedilol Carvedilol A carbazole and propanol derivative that acts as a non-cardioselective beta blocker and vasodilator. It has blocking activity for alpha 1 adrenergic receptors and, at higher doses, may function as a blocker of calcium channels; it also has antioxidant properties. Carvedilol is used in the treatment of hypertension; angina pectoris; and heart failure. It can also reduce the risk of death following myocardial infarction. Class 2 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Beta Blockers) | N/A | 3.125–25 mg twice daily | |
| Metoprolol Metoprolol A selective adrenergic beta-1 blocking agent that is commonly used to treat angina pectoris; hypertension; and cardiac arrhythmias. Antiadrenergic Drugs |
Tartrate:
|
|
|
| Nadolol Nadolol A non-selective beta-adrenergic antagonist with a long half-life, used in cardiovascular disease to treat arrhythmias, angina pectoris, and hypertension. Nadolol is also used for migraine disorders and for tremor. Class 2 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Beta Blockers) | N/A | 10–240 mg daily | |
| Propranolol Propranolol A widely used non-cardioselective beta-adrenergic antagonist. Propranolol has been used for myocardial infarction; arrhythmia; angina pectoris; hypertension; hyperthyroidism; migraine; pheochromocytoma; and anxiety but adverse effects instigate replacement by newer drugs. Antiadrenergic Drugs |
|
10–40 mg 3–4 times daily | |
| NDCCBs | Diltiazem Diltiazem A benzothiazepine derivative with vasodilating action due to its antagonism of the actions of calcium ion on membrane functions. Class 4 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Calcium Channel Blockers) |
|
ER: 120–360 mg daily |
| Verapamil Verapamil A calcium channel blocker that is a class IV anti-arrhythmia agent. Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs |
|
ER: 180–480 mg daily | |
| Others (2nd-line options) | Digoxin Digoxin A cardiotonic glycoside obtained mainly from digitalis lanata; it consists of three sugars and the aglycone digoxigenin. Digoxin has positive inotropic and negative chronotropic activity. It is used to control ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation and in the management of congestive heart failure with atrial fibrillation. Its use in congestive heart failure and sinus rhythm is less certain. The margin between toxic and therapeutic doses is small. Cardiac Glycosides |
|
0.125–0.25 mg daily |
| Amiodarone Amiodarone An antianginal and class III antiarrhythmic drug. It increases the duration of ventricular and atrial muscle action by inhibiting potassium channels and voltage-gated sodium channels. There is a resulting decrease in heart rate and in vascular resistance. Pulmonary Fibrosis |
|
100–200 mg daily |
Cardioversion Cardioversion Atrial Fibrillation, and subsequent maintenance of sinus rhythm Sinus rhythm A heart rate and rhythm driven by the regular firing of the SA node (60–100 beats per minute) Cardiac Physiology, should be managed under the guidance of a cardiologist.
The use of anticoagulation Anticoagulation Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs should be based on the patient’s risk factors for thromboembolism Thromboembolism Obstruction of a blood vessel (embolism) by a blood clot (thrombus) in the blood stream. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and bleeding, but should account for their personal preferences. These factors should be reevaluated periodically.
Is anticoagulation Anticoagulation Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs appropriate?
If appropriate, pick an agent:
| Medication | Mechanism of action | Typical dosing* |
|---|---|---|
| Apixaban Apixaban Anticoagulants | Factor Xa inhibitors | 5 mg twice daily |
| Edoxaban Edoxaban Anticoagulants | 60 mg daily | |
| Rivaroxaban Rivaroxaban A morpholine and thiophene derivative that functions as a factor Xa inhibitor and is used in the treatment and prevention of deep-vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. It is also used for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolization in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation, and for the prevention of atherothrombotic events in patients after an acute coronary syndrome. Anticoagulants | 20 mg daily | |
| Dabigatran Dabigatran A thrombin inhibitor which acts by binding and blocking thrombogenic activity and the prevention of thrombus formation. It is used to reduce the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Anticoagulants | Direct thrombin Thrombin An enzyme formed from prothrombin that converts fibrinogen to fibrin. Hemostasis inhibitors | 150 mg twice daily |
| C | Congestive heart failure Heart Failure A heterogeneous condition in which the heart is unable to pump out sufficient blood to meet the metabolic need of the body. Heart failure can be caused by structural defects, functional abnormalities (ventricular dysfunction), or a sudden overload beyond its capacity. Chronic heart failure is more common than acute heart failure which results from sudden insult to cardiac function, such as myocardial infarction. Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR) | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| H | Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension | 1 |
| A | Age (≥ 75 years) | 2 |
| D | Diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus | 1 |
| S | Stroke, TIA TIA Transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a temporary episode of neurologic dysfunction caused by ischemia without infarction that resolves completely when blood supply is restored. Transient ischemic attack is a neurologic emergency that warrants urgent medical attention. Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA), or thromboembolism Thromboembolism Obstruction of a blood vessel (embolism) by a blood clot (thrombus) in the blood stream. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus | 2 |
| V | Vascular disease | 1 |
| A | Age 65–74 years | 1 |
| Sc | Sex Sex The totality of characteristics of reproductive structure, functions, phenotype, and genotype, differentiating the male from the female organism. Gender Dysphoria category (female) | 1 |
Catheter ablation:[1,3,14,15,21,25]
Left atrial appendage (LAA) obliteration:[1,3,14,15]
The following conditions are differential diagnoses for AF AF Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation:
Diagnosis Codes:
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses.
Atrial Fibrillation (
AFib
Afib
Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses.
Atrial Fibrillation) is coded based on its pattern: paroxysmal (intermittent), persistent (sustained >7 days), or permanent.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | I48.0 | Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation AF that starts spontaneously and terminates spontaneously or with intervention within 7 days of onset; episodes may occur with variable frequency. Atrial Fibrillation |
| ICD-10-CM | I48.11 | Persistent atrial fibrillation Persistent atrial fibrillation AF that fails to self-terminate within 7 days, requires pharmacologic or electrical cardioversion to terminate. Atrial Fibrillation |
| ICD-10-CM | I48.21 | Permanent atrial fibrillation Permanent atrial fibrillation AF that is unresponsive to treatment, patient and doctor decide to no longer pursue a rhythm control strategy. Atrial Fibrillation |
Procedures/Interventions:
These codes are for procedures to manage
AFib
Afib
Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses.
Atrial Fibrillation. Electrical
cardioversion
Cardioversion
Atrial Fibrillation is used to restore
normal sinus rhythm
Normal sinus rhythm
Electrocardiogram (ECG), while catheter ablation is a procedure to electrically isolate the
pulmonary veins
Pulmonary veins
The veins that return the oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
Lungs: Anatomy to prevent
AFib
Afib
Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses.
Atrial Fibrillation recurrence.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CPT | 92960 | Cardioversion Cardioversion Atrial Fibrillation, elective, electrical conversion of arrhythmia; external |
| CPT | 93656 | Comprehensive electrophysiologic evaluation including transseptal catheterizations, insertion and repositioning of multiple electrode catheters with induction or attempted induction of arrhythmia including left atrial pacing and recording, with left atrial ablation… |
Medications:
These codes are for medications to control the
heart rate
Heart rate
The number of times the heart ventricles contract per unit of time, usually per minute.
Cardiac Physiology (rate control) with drugs like
metoprolol
Metoprolol
A selective adrenergic beta-1 blocking agent that is commonly used to treat angina pectoris; hypertension; and cardiac arrhythmias.
Antiadrenergic Drugs, and to prevent stroke (
anticoagulation
Anticoagulation
Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs) with drugs like
apixaban
Apixaban
Anticoagulants.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RxNorm | 6918 | Metoprolol Metoprolol A selective adrenergic beta-1 blocking agent that is commonly used to treat angina pectoris; hypertension; and cardiac arrhythmias. Antiadrenergic Drugs (ingredient) |
| RxNorm | 1364239 | Apixaban Apixaban Anticoagulants (ingredient) |