Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia Tachyarrhythmia A tachyarrhythmia is a rapid heart rhythm, regular or irregular, with a rate > 100 beats/min. Tachyarrhythmia may or may not be accompanied by symptoms of hemodynamic change. Tachyarrhythmias and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. There are many conditions that can cause AF, usually damage to the heart (e.g., coronary artery Coronary Artery Truncus Arteriosus disease, previous myocardial infarction Myocardial infarction MI is ischemia and death of an area of myocardial tissue due to insufficient blood flow and oxygenation, usually from thrombus formation on a ruptured atherosclerotic plaque in the epicardial arteries. Clinical presentation is most commonly with chest pain, but women and patients with diabetes may have atypical symptoms. Myocardial Infarction). Diagnosis is confirmed by an electrocardiogram Electrocardiogram An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG) that will show an “irregularly irregular” heartbeat with no distinct P waves and narrow QRS complexes. AF increases the risk of thromboembolic events. Treatment is primarily based on ventricular rate and rhythm control, which can be achieved through drugs and/or cardioversion. Anticoagulation Anticoagulation Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs is administered if the patient is at significant risk for thromboembolic events.
Last updated: May 27, 2025
Epidemiology
General risk factors for cardiovascular disease
Risk factors for AF
| Cardiac risk factors | Non-cardiac risk factors |
|---|---|
|
|
| P | Pulmonary diseases:
|
|---|---|
| I |
|
| R |
|
| A |
|
| T |
|
| E |
|
| S |
|
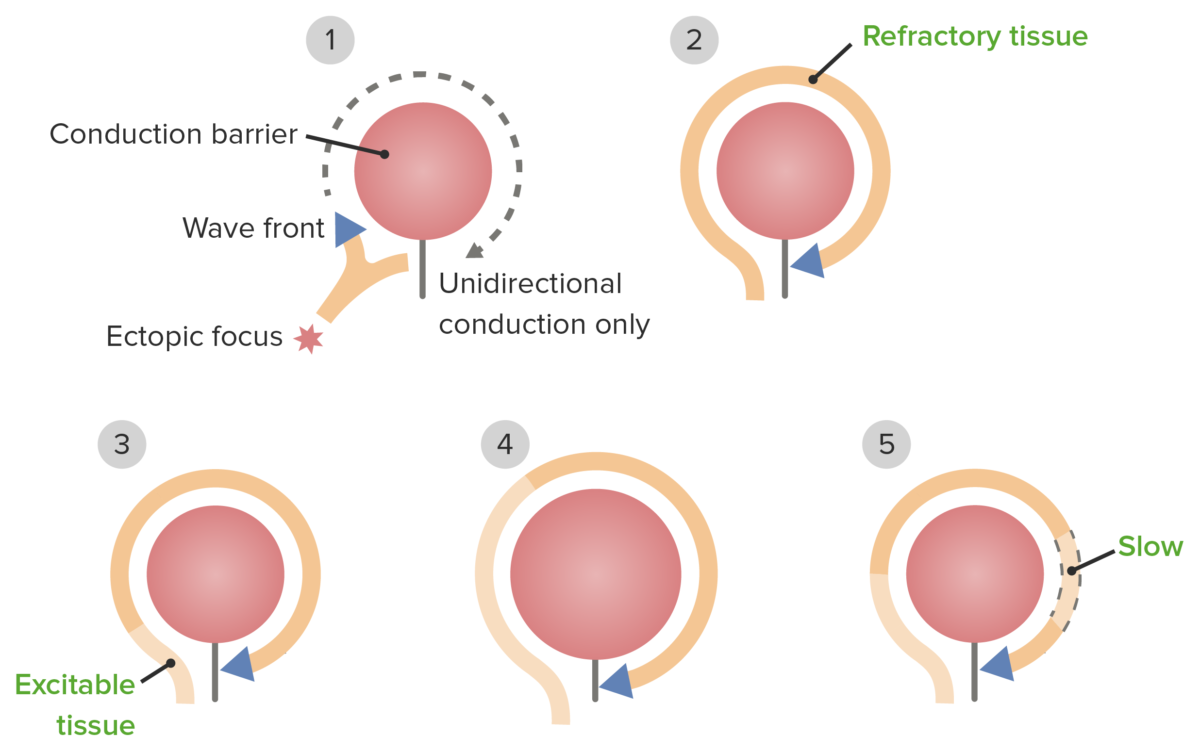
The pathophysiology of re-entrant pathways
Electrocardiogram Electrocardiogram An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG) ( ECG ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG)): confirms diagnosis
Echocardiogram Echocardiogram Transposition of the Great Arteries: used to identify etiology and complications, not for diagnosis
Other tests to rule out underlying conditions:
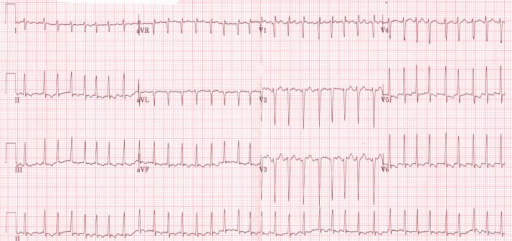
ECG shows an irregularly irregular rhythm of atrial fibrillation in a thyrotoxic patient
Image: “Initial electrocardiogram (ECG) at presentation to the emergency room” by ST4 Diabetes and Endocrinology Princess of Wales Hospital Bridgend, CF31 1RQ UK. License: CC BY 3.0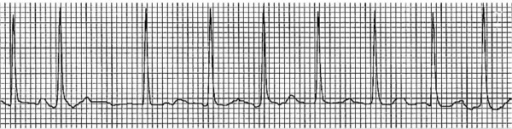
Example of an ECG tracing showing atrial fibrillation with irregularly irregular RR intervals and loss of P waves
Image: “Electrocardiogram showing atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular rate” by Division of Hematology and Oncology, Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, Miami, FL, USA. License: CC BY 2.0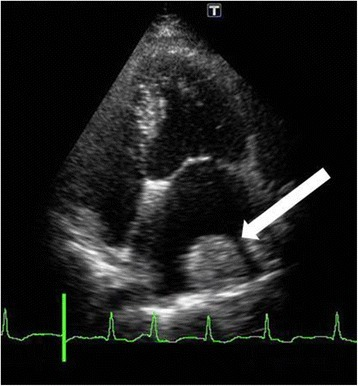
Thrombus formed on the lateral wall of the left atrium (white arrow)
Image: “Fourteen days after cardiac surgery, a thrombus had formed over the lateral left atrium wall (white arrow)” by U.S. National Library of Medicine. License: CC BY 4.0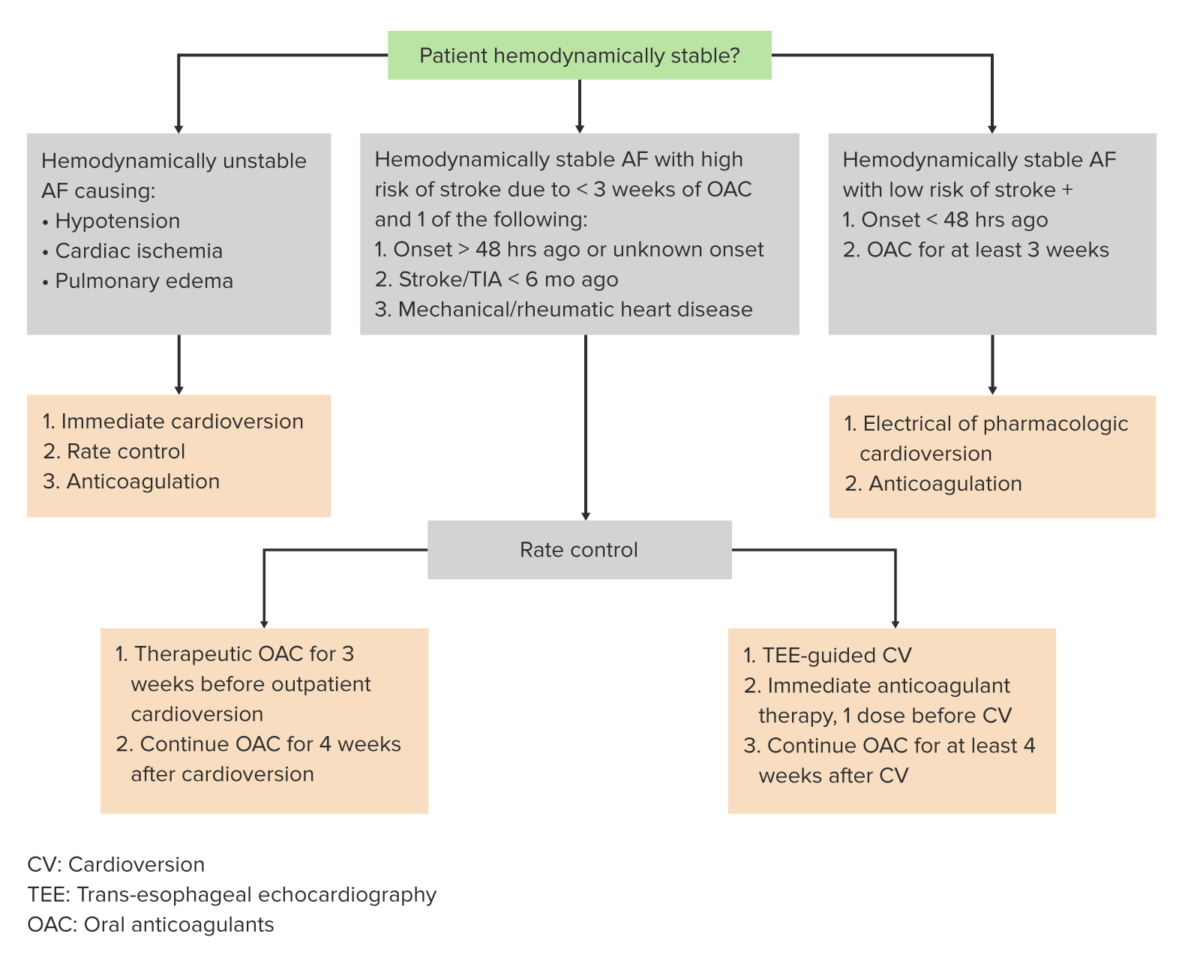
Algorithm for the management of atrial fibrillation
Image by Lecturio.AF management consists of the following:
Special considerations:
| Management principles | Treatment options | |
|---|---|---|
| Hemodynamic status |
|
|
| Rate control vs. rhythm control | Rate control Indication:
|
|
| Rhythm control Indication:
|
|
|
| Anticoagulation Anticoagulation Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs | Warfarin Warfarin An anticoagulant that acts by inhibiting the synthesis of vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors. Warfarin is indicated for the prophylaxis and/or treatment of venous thrombosis and its extension, pulmonary embolism, and atrial fibrillation with embolization. It is also used as an adjunct in the prophylaxis of systemic embolism after myocardial infarction. Warfarin is also used as a rodenticide. Anticoagulants, novel oral anticoagulants Anticoagulants Anticoagulants are drugs that retard or interrupt the coagulation cascade. The primary classes of available anticoagulants include heparins, vitamin K-dependent antagonists (e.g., warfarin), direct thrombin inhibitors, and factor Xa inhibitors. Anticoagulants (NOAC) | Indication:
|
| Aspirin Aspirin The prototypical analgesic used in the treatment of mild to moderate pain. It has anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties and acts as an inhibitor of cyclooxygenase which results in the inhibition of the biosynthesis of prostaglandins. Aspirin also inhibits platelet aggregation and is used in the prevention of arterial and venous thrombosis. Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) (antiplatelet therapy) | Indication:
|
|
| Cardioversion protocol (electrical or pharmacological) | 3 weeks prior and 4 weeks post-cardioversion | |
| Treat underlying cause | Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension, coronary artery Coronary Artery Truncus Arteriosus disease, valvular heart disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Pulmonary disease Diseases involving the respiratory system. Blastomyces/Blastomycosis, thyrotoxicosis Thyrotoxicosis A hypermetabolic syndrome caused by excess thyroid hormones which may come from endogenous or exogenous sources. The endogenous source of hormone may be thyroid hyperplasia; thyroid neoplasms; or hormone-producing extrathyroidal tissue. Thyrotoxicosis is characterized by nervousness; tachycardia; fatigue; weight loss; heat intolerance; and excessive sweating. Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism, sick sinus syndrome Sick Sinus Syndrome Sick sinus syndrome (SSS), also known as sinus node dysfunction, is characterized by degeneration of the sinoatrial (SA) node, the heart’s primary pacemaker. Patients with SSS may be asymptomatic or may present with tachycardia or bradycardia. Sick Sinus Syndrome, etc ETC The electron transport chain (ETC) sends electrons through a series of proteins, which generate an electrochemical proton gradient that produces energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Electron Transport Chain (ETC). | |
| C | Congestive heart failure Heart Failure A heterogeneous condition in which the heart is unable to pump out sufficient blood to meet the metabolic need of the body. Heart failure can be caused by structural defects, functional abnormalities (ventricular dysfunction), or a sudden overload beyond its capacity. Chronic heart failure is more common than acute heart failure which results from sudden insult to cardiac function, such as myocardial infarction. Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR) | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| H | Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension | 1 |
| A | Age (≥ 75 years) | 2 |
| D | Diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus | 1 |
| S | Stroke, TIA TIA Transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a temporary episode of neurologic dysfunction caused by ischemia without infarction that resolves completely when blood supply is restored. Transient ischemic attack is a neurologic emergency that warrants urgent medical attention. Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA), or thromboembolism Thromboembolism Obstruction of a blood vessel (embolism) by a blood clot (thrombus) in the blood stream. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus | 2 |
| V | Vascular disease | 1 |
| A | Age 65–74 years | 1 |
The following conditions are differential diagnoses for AF:
References