Atherosclerosis is a common form of arterial disease in which lipid deposition forms a plaque Plaque Primary Skin Lesions in the blood vessel walls. Atherosclerosis is an incurable disease, for which there are clearly defined risk factors that often can be reduced through a change in lifestyle and behavior of the patient. Atherosclerosis manifests itself as vessel stenosis Stenosis Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) and a source of thromboembolic disease. The clinical manifestations depend on the specific vessels affected and include most notably coronary artery Coronary Artery Truncus Arteriosus disease, carotid disease, and peripheral vascular disease. Atherosclerosis is the most common primary disease of the arterial vascular system and is responsible for coronary heart disease Coronary heart disease Coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease, describes a situation in which an inadequate supply of blood to the myocardium exists due to a stenosis of the coronary arteries, typically from atherosclerosis. Coronary Heart Disease, the leading cause of death worldwide.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Atherosclerosis is a common form of arterial disease in which lipid deposition forms a plaque Plaque Primary Skin Lesions in the blood vessel walls.
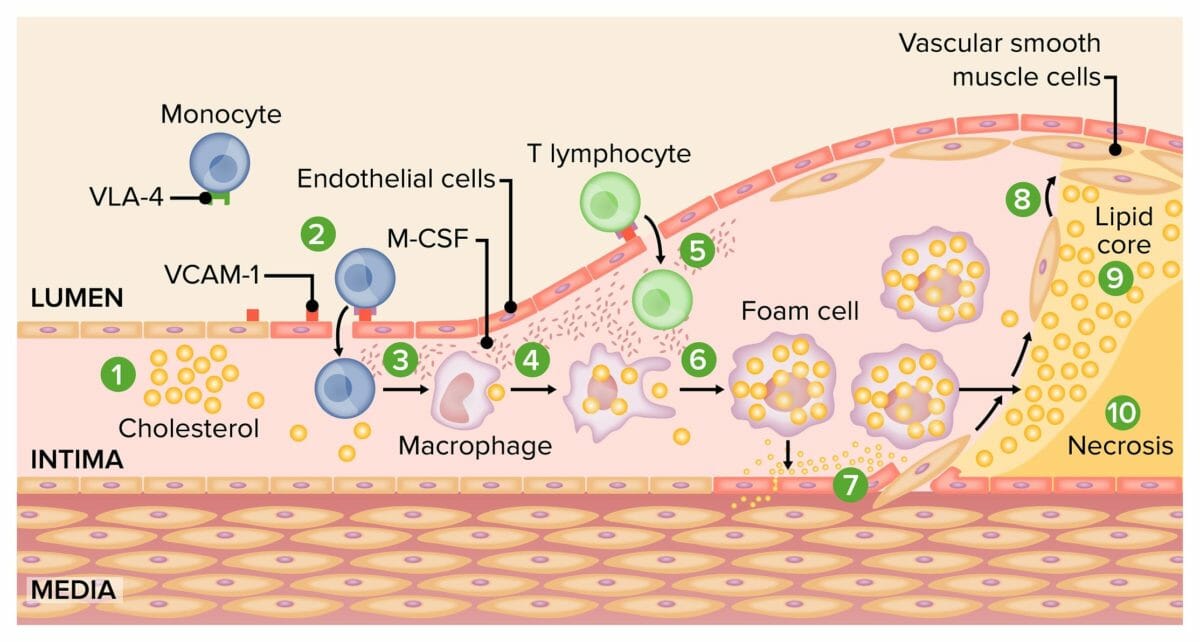
Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis:
1) Activation of endothelial cells by oxidized LDLs
2) Expression of leukocyte adhesion molecules and consequent monocyte adhesion
3) Monocyte transmigration into the intima
4) Differentiation of monocytes into macrophages
5) Plaque formation by joining of the T lymphocytes and macrophages
6) Formation of lipid-rich foam cells
7) Migration and replication of vascular smooth muscle cells
8) Accumulation of smooth muscle cells in the plaque, forming a fibroproliferative lesion
9, 10) Death of foam cells and formation of necrotic core
VCAM-1: vascular cell adhesion protein 1
M-CSF: macrophage colony-stimulating factor
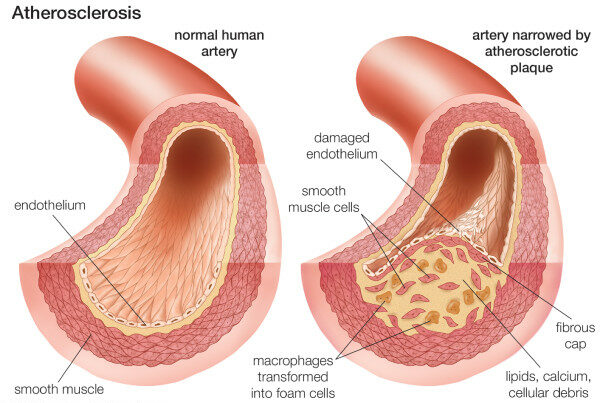
Composition of the atherosclerotic plaque
Image: “Neovascularization of coronary tunica intima (DIT) is the cause of coronary atherosclerosis. Lipoproteins invade coronary intima via neovascularization from adventitial vasa vasorum, but not from the arterial lumen: a hypothesis” by Subbotin, VM/ Encyclopeadia Britannica. License: CC BY 2.0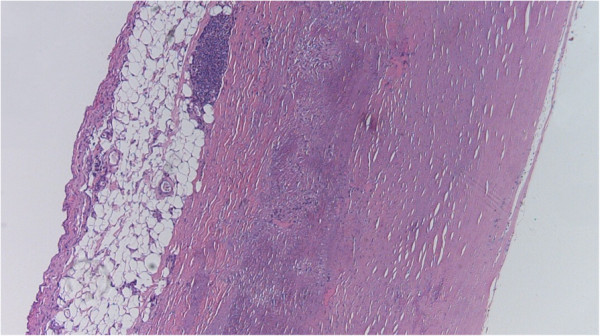
Atherosclerosis grade 1:
This mild form of atherosclerosis is caused by connective tissue proliferation in the tunica intima, also known as intimal fibrosis.
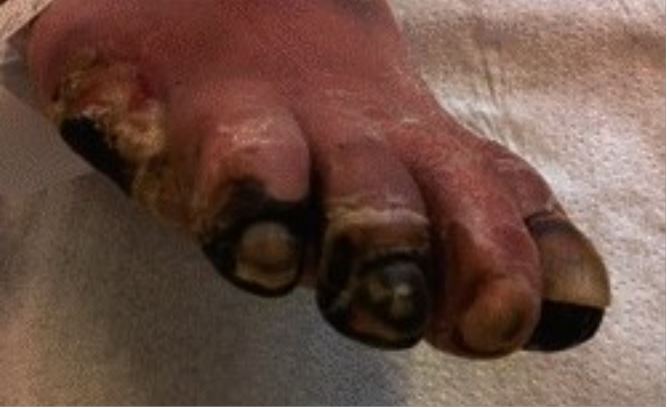
Toe gangrene secondary to peripheral arterial disease of lower extremities
Image: “Education in wound care: Curricula for doctors and nurses, and experiences from the German wound healing society ICW” by Military Medical Research. License: CC BY 4.0, cropped by Lecturio.History:
Physical exam:
Laboratory tests:
Electrocardiography Electrocardiography Recording of the moment-to-moment electromotive forces of the heart as projected onto various sites on the body’s surface, delineated as a scalar function of time. The recording is monitored by a tracing on slow moving chart paper or by observing it on a cardioscope, which is a cathode ray tube display. Electrocardiogram (ECG) (for findings of cardiac ischemia Ischemia A hypoperfusion of the blood through an organ or tissue caused by a pathologic constriction or obstruction of its blood vessels, or an absence of blood circulation. Ischemic Cell Damage):
Vessel imaging:
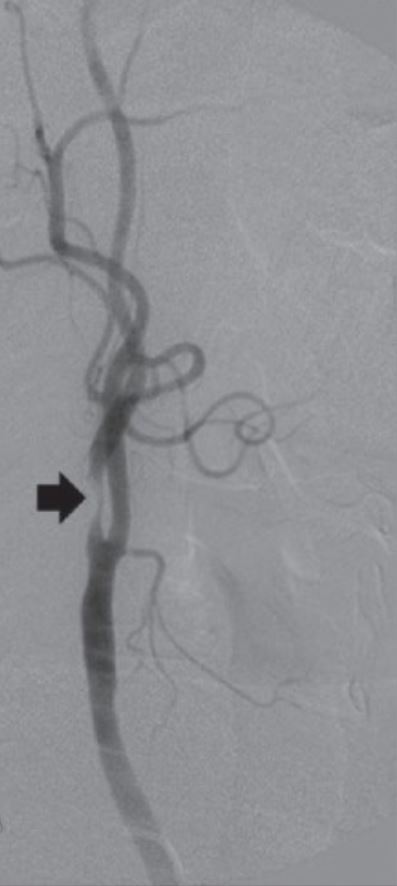
Angiogram of internal carotid artery stenosis (arrow)
Image: “Review: Interventional radiology in peripheral vascular disease” by Imaging. License: CC BY 2.0, cropped by Lecturio.The following diseases are consequences of atherosclerosis: