Atelectasis is the partial or complete collapse of a part of the lung. Atelectasis is almost always a secondary phenomenon from conditions causing bronchial obstruction, external compression External Compression Blunt Chest Trauma, surfactant Surfactant Substances and drugs that lower the surface tension of the mucoid layer lining the pulmonary alveoli. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) deficiency, or scarring Scarring Inflammation. Hypoxemia Hypoxemia Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome can occur as a result of blood flowing through unventilated lung segments. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are often asymptomatic. However, dyspnea Dyspnea Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea, cough, chest pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, and fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever can also occur. The diagnosis is made with imaging. Management includes treatment of the underlying etiology, lung expansion exercises, chest physiotherapy Physiotherapy Spinal Stenosis, bronchodilators Bronchodilators Asthma Drugs, and bronchoscopy Bronchoscopy Endoscopic examination, therapy or surgery of the bronchi. Laryngomalacia and Tracheomalacia in select cases.
Last updated: Mar 25, 2025
Atelectasis is the partial or complete collapse of lung tissue.
Atelectasis is classified on the basis of the underlying pathophysiology.
Etiology:
Pathophysiology:
Relaxation atelectasis:
Compressive atelectasis:
Adhesive atelectasis:
Cicatricial atelectasis:
Replacement atelectasis:
Rounded atelectasis:
Findings:
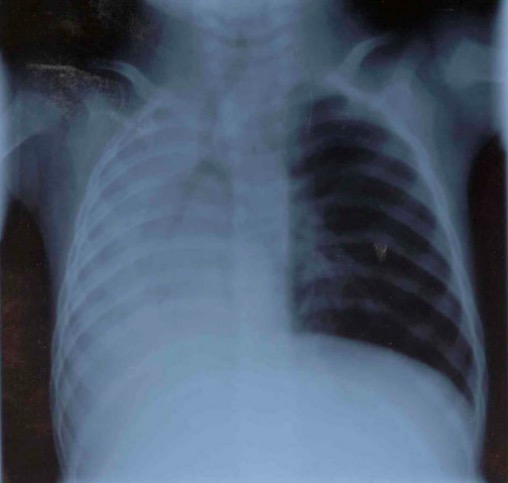
Total atelectasis of the right lung on chest X-ray:
Note the tracheal and mediastinal shift toward the right, with compensatory hyperinflation of the left lung.
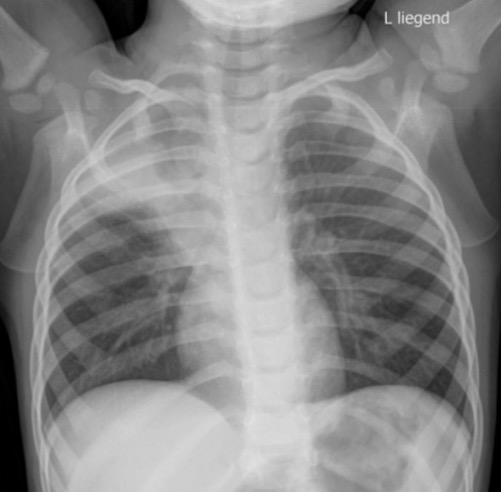
Chest X-ray demonstrating right upper lobe atelectasis with lung opacification and evidence of volume loss
Image: “Chest X-ray of case 2” by Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Graubuenden Cantonal Hospital, Chur, Switzerland. License: CC BY 2.0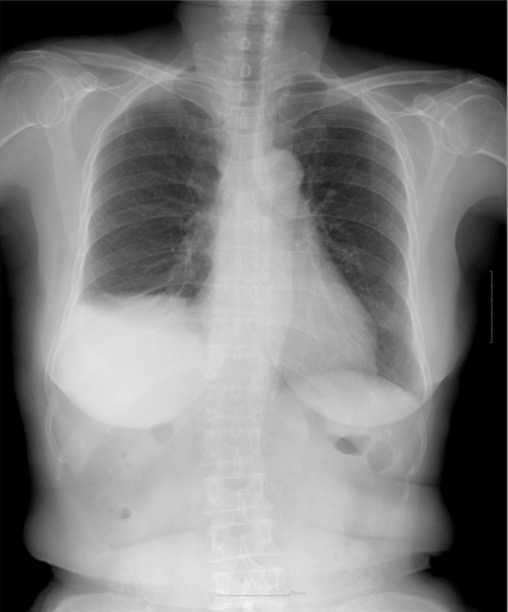
Chest X-ray showing right basilar atelectasis with a right pleural effusion and hemidiaphragm elevation
Image: “Chest X-ray at 3 months” by Helen Ki Shinn, MD. License: CC BY 4.0Findings are similar to chest X-ray X-ray Penetrating electromagnetic radiation emitted when the inner orbital electrons of an atom are excited and release radiant energy. X-ray wavelengths range from 1 pm to 10 nm. Hard x-rays are the higher energy, shorter wavelength x-rays. Soft x-rays or grenz rays are less energetic and longer in wavelength. The short wavelength end of the x-ray spectrum overlaps the gamma rays wavelength range. The distinction between gamma rays and x-rays is based on their radiation source. Pulmonary Function Tests, but CT may be more sensitive in determining an etiology:
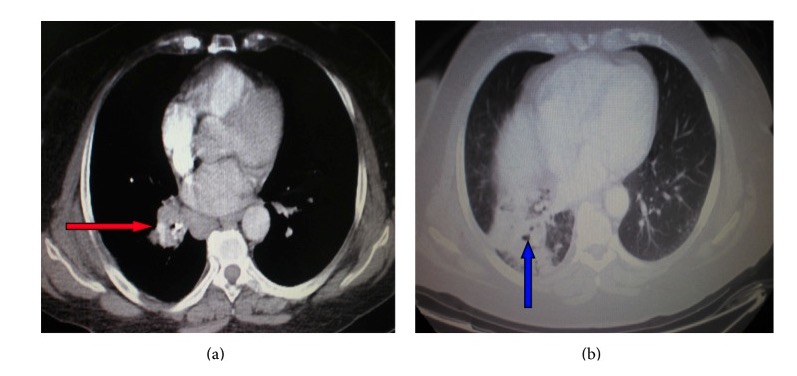
CT of the chest showing a right hilar mass (red arrow) compressing the bronchus and leading to right lower lobe atelectasis (blue arrow)
Image: “ Atelectasis” by Department of Pneumonology, Army General Hospital of Athens, 138 Mesogion & Katehaki Avenue, 115 25 Athens, Greece. License: CC BY 3.0In addition to treating the underlying etiology of atelectasis, the following options can be used for prevention and treatment:
Bronchoscopy is a procedure that allows visualization of the airways by way of a bronchoscope.
Image by Lecturio.