Ataxia-telangiectasia, also known as Louis-Bar syndrome, is a neurocutaneous syndrome, which involves multiple systems but mainly affects the neurological system. Ataxia-telangiectasia is an autosomal recessive Autosomal recessive Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal recessive diseases are only expressed when 2 copies of the recessive allele are inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance genetic disorder caused by a mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations in the ATM gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics (ATM serine Serine A non-essential amino acid occurring in natural form as the l-isomer. It is synthesized from glycine or threonine. It is involved in the biosynthesis of purines; pyrimidines; and other amino acids. Synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids/threonine kinase or the ataxia-telangiectasia mutated gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics). Ataxia-telangiectasia presents with progressive ataxia, telangiectasias, extrapyramidal symptoms, dermatological manifestations, immune dysfunction, and progressive pulmonary disease Pulmonary disease Diseases involving the respiratory system. Blastomyces/Blastomycosis. Diagnosis is based on clinical presentation and confirmed with neuroimaging Neuroimaging Non-invasive methods of visualizing the central nervous system, especially the brain, by various imaging modalities. Febrile Infant and genetic testing Genetic Testing Detection of a mutation; genotype; karyotype; or specific alleles associated with genetic traits, heritable diseases, or predisposition to a disease, or that may lead to the disease in descendants. It includes prenatal genetic testing. Myotonic Dystrophies. Management is supportive with symptom management. Prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas is poor secondary to numerous complications.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Ataxia-telangiectasia is a rare, autosomal recessive Autosomal recessive Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal recessive diseases are only expressed when 2 copies of the recessive allele are inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive ataxia and multisystem dysfunction due to a defect in the ATM gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics (ATM serine Serine A non-essential amino acid occurring in natural form as the l-isomer. It is synthesized from glycine or threonine. It is involved in the biosynthesis of purines; pyrimidines; and other amino acids. Synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids/threonine kinase or the ataxia-telangiectasia mutated gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics).
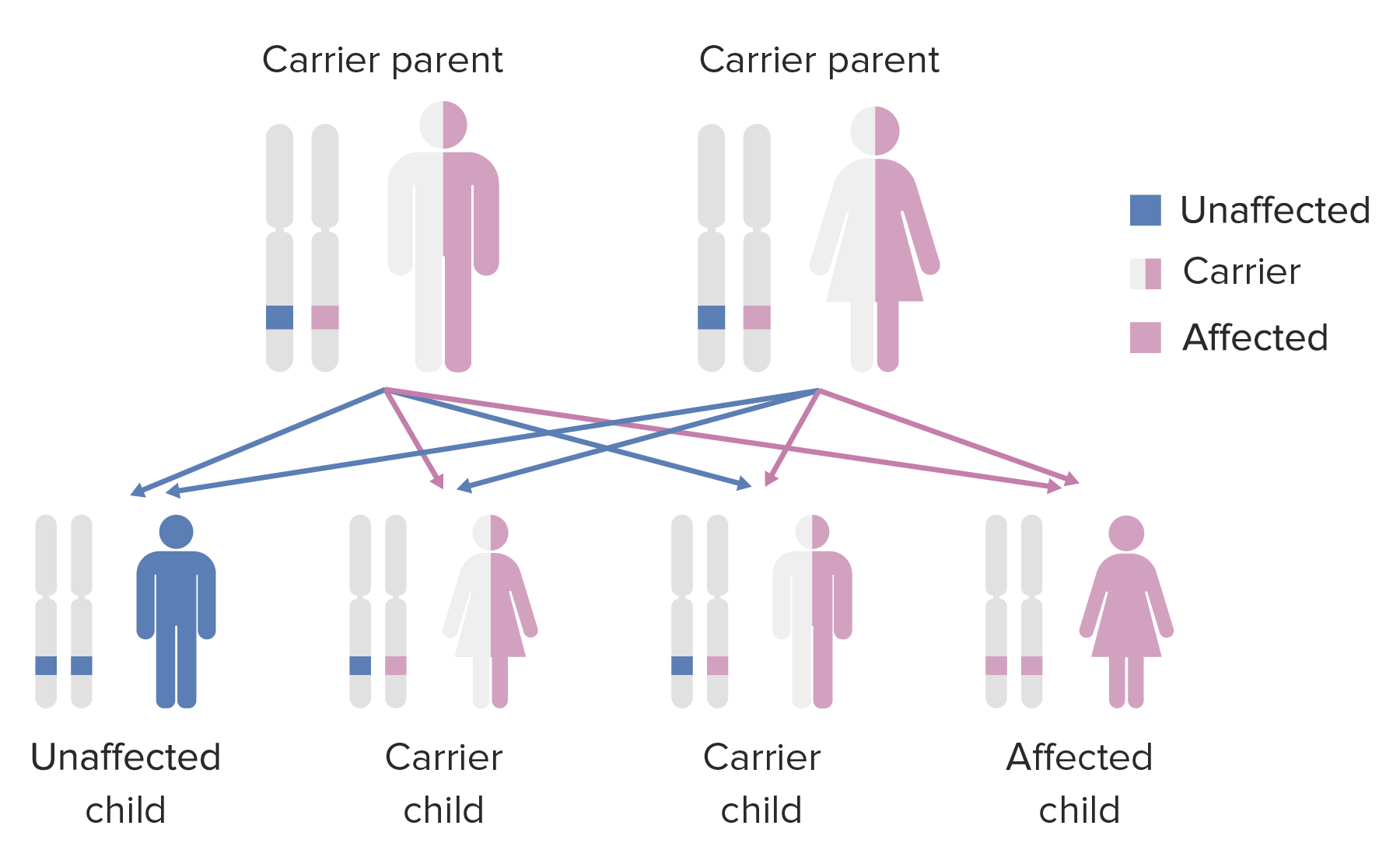
Diagram of the inheritance pattern of autosomal recessive conditions
Image by Lecturio.Ataxia-telangiectasia is caused by mutations in the ATM gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics. Mutations may appear in a variety of ways:
Mutations in the ATM gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics increase the risk of cancer and radiosensitivity. The mutations lead to a dysfunctional protein, which causes:
Symptoms of ataxia present in the 1st 5 years of life and progress with the age of the affected individual:
Responsible for many of the motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology abnormalities characteristic of ataxia-telangiectasia:
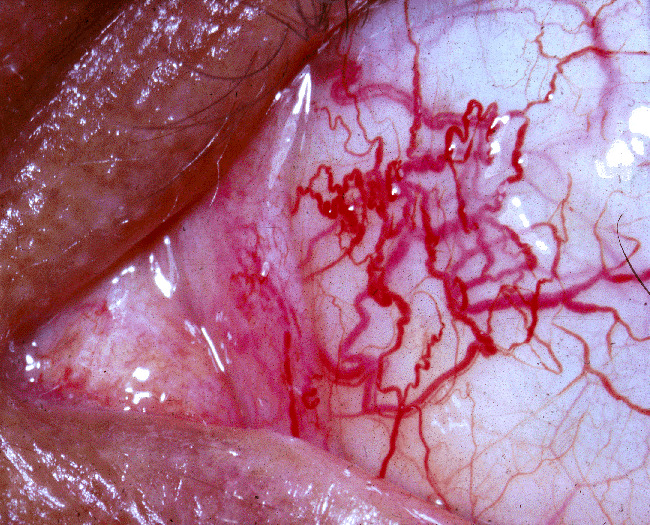
Ocular telangiectasias observed in an individual with ataxia-telangiectasia
Image: “Ataxia-telangiectasia” by National Eye Institute. License: Public Domain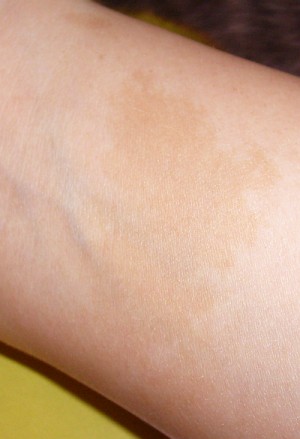
Café au lait macule is 1 of the dermatologic manifestations of ataxia-telangiectasia
Image: “Cafe au lait fleck” by Denise Nepraunig. License: Public DomainDiagnosis of ataxia-telangiectasia is mainly based on clinical presentation. The diagnosis is confirmed with laboratory testing, genetic testing Genetic Testing Detection of a mutation; genotype; karyotype; or specific alleles associated with genetic traits, heritable diseases, or predisposition to a disease, or that may lead to the disease in descendants. It includes prenatal genetic testing. Myotonic Dystrophies, and imaging studies.
Management of ataxia-telangiectasia is supportive with symptom management: