The apophysis is a secondary ossification center Secondary ossification center Development of the Limbs found on non-weight-bearing segments of bones. The apophysis is also the site of ligament or tendon insertion and is involved in the peripheral growth of the bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types. These secondary growth centers are generally open in late childhood and may not close until early adulthood. With overuse, the apophysis may become inflamed and painful, becoming vulnerable to tearing and avulsion. An acute apophyseal avulsion fracture Avulsion fracture Tearing away of the cortical bone fragment at the location of a strong ligament or tendon attachment. The bone fragment detachment site often occurs near a soft site (e.g., growth plate) at the base where ligaments; tendons; or joint capsules attach. Overview of Bone Fractures occurs when a portion of the apophysis is pulled off by the ligament, usually secondary to explosive movements and eccentric muscular contractions. Apophyseal avulsion fractures are primarily treated conservatively, but may require surgical repair if the avulsed fragment is large or significantly displaced.
Last updated: Jan 7, 2025
An avulsion fracture Avulsion fracture Tearing away of the cortical bone fragment at the location of a strong ligament or tendon attachment. The bone fragment detachment site often occurs near a soft site (e.g., growth plate) at the base where ligaments; tendons; or joint capsules attach. Overview of Bone Fractures occurs when part of an apophysis is ripped off by the ligament due to a sudden forceful eccentric or concentric contraction of the muscle attached to it.
Apophyses exist on many bones and are the insertion site of a number of ligaments. Avulsion fractures can occur at any of these sites.
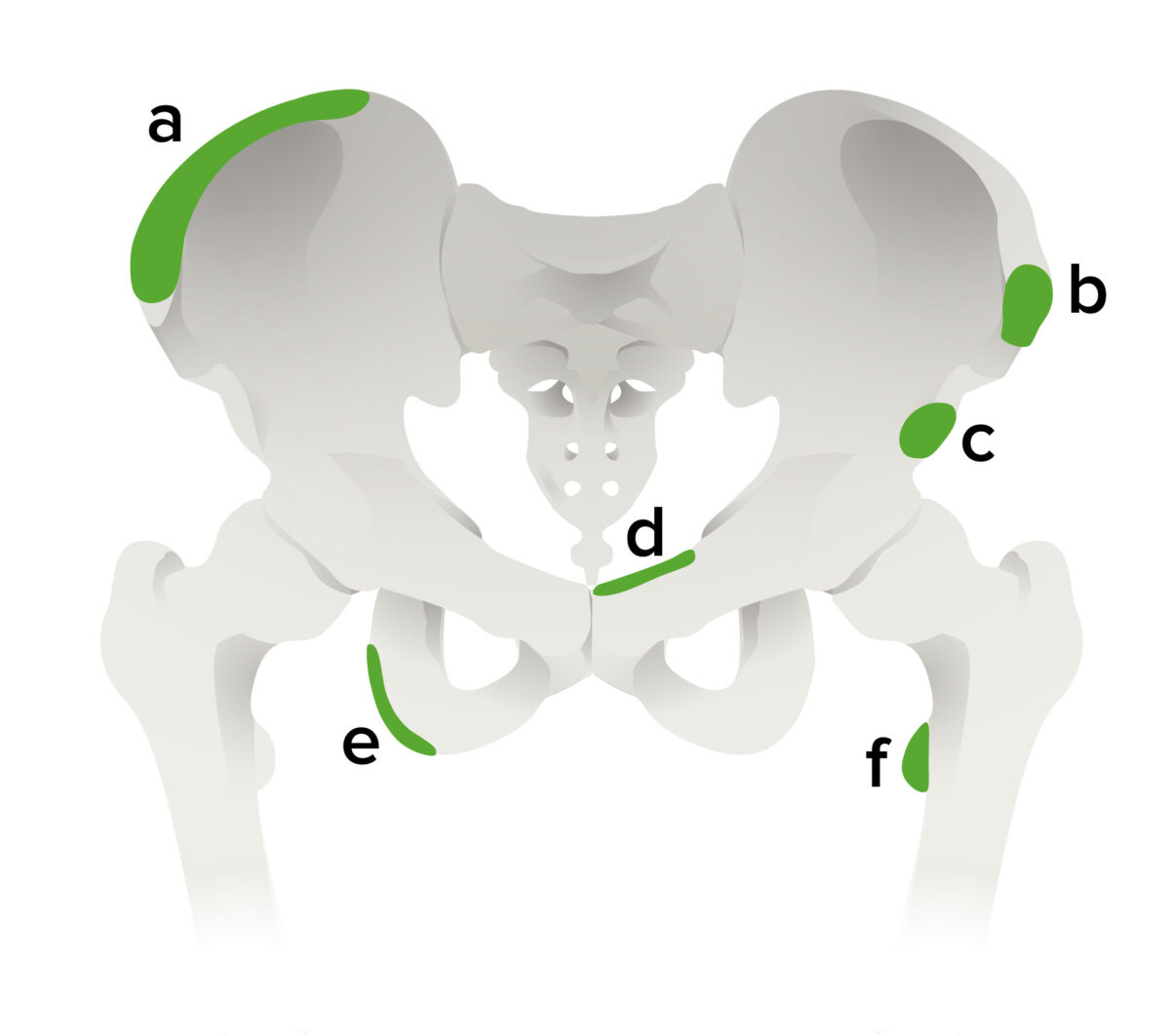
Most frequent sites of pelvic apophyseal avulsion fractures:
a: iliac crest (attachment of the obliques and rectus abdominis muscles)
b: anterior superior iliac spine (attachment of sartorius muscle; seen most commonly in adolescent sprinters)
c: anterior inferior iliac spine (attachment of rectus femoris)
d: superior aspect of the symphysis pubis (insertion of rectus abdominis muscle)
e: ischial tuberosity (hamstring insertion avulsion seen in adolescent sprinters; frequently misdiagnosed as acute hamstring tendon or muscle injury)
f: lesser trochanter of the femur (insertion of iliopsoas muscle, rarely injured in adolescents during traumatic injury)
Acute apophyseal injuries are generally non-contact related, but rather due to a sudden explosive eccentric muscle contraction.
Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship present with:
Exam can reveal:
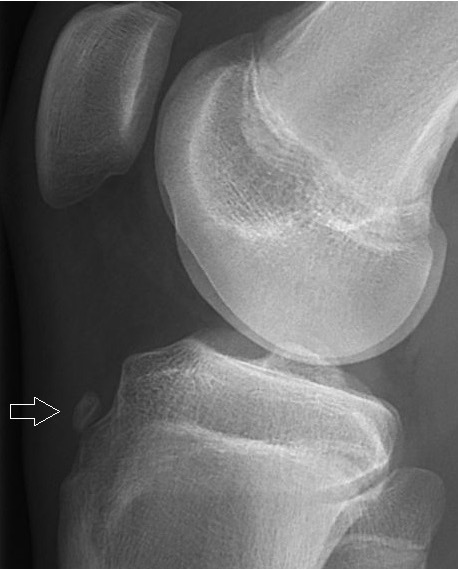
X-ray of a 15-year-old boy showing an older avulsion fracture of the tibial tuberosity:
Avulsed fragments of bone (arrow) are sometimes visible on X-ray of acute injuries, while soft-tissue swelling is a non-specific finding seen with many kinds of fractures.
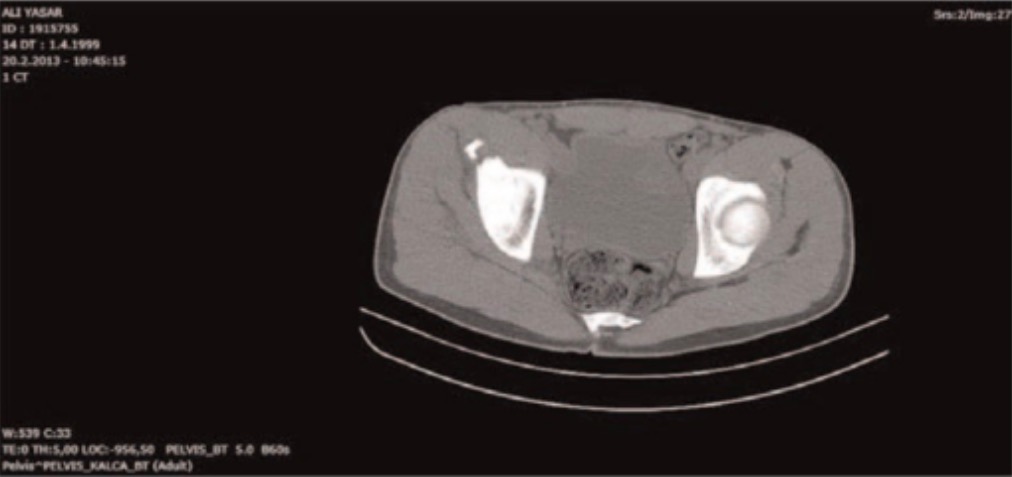
Axial CT scan of the pelvis showing the avulsion fracture of the left anterior superior iliac spine:
While X-ray is sufficient to diagnose avulsion fractions, CT is sometimes utilized to evaluate the bone fragment size and extent of displacement in perioperative planning.
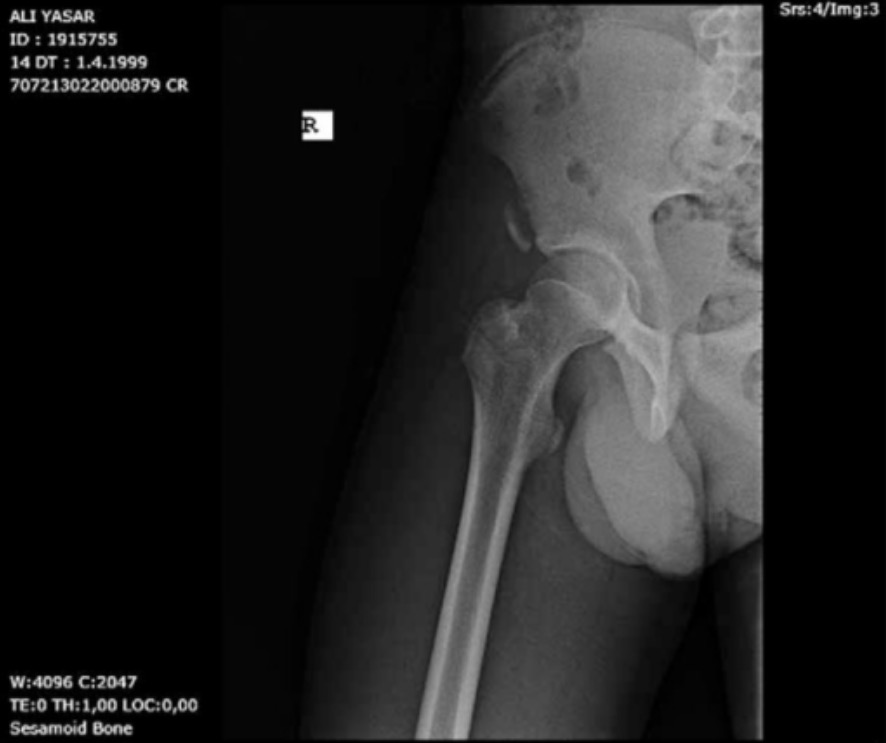
Pelvic anteroposterior X-ray shows a right anterior inferior iliac spine avulsion fracture.
Image: “Pelvis anteroposterior X-ray” by From the Faculty of Medicine (SS, UT, Birhan OKTAS), Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Kırıkkale University, Kırıkkale, Turkey. License: CC BY 4.0Management of most acute avulsion injuries is non-surgical and based on the location and amount of displacement Displacement The process by which an emotional or behavioral response that is appropriate for one situation appears in another situation for which it is inappropriate. Defense Mechanisms of the avulsed bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types.
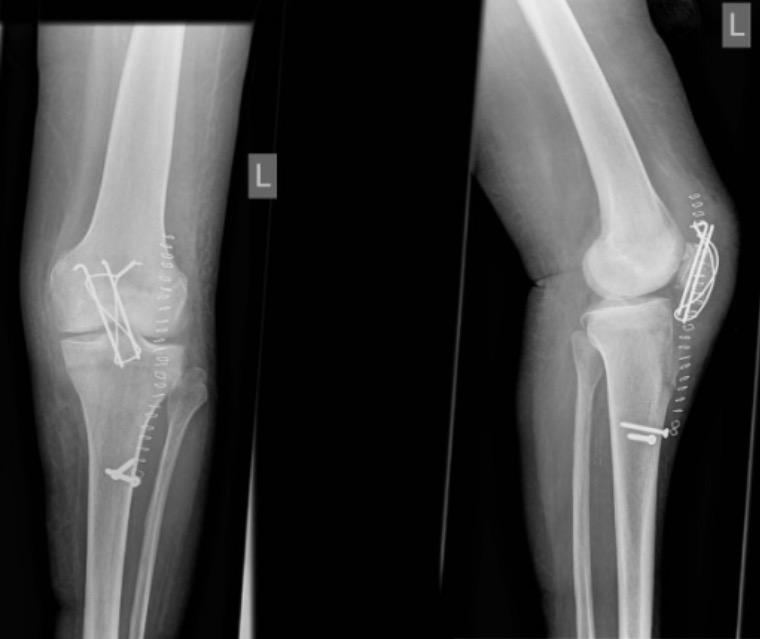
Surgical refixation of avulsion fracture of the tibial tuberosity: postoperative anteroposterior and lateral radiographs of left knee after refixation of avulsion fracture of the tibial tuberosity
Image: “Radiographs of left knee” by Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology, Kantonsspital Bruderholz, CH-4101 Bruderholz, Switzerland. License: CC BY 2.0Additional important pediatric skeletal injuries: