Antivirals for hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus include the nucleoside/nucleotide analogs, also known as nucleoside/ nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors Anti-HIV Drugs (NRTIs). Because of their similar chemical structure to nucleosides Nucleosides Purine or pyrimidine bases attached to a ribose or deoxyribose. Nucleic Acids and nucleotides Nucleotides The monomeric units from which DNA or RNA polymers are constructed. They consist of a purine or pyrimidine base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Nucleic Acids, NRTIs are able to integrate into viral DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure during the replication process. This process inhibits the function of viral RNA-dependent DNA polymerase RNA-dependent DNA polymerase An enzyme that synthesizes DNA on an RNA template. It is encoded by the pol gene of retroviruses and by certain retrovirus-like elements. Virology, resulting in chain termination. All of these medications are administered orally and are excreted by the kidneys Kidneys The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs located retroperitoneally against the posterior wall of the abdomen on either side of the spine. As part of the urinary tract, the kidneys are responsible for blood filtration and excretion of water-soluble waste in the urine. Kidneys: Anatomy. Indications include chronic hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus infection, and some (such as lamivudine Lamivudine A reverse transcriptase inhibitor and zalcitabine analog in which a sulfur atom replaces the 3' carbon of the pentose ring. It is used to treat HIV disease. Anti-HIV Drugs) are also used for HIV HIV Anti-HIV Drugs. Adverse effects include GI symptoms, evidence of mitochondrial toxicity Toxicity Dosage Calculation (such as lactic acidosis Lactic Acidosis Oxazolidinones), and rebound infection upon discontinuation.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Antivirals for hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus have structures similar to those of nucleotides Nucleotides The monomeric units from which DNA or RNA polymers are constructed. They consist of a purine or pyrimidine base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Nucleic Acids and nucleosides Nucleosides Purine or pyrimidine bases attached to a ribose or deoxyribose. Nucleic Acids, thus they are classified as nucleoside/nucleotide analogs (also known as nucleoside/ nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors Anti-HIV Drugs (NRTIs)).
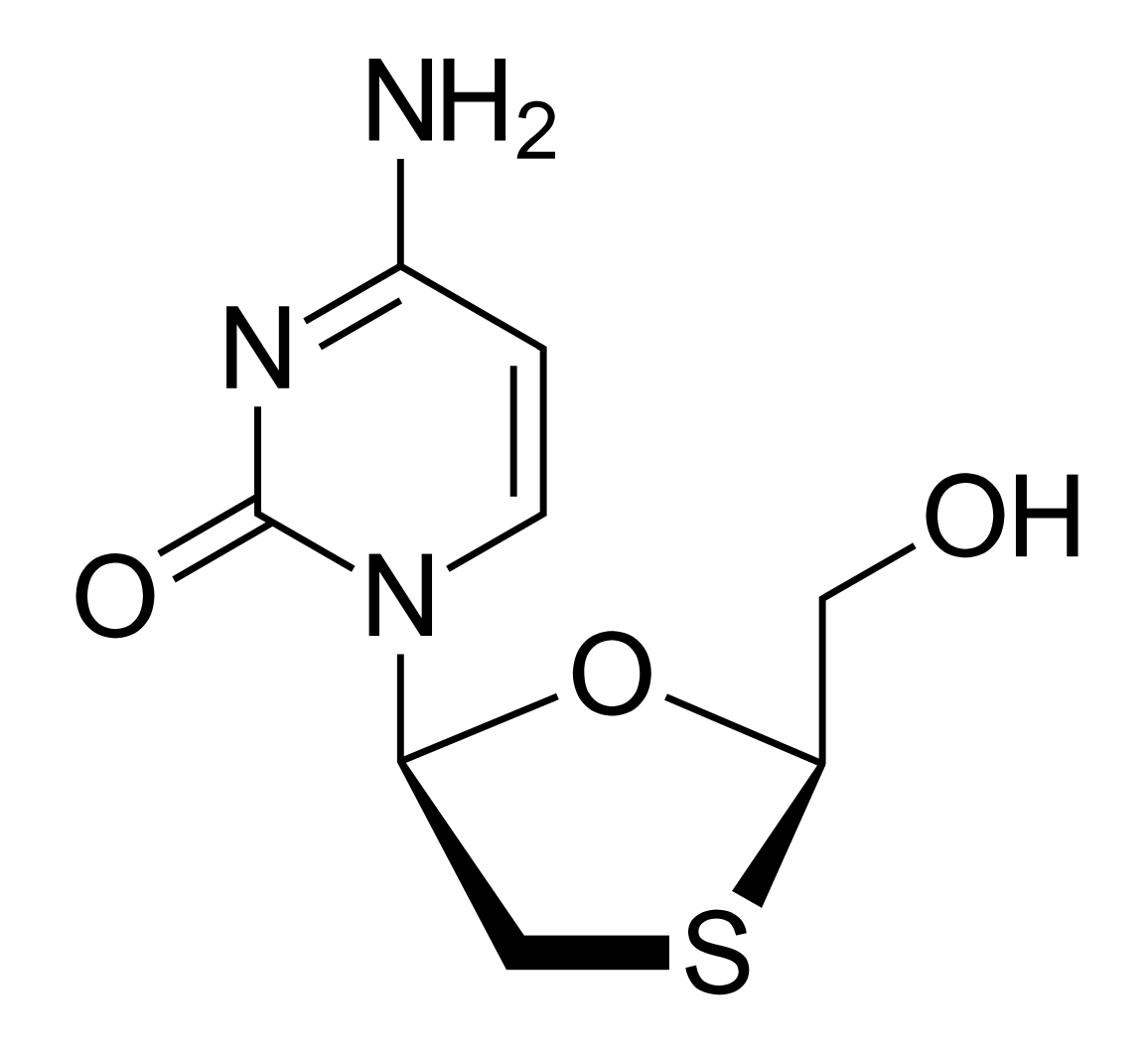
Chemical structure of lamivudine
Image: “2D structure of lamivudine. Created with ChemDoodle and Adobe Illustrator” by Vaccinationist. License: Public Domain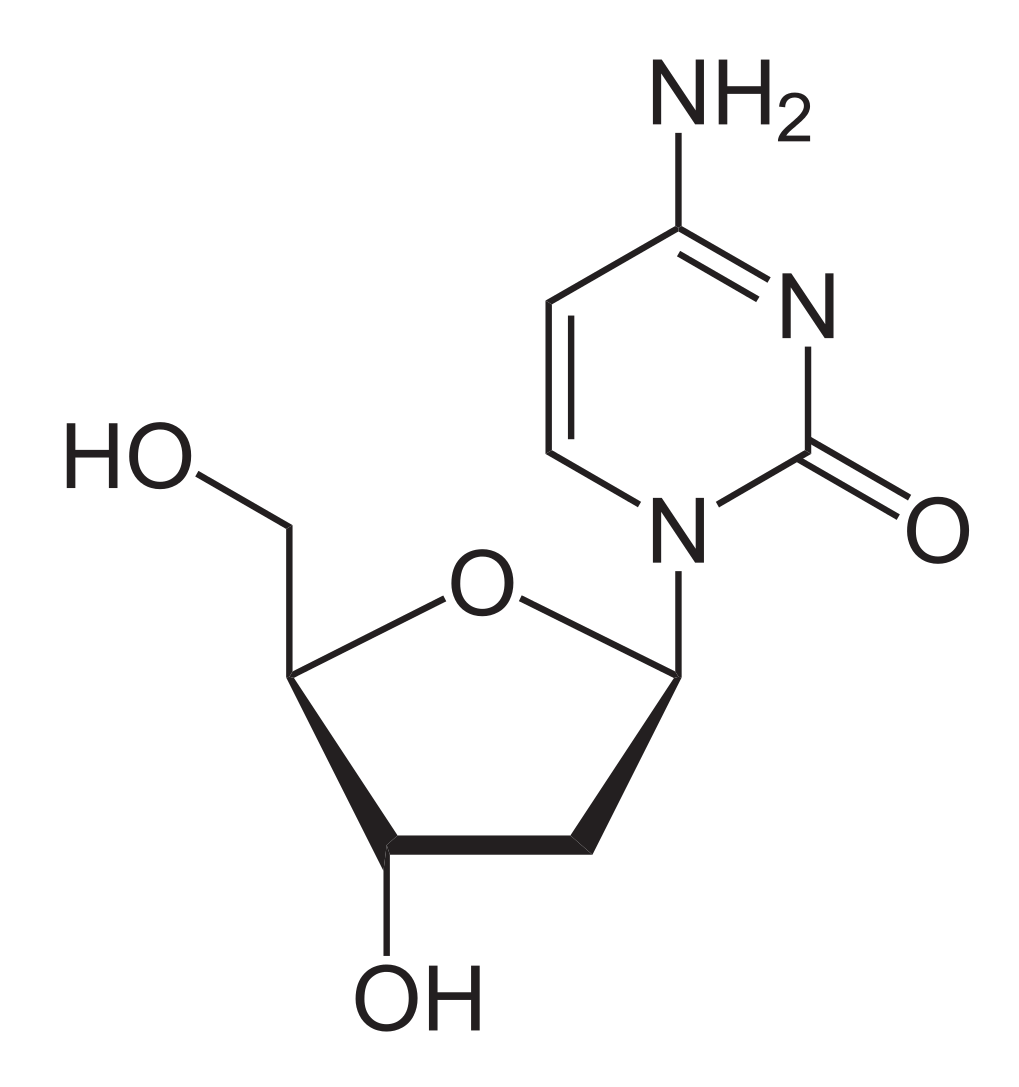
Chemical structure of deoxycytidine:
Note the similarity that lamivudine has to this nucleoside.
All of these medications are excreted by the kidneys Kidneys The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs located retroperitoneally against the posterior wall of the abdomen on either side of the spine. As part of the urinary tract, the kidneys are responsible for blood filtration and excretion of water-soluble waste in the urine. Kidneys: Anatomy.
Indications for treatment:
Differences among medications: