Antitumor antibiotics, also known as antineoplastic antibiotics, are the product of soil microbes, Streptomyces bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology. The commonly used types of antitumor antibiotics—bleomycin, dactinomycin, and anthracyclines—have a wide spectrum of activity against hematologic malignancies and solid tumors. Bleomycin differs from the rest of the drugs owing to its cell cycle Cell cycle The phases of the cell cycle include interphase (G1, S, and G2) and mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase). The cell's progression through these phases is punctuated by checkpoints regulated by cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, tumor suppressors, and their antagonists. Cell Cycle–specific action during the G2 phase G2 Phase The period of the cell cycle following DNA synthesis (S phase) and preceding m phase (cell division phase). The chromosomes are tetraploid in this point. Cell Cycle. Mechanisms of actions of these drugs include free radical Free Radical Highly reactive molecules with an unsatisfied electron valence pair. Free radicals are produced in both normal and pathological processes. They are proven or suspected agents of tissue damage in a wide variety of circumstances including radiation, damage from environment chemicals, and aging. Natural and pharmacological prevention of free radical damage is being actively investigated. Nitroimidazoles damage to DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure, topoisomerase II Topoisomerase II DNA topoisomerases that catalyze ATP-dependent breakage of both strands of DNA, passage of the unbroken strands through the breaks, and rejoining of the broken strands. These enzymes bring about relaxation of the supercoiled DNA and resolution of a knotted circular DNA duplex. Fluoroquinolones inhibition, binding of DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure via intercalation, and alteration of cell membrane Cell Membrane A cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates the cell contents from the outside environment. A cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer and proteins that function to protect cellular DNA and mediate the exchange of ions and molecules. The Cell: Cell Membrane fluidity and transport of ions. Important adverse effects include cardiotoxicity (acute and chronic) and myelosuppression Myelosuppression Oxazolidinones.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Antitumor antibiotics, agents isolated from strains of Streptomyces, are used for cancer treatment owing to their ability to interfere with DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure and/or RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), thus leading to cancer cell death Cell death Injurious stimuli trigger the process of cellular adaptation, whereby cells respond to withstand the harmful changes in their environment. Overwhelmed adaptive mechanisms lead to cell injury. Mild stimuli produce reversible injury. If the stimulus is severe or persistent, injury becomes irreversible. Apoptosis is programmed cell death, a mechanism with both physiologic and pathologic effects. Cell Injury and Death. The effects of these drugs are too toxic for use in bacterial infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease.
Agents within this class include:
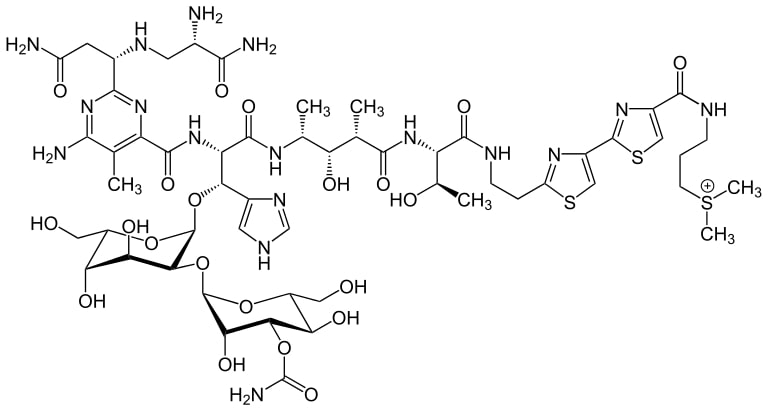
Structure of bleomycin
Image: “Bleomycin A2” by Yikrazuul. License: Public Domain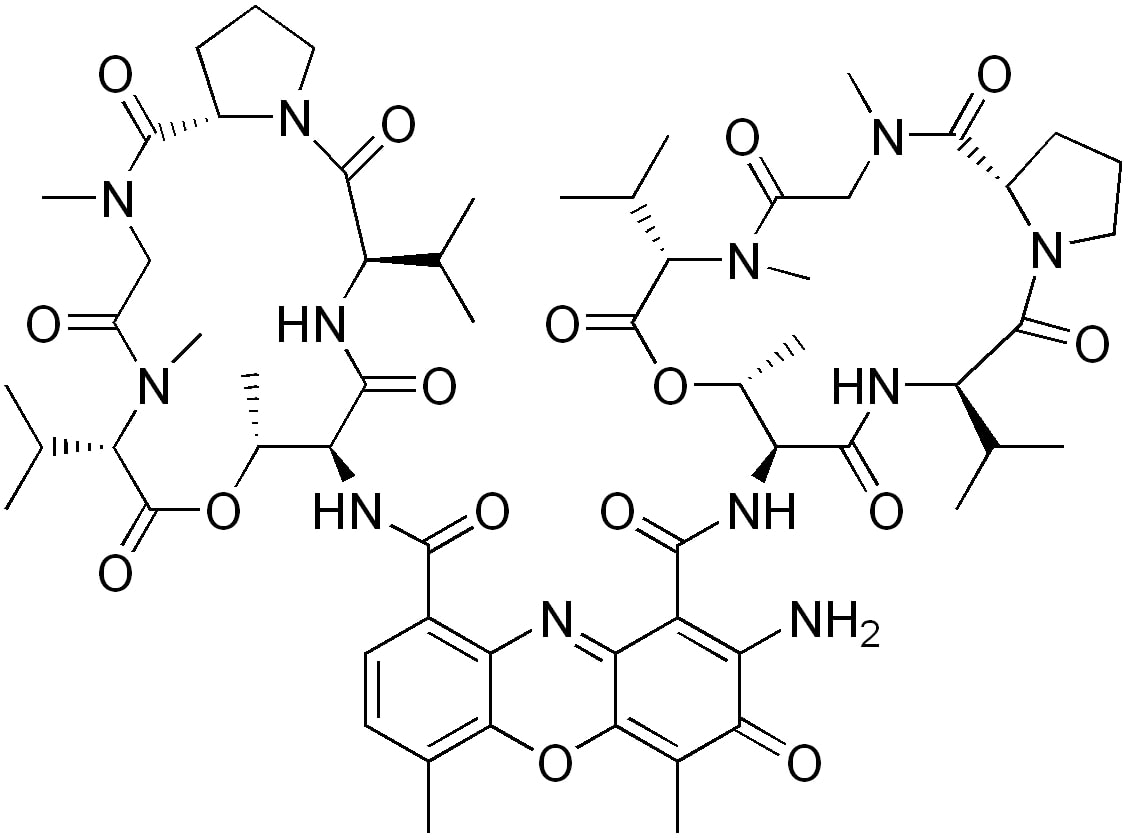
Structure of dactinomycin
Image: “Actinomycin D” by Edgar181. License: Public Domain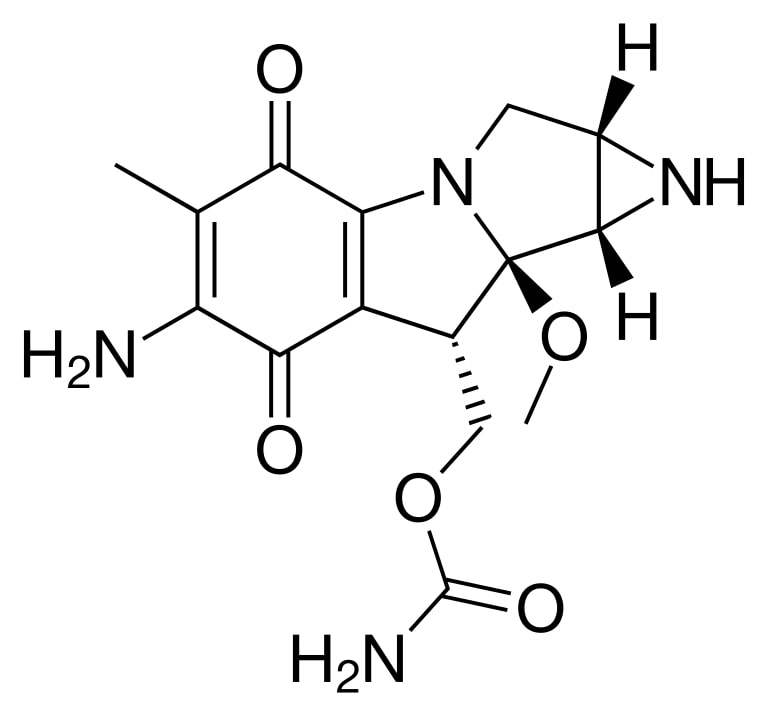
Structure of mitomycin
Image: “Mitomycin” by Fvasconcellos. License: Public Domain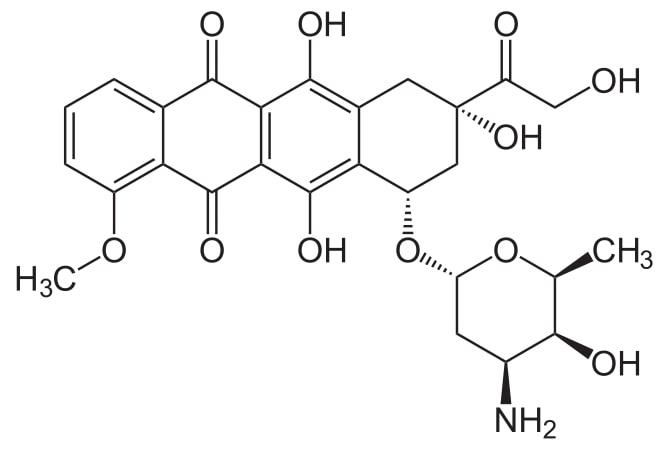
Structure of doxorubicin
Image: “Doxorubicin2” by NEUROtiker. License: Public Domain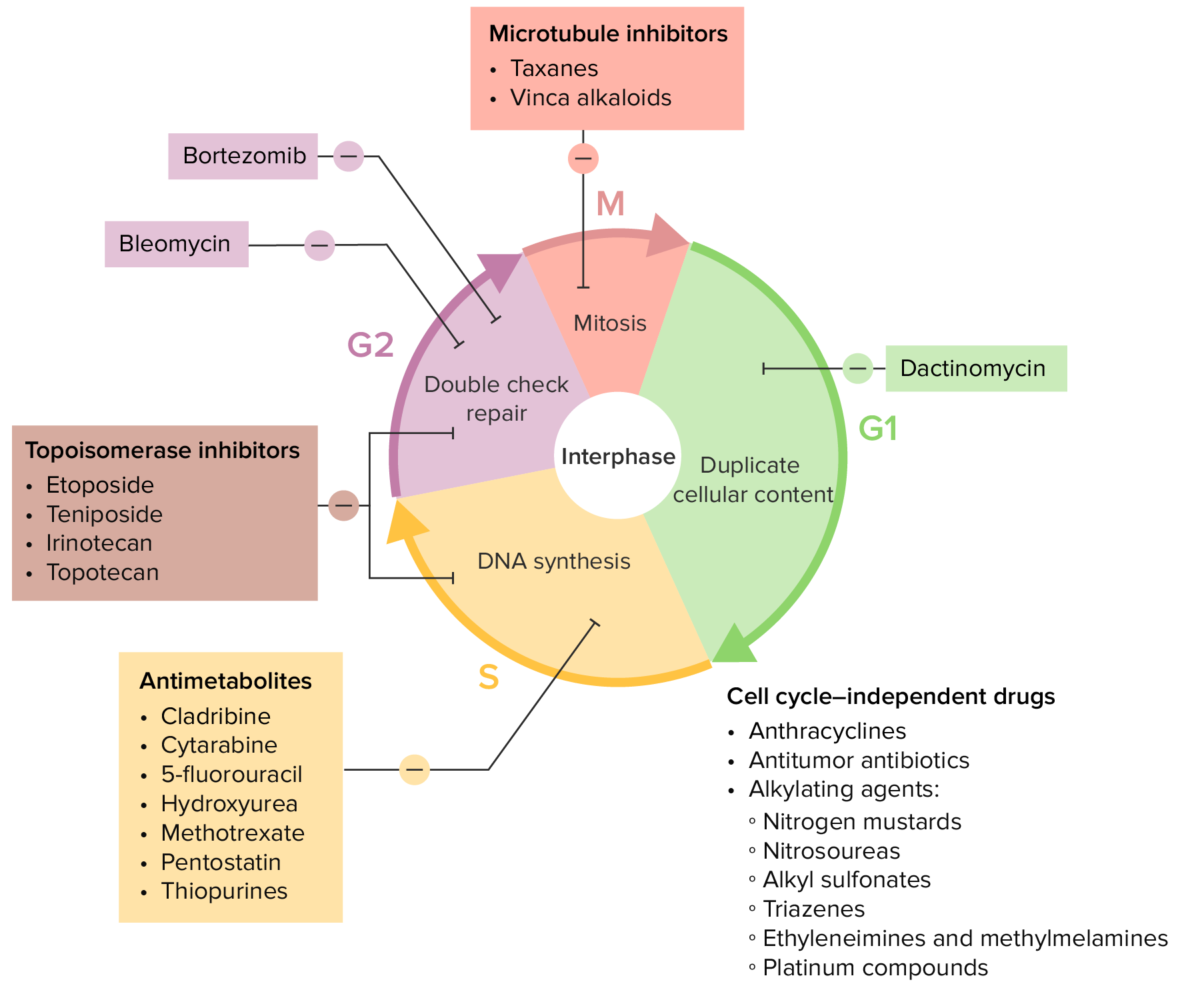
Various chemotherapy drugs and their effects on the cell cycle
Image by Lecturio.| Drug class | Mechanism |
|---|---|
Antitumor antibiotics:
|
Intercalate between bases Bases Usually a hydroxide of lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium or cesium, but also the carbonates of these metals, ammonia, and the amines. Acid-Base Balance, leading to blockage of DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure or RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and prevention of DNA replication DNA replication The entire DNA of a cell is replicated during the S (synthesis) phase of the cell cycle. The principle of replication is based on complementary nucleotide base pairing: adenine forms hydrogen bonds with thymine (or uracil in RNA) and guanine forms hydrogen bonds with cytosine. DNA Replication |
| Anthracyclines |
|
| Alkylating agents |
|
| Drug class | Cell cycle Cell cycle The phases of the cell cycle include interphase (G1, S, and G2) and mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase). The cell’s progression through these phases is punctuated by checkpoints regulated by cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, tumor suppressors, and their antagonists. Cell Cycle phase affected | Mechanism of action |
|---|---|---|
| Antifolates Antifolates Inhibitors of the enzyme, dihydrofolate reductase, which converts dihydrofolate (fh2) to tetrahydrofolate (fh4). They are frequently used in cancer chemotherapy. Antimetabolite Chemotherapy | Cell cycle Cell cycle The phases of the cell cycle include interphase (G1, S, and G2) and mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase). The cell’s progression through these phases is punctuated by checkpoints regulated by cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, tumor suppressors, and their antagonists. Cell Cycle arrest at S phase S Phase Phase of the cell cycle following g1 and preceding g2 when the entire DNA content of the nucleus is replicated. It is achieved by bidirectional replication at multiple sites along each chromosome. Cell Cycle | Inhibit:
|
| Bleomycin | Cell cycle Cell cycle The phases of the cell cycle include interphase (G1, S, and G2) and mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase). The cell’s progression through these phases is punctuated by checkpoints regulated by cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, tumor suppressors, and their antagonists. Cell Cycle arrest at G2 phase G2 Phase The period of the cell cycle following DNA synthesis (S phase) and preceding m phase (cell division phase). The chromosomes are tetraploid in this point. Cell Cycle | Binds DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure, leading to single- and double-stranded breaks |
| Fluoropyrimidines | Cell cycle Cell cycle The phases of the cell cycle include interphase (G1, S, and G2) and mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase). The cell’s progression through these phases is punctuated by checkpoints regulated by cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, tumor suppressors, and their antagonists. Cell Cycle arrest at S phase S Phase Phase of the cell cycle following g1 and preceding g2 when the entire DNA content of the nucleus is replicated. It is achieved by bidirectional replication at multiple sites along each chromosome. Cell Cycle | Inhibit thymidylate synthase Thymidylate synthase An enzyme of the transferase class that catalyzes the reaction 5, 10-methylenetetrahydrofolate and dump to dihydrofolate and dtmp in the synthesis of thymidine triphosphate. Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism |
| Deoxycytidine analogs | Cell cycle Cell cycle The phases of the cell cycle include interphase (G1, S, and G2) and mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase). The cell’s progression through these phases is punctuated by checkpoints regulated by cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, tumor suppressors, and their antagonists. Cell Cycle arrest at S phase S Phase Phase of the cell cycle following g1 and preceding g2 when the entire DNA content of the nucleus is replicated. It is achieved by bidirectional replication at multiple sites along each chromosome. Cell Cycle | Inhibit:
|
| Purine analogs Purine Analogs Antimetabolite Chemotherapy | Cell cycle Cell cycle The phases of the cell cycle include interphase (G1, S, and G2) and mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase). The cell’s progression through these phases is punctuated by checkpoints regulated by cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, tumor suppressors, and their antagonists. Cell Cycle arrest at S phase S Phase Phase of the cell cycle following g1 and preceding g2 when the entire DNA content of the nucleus is replicated. It is achieved by bidirectional replication at multiple sites along each chromosome. Cell Cycle | Inhibition of de novo purine synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) |
| Topoisomerase II Topoisomerase II DNA topoisomerases that catalyze ATP-dependent breakage of both strands of DNA, passage of the unbroken strands through the breaks, and rejoining of the broken strands. These enzymes bring about relaxation of the supercoiled DNA and resolution of a knotted circular DNA duplex. Fluoroquinolones inhibitors | Cell cycle Cell cycle The phases of the cell cycle include interphase (G1, S, and G2) and mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase). The cell’s progression through these phases is punctuated by checkpoints regulated by cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, tumor suppressors, and their antagonists. Cell Cycle arrest at S and G2 phases | Inhibit topoisomerase II Topoisomerase II DNA topoisomerases that catalyze ATP-dependent breakage of both strands of DNA, passage of the unbroken strands through the breaks, and rejoining of the broken strands. These enzymes bring about relaxation of the supercoiled DNA and resolution of a knotted circular DNA duplex. Fluoroquinolones |
| Taxanes Taxanes A group of diterpenoid cyclodecanes named for the taxanes that were discovered in the taxus tree. The action on microtubules has made some of them useful as antineoplastic agents. Microtubule and Topoisomerase Inhibitors | Cell cycle Cell cycle The phases of the cell cycle include interphase (G1, S, and G2) and mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase). The cell’s progression through these phases is punctuated by checkpoints regulated by cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, tumor suppressors, and their antagonists. Cell Cycle arrest at metaphase Metaphase The phase of cell nucleus division following prometaphase, in which the chromosomes line up across the equatorial plane of the spindle apparatus prior to separation. Cell Cycle of the M phase | Hyperstabilization of microtubules Microtubules Slender, cylindrical filaments found in the cytoskeleton of plant and animal cells. They are composed of the protein tubulin and are influenced by tubulin modulators. The Cell: Cytosol and Cytoskeleton |
| Vinca alkaloids Vinca Alkaloids A group of indole-indoline dimers which are alkaloids obtained from the vinca genus of plants. They inhibit polymerization of tubulin into microtubules thus blocking spindle formation and arresting cells in metaphase. They are some of the most useful antineoplastic agents. Microtubule and Topoisomerase Inhibitors | Cell arrest during metaphase Metaphase The phase of cell nucleus division following prometaphase, in which the chromosomes line up across the equatorial plane of the spindle apparatus prior to separation. Cell Cycle of the M phase | Binds to beta-tubulin and prevents microtubule polymerization |