Antiprogestins are competitive inhibitors of progestins Progestins Compounds that interact with progesterone receptors in target tissues to bring about the effects similar to those of progesterone. Primary actions of progestins, including natural and synthetic steroids, are on the uterus and the mammary gland in preparation for and in maintenance of pregnancy. Hormonal Contraceptives at the progesterone Progesterone The major progestational steroid that is secreted primarily by the corpus luteum and the placenta. Progesterone acts on the uterus, the mammary glands and the brain. It is required in embryo implantation; pregnancy maintenance, and the development of mammary tissue for milk production. Progesterone, converted from pregnenolone, also serves as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of gonadal steroid hormones and adrenal corticosteroids. Gonadal Hormones receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors. Mifepristone is the only antiprogestin currently used in the United States. The most common clinical use of mifepristone is for the termination of pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care. Mifepristone is often combined with a prostaglandin such as misoprostol Misoprostol A synthetic analog of natural prostaglandin e1. It produces a dose-related inhibition of gastric acid and pepsin secretion, and enhances mucosal resistance to injury. It is an effective anti-ulcer agent and also has oxytocic properties. Eicosanoids. Selective progesterone Progesterone The major progestational steroid that is secreted primarily by the corpus luteum and the placenta. Progesterone acts on the uterus, the mammary glands and the brain. It is required in embryo implantation; pregnancy maintenance, and the development of mammary tissue for milk production. Progesterone, converted from pregnenolone, also serves as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of gonadal steroid hormones and adrenal corticosteroids. Gonadal Hormones receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors modulators (SPRMs) are closely related drugs with a slightly different mechanism of action, and act as either agonists or antagonists depending on the cellular environment. Ulipristal is the only SPRM used clinically in the US. It is used as an emergency contraceptive, and works by inhibiting luteinizing hormone and delaying ovulation Ovulation The discharge of an ovum from a rupturing follicle in the ovary. Menstrual Cycle. The common side effects of antiprogestins and SPRMs include nausea Nausea An unpleasant sensation in the stomach usually accompanied by the urge to vomit. Common causes are early pregnancy, sea and motion sickness, emotional stress, intense pain, food poisoning, and various enteroviruses. Antiemetics, vomiting Vomiting The forcible expulsion of the contents of the stomach through the mouth. Hypokalemia, and abdominal pain Abdominal Pain Acute Abdomen.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Mifepristone is a synthetic steroid hormone.
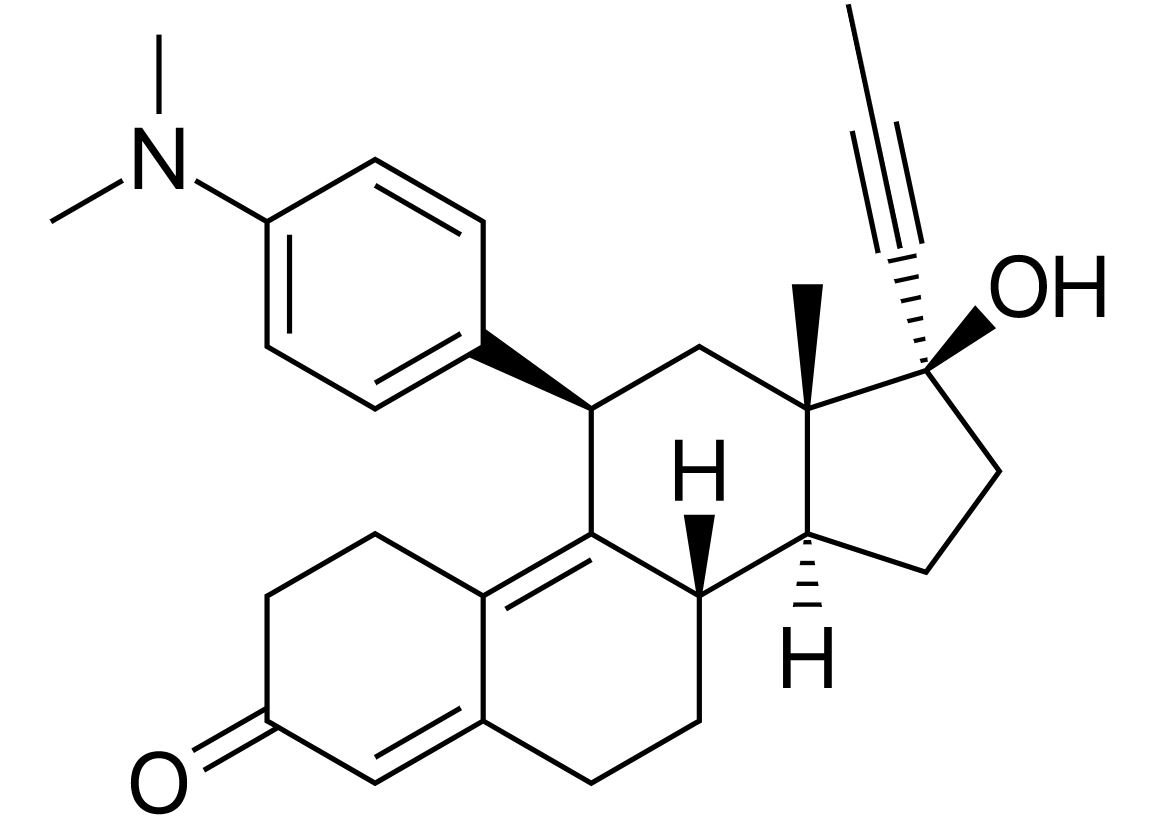
Chemical structure of mifepristone:
A frequently prescribed antiprogestin, mifepristone is a derivative of 19-norprogestin.
Antiprogestin actions:
Antiglucocorticoid effect:
The following information is for the representative antiprogestin, mifepristone:
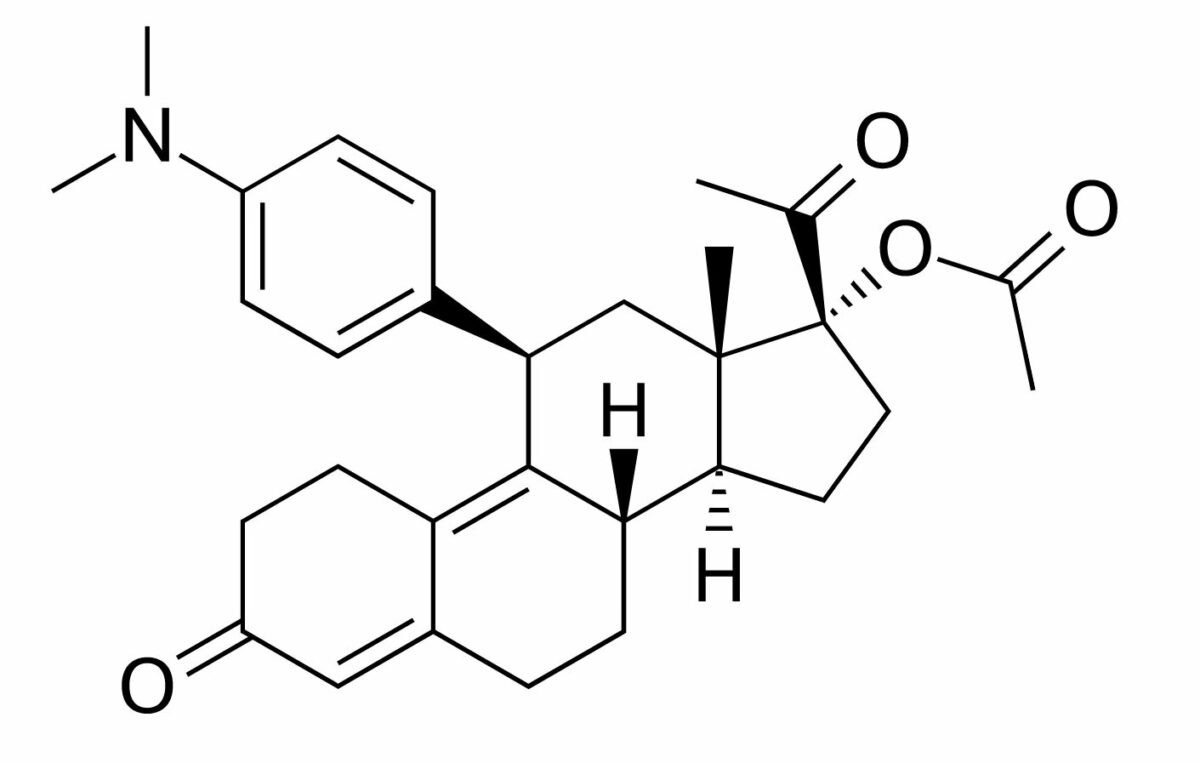
Chemical structure of ulipristal, a selective progesterone receptor modulator:
A derivative of 19-norprogesterone
The following information is for the stereotypical SPRM, ulipristal:
Ulipristal is indicated for emergency contraception Emergency contraception Means of postcoital intervention to avoid pregnancy, such as the administration of postcoital contraceptives to prevent fertilization of an egg or implantation of a fertilized egg. Hormonal Contraceptives.
| Category | Antiprogestins | SPRMs |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism of action | Antagonists of progesterone Progesterone The major progestational steroid that is secreted primarily by the corpus luteum and the placenta. Progesterone acts on the uterus, the mammary glands and the brain. It is required in embryo implantation; pregnancy maintenance, and the development of mammary tissue for milk production. Progesterone, converted from pregnenolone, also serves as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of gonadal steroid hormones and adrenal corticosteroids. Gonadal Hormones receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors A and B |
|
| Half-life Half-Life The time it takes for a substance (drug, radioactive nuclide, or other) to lose half of its pharmacologic, physiologic, or radiologic activity. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics | 18 hours | 32–38 hours |
| Time to peak | 90 minutes | 1 hour |
| Primary indications |
|
Emergency contraception Emergency contraception Means of postcoital intervention to avoid pregnancy, such as the administration of postcoital contraceptives to prevent fertilization of an egg or implantation of a fertilized egg. Hormonal Contraceptives |
| Contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation |
|
Pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care |