Antiretroviral therapy (ART) targets the replication cycle of the human immunodeficiency Immunodeficiency Chédiak-Higashi Syndrome virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology (HIV) and is classified based on the viral enzyme or mechanism that is inhibited. The goal of therapy is to suppress viral replication to reach the outcome of undetected viral load Viral load The quantity of measurable virus in a body fluid. Change in viral load, measured in plasma, is sometimes used as a surrogate marker in disease progression. HIV Infection and AIDS. Currently, reverse transcriptase Reverse transcriptase A reverse transcriptase encoded by the pol gene of HIV. It is a heterodimer of 66 kda and 51 kda subunits that are derived from a common precursor protein. The heterodimer also includes an RNAse h activity that plays an essential role the viral replication process. HIV Infection and AIDS, protease Protease Enzyme of the human immunodeficiency virus that is required for post-translational cleavage of gag and gag-pol precursor polyproteins into functional products needed for viral assembly. HIV protease is an aspartic protease encoded by the amino terminus of the pol gene. HIV Infection and AIDS, integrase Integrase Enzyme of the human immunodeficiency virus that is required to integrate viral DNA into cellular DNA in the nucleus of a host cell. HIV integrase is a DNA nucleotidyltransferase encoded by the pol gene. HIV Infection and AIDS, and entry inhibitors are used in combined ART (cART) regimens. Combination therapy (3-drug regimen) is used to prevent drug resistance Resistance Physiologically, the opposition to flow of air caused by the forces of friction. As a part of pulmonary function testing, it is the ratio of driving pressure to the rate of air flow. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing and cross-resistance, which develop through genetic mutations Genetic Mutations Carcinogenesis.
Last updated: Jul 12, 2023
Contents
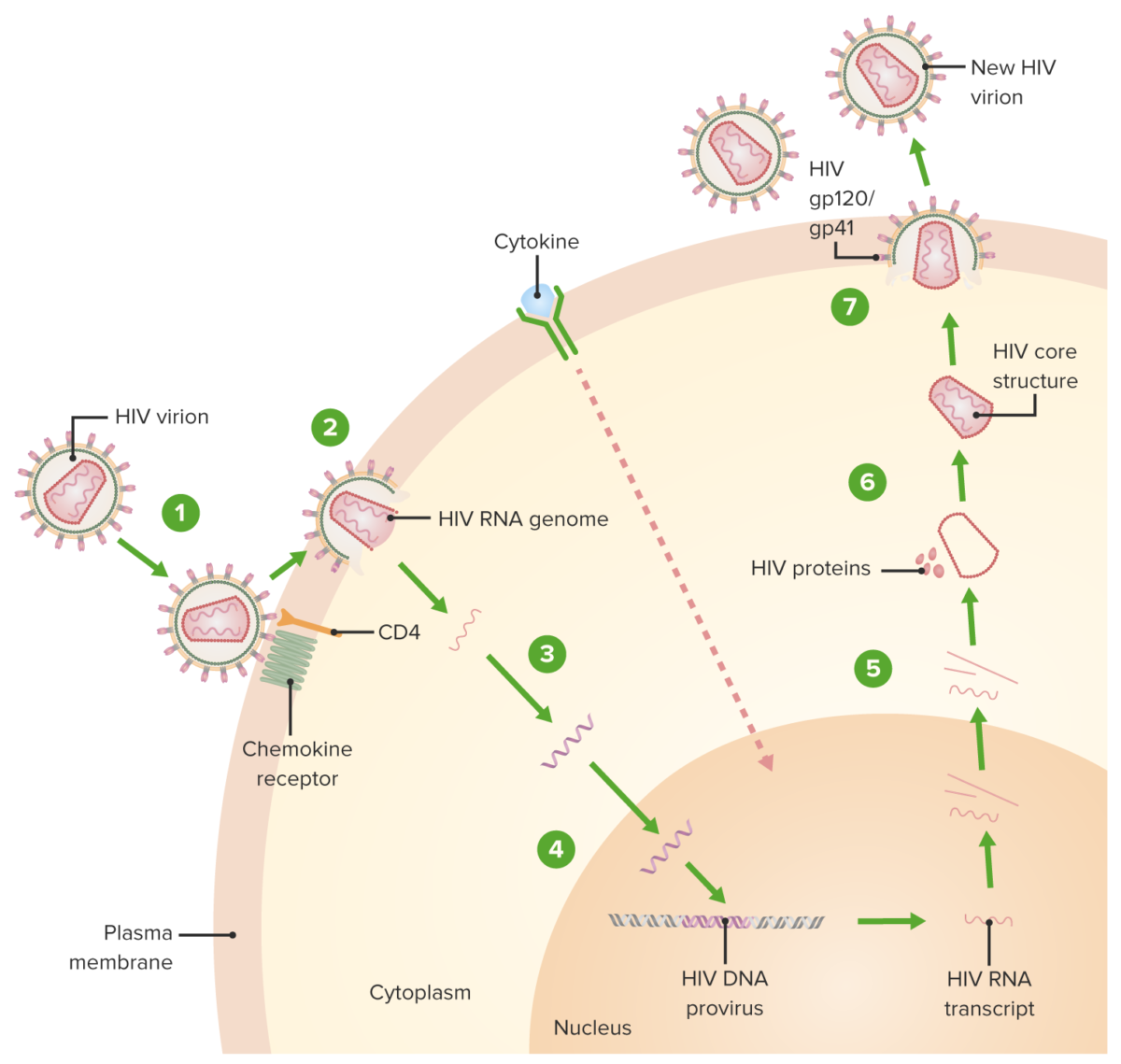
HIV replication cycle:
1. Virion binds the CD4 receptor and a chemokine receptor, followed by a conformational change that facilitates fusion of the virion and the host cell.
2. A capsid protein shell (surrounding the viral RNA and proteins) is uncoated as the virion traverses the cytoplasm.
3. Reverse transcriptase-mediated synthesis of proviral DNA occurs.
4. Viral DNA is transported across the nucleus and integrated into the host DNA, facilitated by integrase.
5. Viral DNA is transcribed, and multiple copies of new HIV RNA form and are transported to the cytoplasm. New HIV RNA becomes the genome of a new virus. Cytokine activation of the cell also occurs.
6. New viral RNA + proteins + enzymes move to the cell surface and form a noninfectious particle.
7. Particle (viral RNA + proteins) eventually buds out of the host cell with the immature HIV. Viral protein protease (enzyme) then cleaves newly synthesized polyproteins producing a mature HIV.
| Type of drug | Mechanism of action |
|---|---|
Reverse transcriptase
Reverse transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase encoded by the pol gene of HIV. It is a heterodimer of 66 kda and 51 kda subunits that are derived from a common precursor protein. The heterodimer also includes an RNAse h activity that plays an essential role the viral replication process.
HIV Infection and AIDS inhibitors
|
|
| Integrase Integrase Enzyme of the human immunodeficiency virus that is required to integrate viral DNA into cellular DNA in the nucleus of a host cell. HIV integrase is a DNA nucleotidyltransferase encoded by the pol gene. HIV Infection and AIDS strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs) |
|
| Protease Protease Enzyme of the human immunodeficiency virus that is required for post-translational cleavage of gag and gag-pol precursor polyproteins into functional products needed for viral assembly. HIV protease is an aspartic protease encoded by the amino terminus of the pol gene. HIV Infection and AIDS inhibitors (PIs) |
|
Entry inhibitors:
|
|
| Post-attachment inhibitor | Binds CD4 molecule, blocking entry but not the attachment |
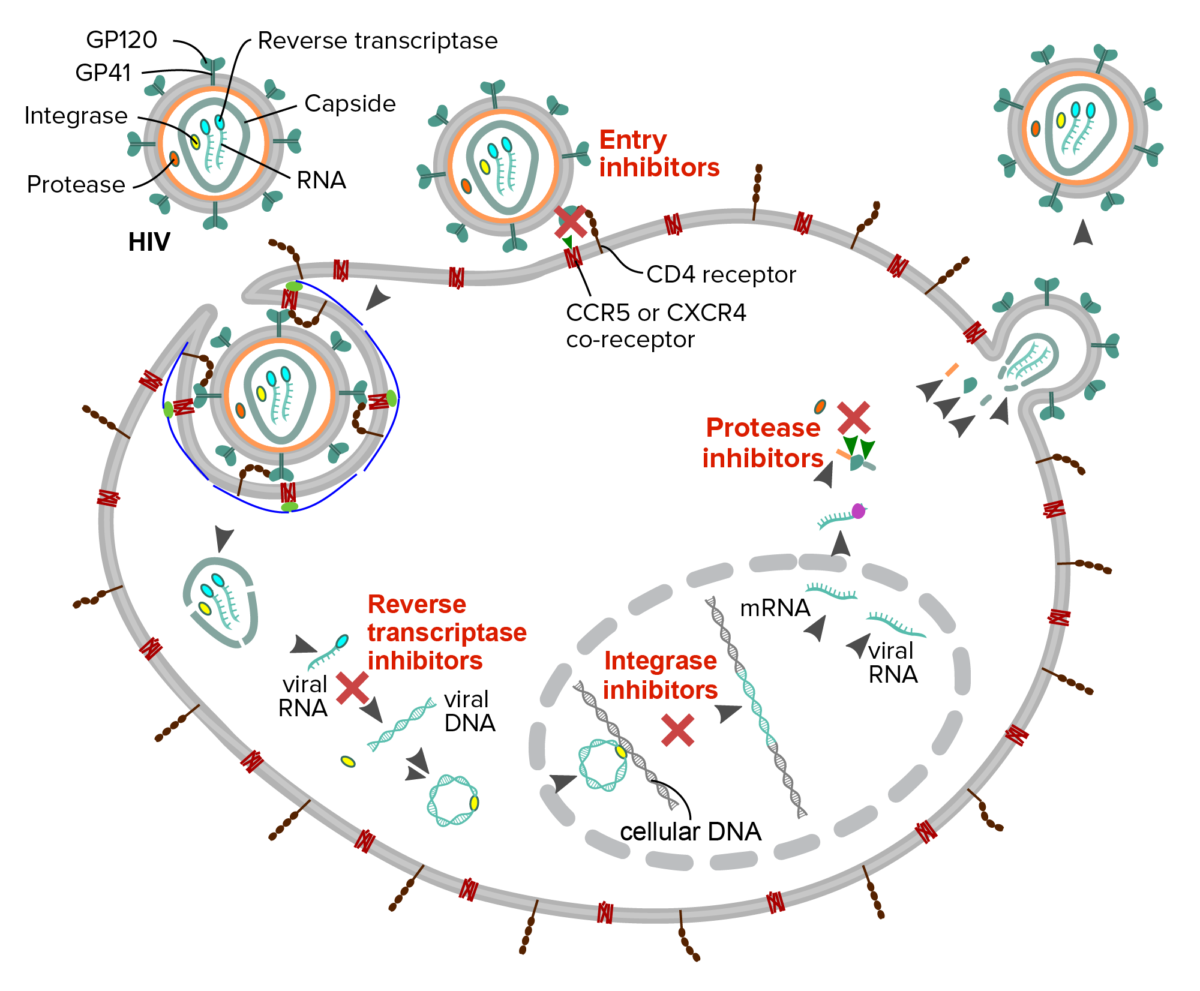
Schematic description of the mechanism of four classes of antiretroviral drugs against HIV:
Fusion or entry inhibitors: interfere with the binding, fusion or entry of the HIV virion
Reverse transcriptase inhibitors: interfere with the reverse transcription of viral RNA into DNA
Integrase inhibitor: prevent the insertion of the viral genome into the host DNA
Protease inhibitors: block cleavage of protein precursors necessary for the production of infectious viral particles
| Drug | Adverse effects | Interactions/ contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation |
|---|---|---|
Zidovudine (AZT):
|
|
|
| Emtricitabine: structurally similar to lamivudine |
|
Do not combine with lamivudine (the drugs compete with intracellular phosphorylation Phosphorylation The introduction of a phosphoryl group into a compound through the formation of an ester bond between the compound and a phosphorus moiety. Post-translational Protein Processing). |
| Lamivudine: active against the hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology |
|
Do not combine with emtricitabine (the drugs compete with intracellular phosphorylation Phosphorylation The introduction of a phosphoryl group into a compound through the formation of an ester bond between the compound and a phosphorus moiety. Post-translational Protein Processing). |
| Abacavir | Hypersensitivity reaction (potentially fatal): fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, rash Rash Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever, abdominal pain Abdominal Pain Acute Abdomen, vomiting Vomiting The forcible expulsion of the contents of the stomach through the mouth. Hypokalemia, dyspnea Dyspnea Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea |
|
| Tenofovir (NtRTI): TAF and TDF (TAF: active against the hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology) |
|
|
Non-competitive inhibitors of reverse transcriptase Reverse transcriptase A reverse transcriptase encoded by the pol gene of HIV. It is a heterodimer of 66 kda and 51 kda subunits that are derived from a common precursor protein. The heterodimer also includes an RNAse h activity that plays an essential role the viral replication process. HIV Infection and AIDS:
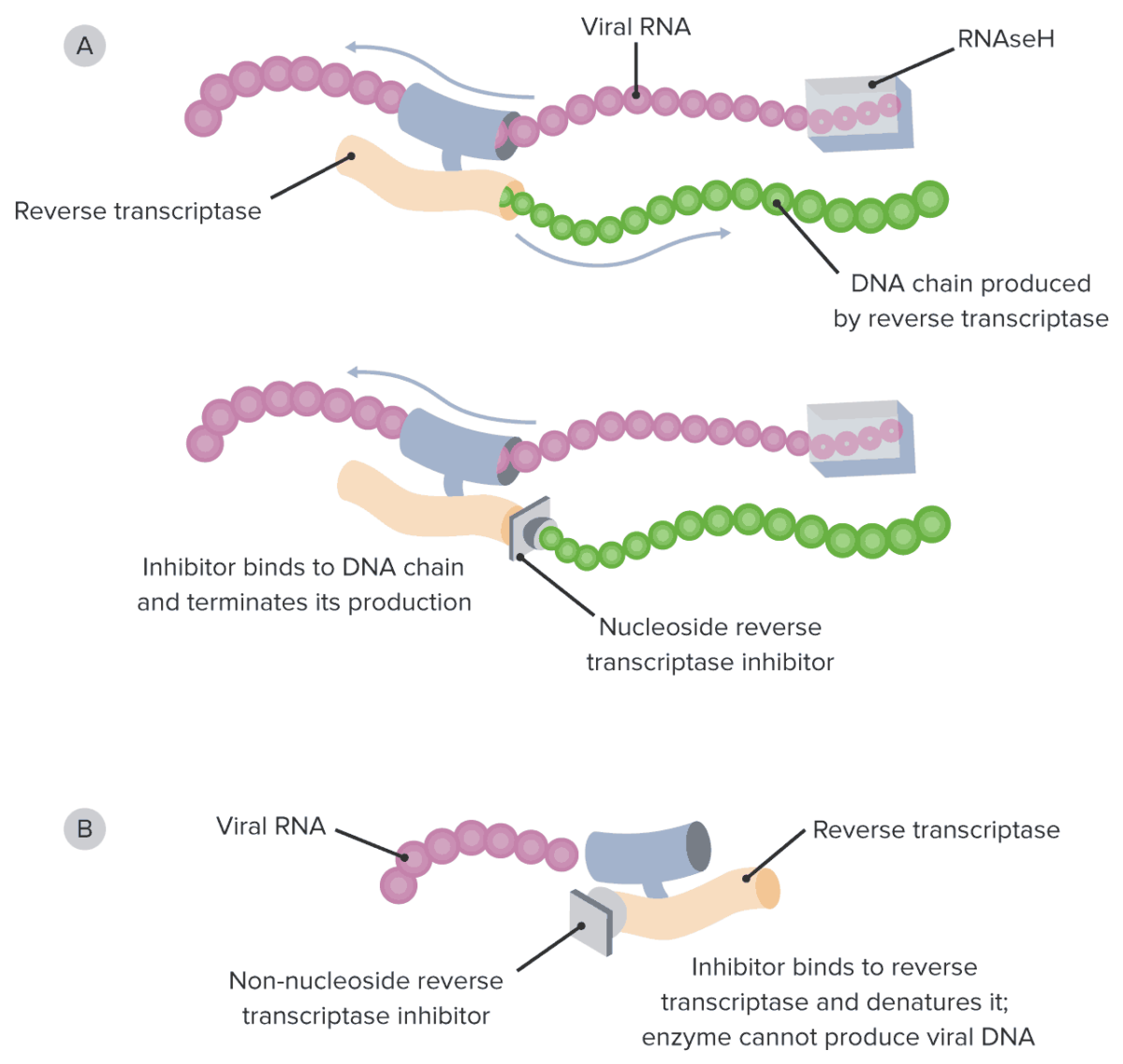
Diagram of the mechanism of action of NRTIs and NNRTIs:
A: Note how NRTIs block the growing viral DNA genome by substituting the naturally occurring nucleosides and functioning as chain terminators.
B: On the other hand, NNRTIs bind directly to the reverse transcriptase enzyme, directly preventing viral DNA synthesis.
NRTI: nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor
NNRTI: non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor
RNAseH: ribonuclease H
| Drug | Adverse effects | Interactions/ contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation |
|---|---|---|
| Etravirine: most commonly used NNRTI in resistant HIV cases |
|
Can interact with other antiretroviral drugs (e.g., if in combination, dose of maraviroc should be doubled) |
| Efavirenz |
|
Avoid in long QT syndrome Long QT syndrome Long QT syndrome (LQTS) is a disorder of ventricular myocardial repolarization that produces QT prolongation on electrocardiogram (ECG). Long QT syndrome is associated with an increased risk of developing life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, specifically torsades de pointes. Long QT Syndrome, liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy disease, psychiatric illness |
| Doravirine | CNS/psychiatric effects similar to efavirenz (but much less common) | Use with rifampin Rifampin A semisynthetic antibiotic produced from streptomyces mediterranei. It has a broad antibacterial spectrum, including activity against several forms of Mycobacterium. In susceptible organisms it inhibits dna-dependent RNA polymerase activity by forming a stable complex with the enzyme. It thus suppresses the initiation of RNA synthesis. Rifampin is bactericidal, and acts on both intracellular and extracellular organisms. Epiglottitis contraindicated (↓ doravirine exposure) |
| Rilpivirine |
|
|
| Nevirapine: not initial treatment of treatment-naive patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship (↑ toxicity Toxicity Dosage Calculation) |
|
|
| Drug | Adverse effects | Interactions/ contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation |
|---|---|---|
| Atazanavir |
|
|
| Darunavir |
|
|
| Ritonavir: booster |
|
One of the most potent known inhibitors of CYP3A4 CYP3A4 Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers); avoid taking drugs with narrow therapeutic index Therapeutic Index An indicator of the benefits and risks of treatment. Dosage Calculation. |
| Lopinavir: coformulated with ritonavir |
|
Not for initial treatment (related to potency and toxicity Toxicity Dosage Calculation) |
| Drug | Adverse effects | Interactions/ contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation |
|---|---|---|
| Raltegravir |
|
Enzyme inducers (e.g., rifampin Rifampin A semisynthetic antibiotic produced from streptomyces mediterranei. It has a broad antibacterial spectrum, including activity against several forms of Mycobacterium. In susceptible organisms it inhibits dna-dependent RNA polymerase activity by forming a stable complex with the enzyme. It thus suppresses the initiation of RNA synthesis. Rifampin is bactericidal, and acts on both intracellular and extracellular organisms. Epiglottitis) increase its metabolism by inducing UDP-glucuronosyltransferase. |
| Dolutegravir | Mild reversible creatinine elevation (inhibits the renal transporter, OCT2) |
|
| Elvitegravir: administered with cobicistat or ritonavir | GI symptoms | Currently available only in a fixed-dose combination with tenofovir, emtricitabine, and cobicistat (which ↑ drug-drug interactions) |
| Bictegravir: coformulated with emtricitabine and TAF |
|
Intake with rifampin Rifampin A semisynthetic antibiotic produced from streptomyces mediterranei. It has a broad antibacterial spectrum, including activity against several forms of Mycobacterium. In susceptible organisms it inhibits dna-dependent RNA polymerase activity by forming a stable complex with the enzyme. It thus suppresses the initiation of RNA synthesis. Rifampin is bactericidal, and acts on both intracellular and extracellular organisms. Epiglottitis or dofetilide Dofetilide Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers) contraindicated |

Schematic diagram of viral entry and steps inhibited by enfuvirtide and maraviroc:
The trimeric gp120 subunit of the viral envelope glycoprotein complex binds CD4 on the target cell surface, triggering a conformational change that promotes interactions with chemokine receptors (in this case CCR5). The trimeric transmembrane subunit gp41 is activated to mediate membrane fusion so that the viral contents can enter the cell. Maraviroc blocks the CCR5 coreceptor. Enfuvirtide binds gp41, preventing fusion.