Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder marked by self-imposed starvation and inappropriate dietary habits due to a morbid fear of weight gain and disturbed perception Perception The process by which the nature and meaning of sensory stimuli are recognized and interpreted. Psychiatric Assessment of body shape and weight. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship have strikingly low BMI BMI An indicator of body density as determined by the relationship of body weight to body height. Bmi=weight (kg)/height squared (m2). Bmi correlates with body fat (adipose tissue). Their relationship varies with age and gender. For adults, bmi falls into these categories: below 18. 5 (underweight); 18. 5-24. 9 (normal); 25. 0-29. 9 (overweight); 30. 0 and above (obese). Obesity and diverse physiological and psychological complications. The condition is most commonly seen in adolescent girls. Treatment consists of psychotherapy Psychotherapy Psychotherapy is interpersonal treatment based on the understanding of psychological principles and mechanisms of mental disease. The treatment approach is often individualized, depending on the psychiatric condition(s) or circumstance. Psychotherapy (CBT) and patient hospitalization Hospitalization The confinement of a patient in a hospital. Delirium for intensive care and management of complications. Pharmacotherapy has a limited role.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by self-imposed starvation and inappropriate dietary habits due to an intense fear of weight gain and disturbed perception Perception The process by which the nature and meaning of sensory stimuli are recognized and interpreted. Psychiatric Assessment of body shape and weight.
Complex interaction between biological, psychological, and social factors:
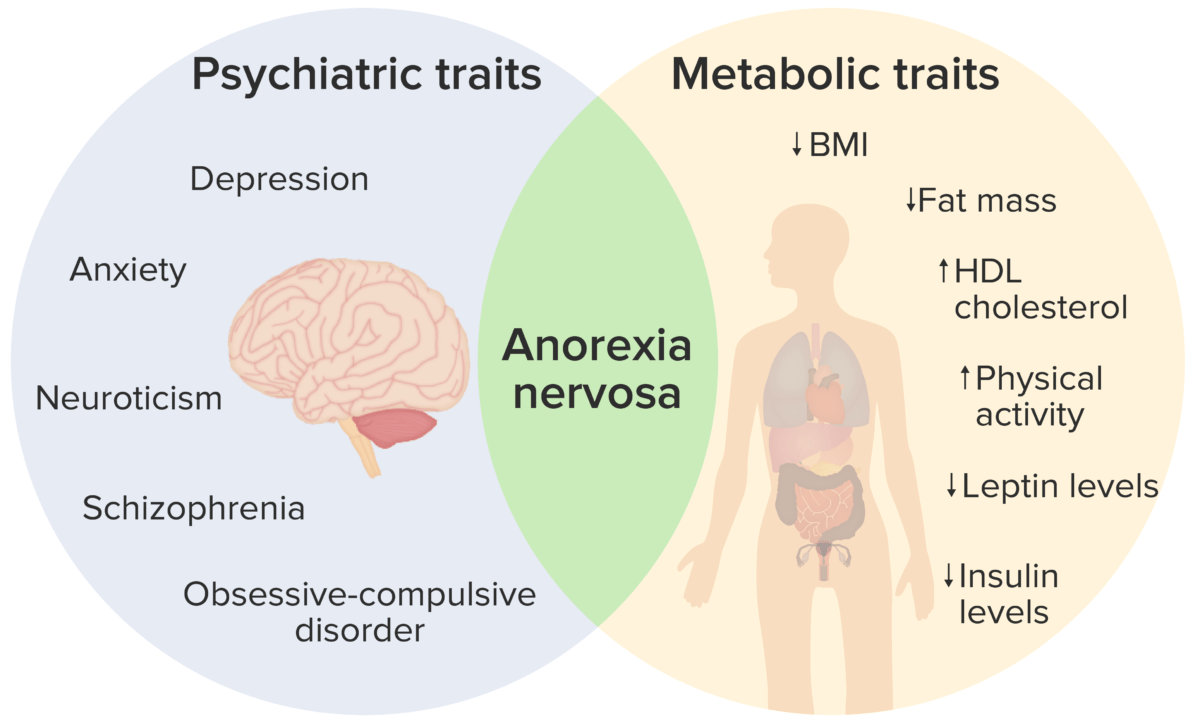
Anorexia nervosa presents with both psychiatric and metabolic traits:
The clinical presentation observed is due to an interaction between the 2 types of traits, resulting in the clinical signs and symptoms listed above.
Anorexia nervosa affects almost all body systems and can present with a variety of symptoms and signs.
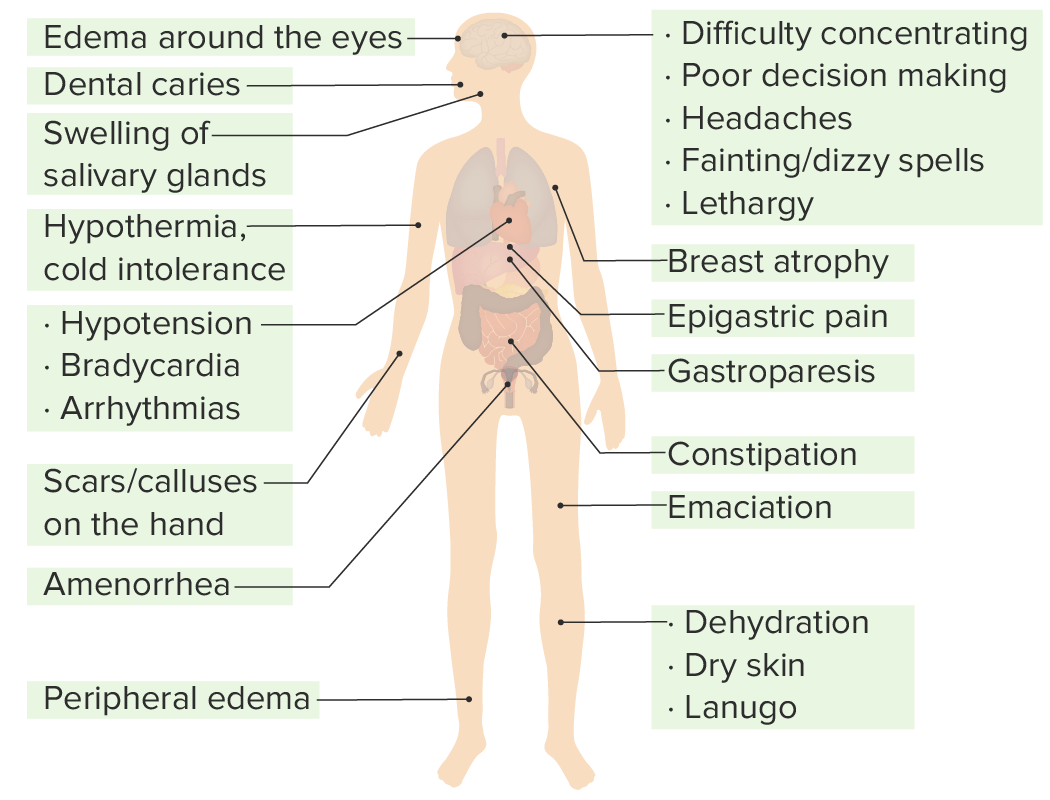
Clinical signs and symptoms of anorexia nervosa observed in different systems of the body:
Anorexia nervosa affects almost all systems.
Diagnosis is clinical, based on observed criteria:
Treatment involves a combination of psychotherapy Psychotherapy Psychotherapy is interpersonal treatment based on the understanding of psychological principles and mechanisms of mental disease. The treatment approach is often individualized, depending on the psychiatric condition(s) or circumstance. Psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy.
Consider hospitalizing patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with:
Refeeding syndrome Refeeding syndrome A condition of metabolic imbalance that is caused by complications of initially feeding a severely malnourished patient too aggressively. Usually occurring within the first 5 days of refeeding, this syndrome is characterized by water-electrolyte imbalance; glucose intolerance; cardiac arrhythmias; and diarrhea. Failure to Thrive: