Androgens are naturally occurring steroid hormones Steroid hormones Steroid hormones produced by the gonads. They stimulate reproductive organs, germ cell maturation, and the secondary sex characteristics in the males and the females. The major sex steroid hormones include estradiol; progesterone; and testosterone. Hormones: Overview and Types responsible for development and maintenance of the male sex Sex The totality of characteristics of reproductive structure, functions, phenotype, and genotype, differentiating the male from the female organism. Gender Dysphoria characteristics, including penile, scrotal, and clitoral growth, development of sexual hair, deepening of the voice, and musculoskeletal growth. Androgens are primarily given to treat hypogonadism Hypogonadism Hypogonadism is a condition characterized by reduced or no sex hormone production by the testes or ovaries. Hypogonadism can result from primary (hypergonadotropic) or secondary (hypogonadotropic) failure. Symptoms include infertility, increased risk of osteoporosis, erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, and regression (or absence) of secondary sexual characteristics. Hypogonadism, gender Gender Gender Dysphoria dysphoria in transgender Transgender Persons having a sense of persistent identification with, and expression of, gender-coded behaviors not typically associated with one's anatomical sex at birth, with or without a desire to undergo sex reassignment procedures. Gender Dysphoria men, and low testosterone in older men (controversial). Antiandrogenic drugs decrease the effect of androgens. Classes include androgen receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors blockers, 5α-reductase inhibitors, and androgen synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) inhibitors. Both men and women may use antiandrogens, which treat advanced prostate Prostate The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system. The gland surrounds the bladder neck and a portion of the urethra. The prostate is an exocrine gland that produces a weakly acidic secretion, which accounts for roughly 20% of the seminal fluid. cancer, benign Benign Fibroadenoma prostatic hyperplasia Hyperplasia An increase in the number of cells in a tissue or organ without tumor formation. It differs from hypertrophy, which is an increase in bulk without an increase in the number of cells. Cellular Adaptation ( BPH BPH Benign prostatic hyperplasia (bph) is a condition indicating an increase in the number of stromal and epithelial cells within the prostate gland (transition zone). Benign prostatic hyperplasia is common in men > 50 years of age and may greatly affect their quality of life. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia), alopecia Alopecia Alopecia is the loss of hair in areas anywhere on the body where hair normally grows. Alopecia may be defined as scarring or non-scarring, localized or diffuse, congenital or acquired, reversible or permanent, or confined to the scalp or universal; however, alopecia is usually classified using the 1st 3 factors. Alopecia, and hirsutism Hirsutism A condition observed in women and children when there is excess coarse body hair of an adult male distribution pattern, such as facial and chest areas. It is the result of elevated androgens from the ovaries, the adrenal glands, or exogenous sources. The concept does not include hypertrichosis, which is an androgen-independent excessive hair growth. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Androgens are hormones Hormones Hormones are messenger molecules that are synthesized in one part of the body and move through the bloodstream to exert specific regulatory effects on another part of the body. Hormones play critical roles in coordinating cellular activities throughout the body in response to the constant changes in both the internal and external environments. Hormones: Overview and Types, which lead to the development and maintenance of male sex Sex The totality of characteristics of reproductive structure, functions, phenotype, and genotype, differentiating the male from the female organism. Gender Dysphoria characteristics.
Androgens are produced naturally in the gonads Gonads The gamete-producing glands, ovary or testis. Hormones: Overview and Types ( testes Testes Gonadal Hormones and ovaries Ovaries Ovaries are the paired gonads of the female reproductive system that contain haploid gametes known as oocytes. The ovaries are located intraperitoneally in the pelvis, just posterior to the broad ligament, and are connected to the pelvic sidewall and to the uterus by ligaments. These organs function to secrete hormones (estrogen and progesterone) and to produce the female germ cells (oocytes). Ovaries: Anatomy) and the adrenal glands Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands are a pair of retroperitoneal endocrine glands located above the kidneys. The outer parenchyma is called the adrenal cortex and has 3 distinct zones, each with its own secretory products. Beneath the cortex lies the adrenal medulla, which secretes catecholamines involved in the fight-or-flight response. Adrenal Glands: Anatomy. The naturally produced androgenic hormones Hormones Hormones are messenger molecules that are synthesized in one part of the body and move through the bloodstream to exert specific regulatory effects on another part of the body. Hormones play critical roles in coordinating cellular activities throughout the body in response to the constant changes in both the internal and external environments. Hormones: Overview and Types include:
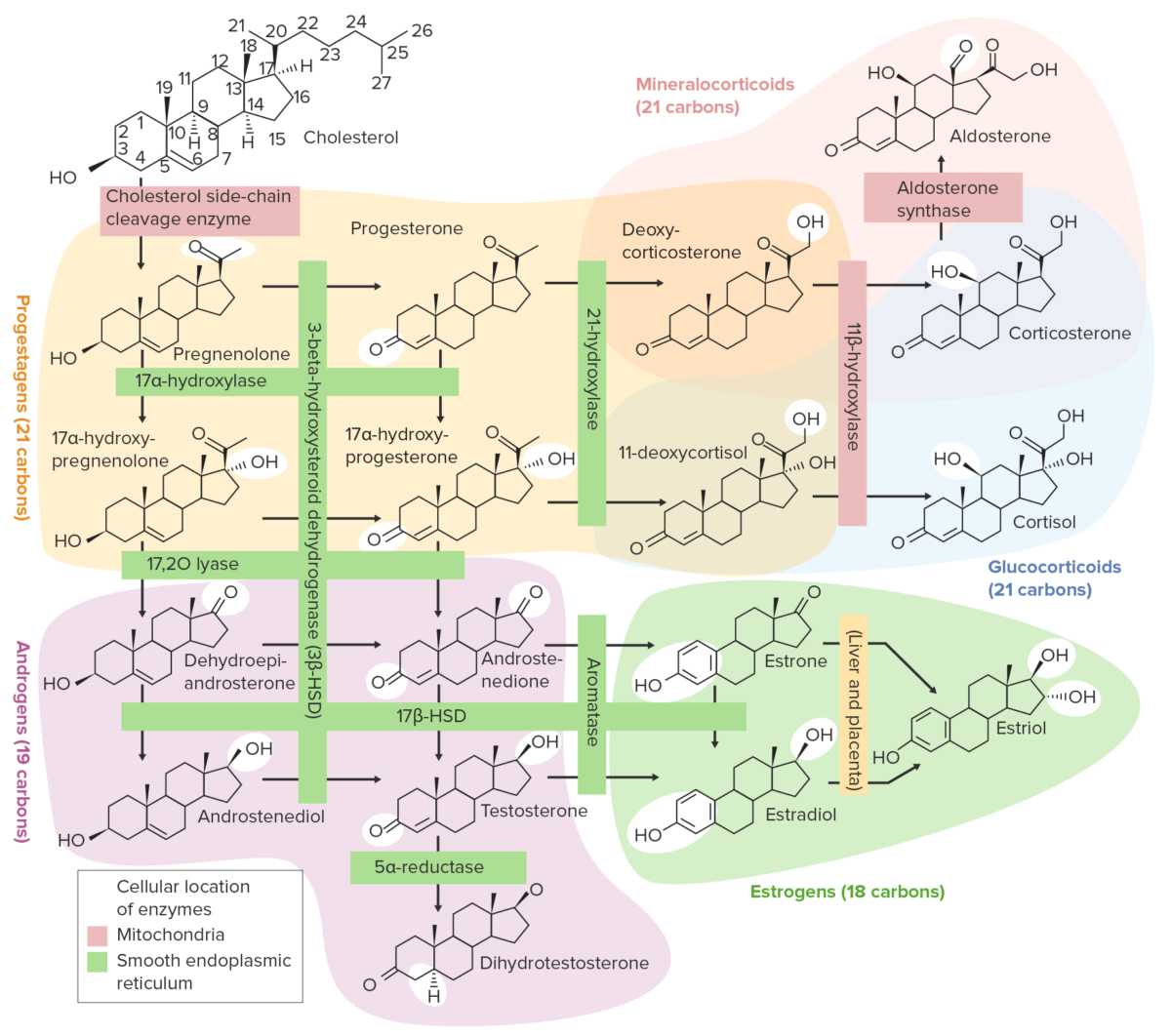
Overview of steroidogenesis pathways
Image by Lecturio.The physiologic effects of endogenously produced androgens and medications are identical and include:
Antiandrogenic medications block the action of androgens.
Antiandrogens are generally classified according to the mechanism of action.
| Class | Drugs in the class | Mechanism of action | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Androgen receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors antagonists |
|
Blocks androgen receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors via competitive inhibition Competitive inhibition Enzyme Inhibition | Use of flutamide is more limited due to relatively higher toxicity Toxicity Dosage Calculation; newer agents are typically preferred. |
| Spironolactone Spironolactone A potassium sparing diuretic that acts by antagonism of aldosterone in the distal renal tubules. It is used mainly in the treatment of refractory edema in patients with congestive heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, or hepatic cirrhosis. Its effects on the endocrine system are utilized in the treatments of hirsutism and acne but they can lead to adverse effects. Potassium-sparing Diuretics* | Blocks aldosterone Aldosterone A hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex that regulates electrolyte and water balance by increasing the renal retention of sodium and the excretion of potassium. Hyperkalemia and androgen receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors via competitive inhibition Competitive inhibition Enzyme Inhibition | Diuretic activity | |
| 5α-reductase inhibitors |
|
Blocks conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone Dihydrotestosterone A potent androgenic metabolite of testosterone. It is produced by the action of the enzyme 3-oxo-5-alpha-steroid 4-dehydrogenase. Gonadal Hormones ( DHT DHT A potent androgenic metabolite of testosterone. It is produced by the action of the enzyme 3-oxo-5-alpha-steroid 4-dehydrogenase. Gonadal Hormones) via competitive inhibition Competitive inhibition Enzyme Inhibition of type II 5α-reductase |
|
| Androgen synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) inhibitors | Ketoconazole Ketoconazole Broad spectrum antifungal agent used for long periods at high doses, especially in immunosuppressed patients. Azoles* | Inhibits 17ɑ-hydroxylase and 17,20-lyase ( enzymes Enzymes Enzymes are complex protein biocatalysts that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed by them. Due to the body’s constant metabolic needs, the absence of enzymes would make life unsustainable, as reactions would occur too slowly without these molecules. Basics of Enzymes required for androgen synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)) | Significant antifungal Antifungal Azoles activity |
| Drug | Absorption Absorption Absorption involves the uptake of nutrient molecules and their transfer from the lumen of the GI tract across the enterocytes and into the interstitial space, where they can be taken up in the venous or lymphatic circulation. Digestion and Absorption | Distribution | Metabolism | Excretion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flutamide | Rapid and complete | PB: approximately 95% | Extensive hepatic metabolism to multiple metabolites |
|
| Spironolactone Spironolactone A potassium sparing diuretic that acts by antagonism of aldosterone in the distal renal tubules. It is used mainly in the treatment of refractory edema in patients with congestive heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, or hepatic cirrhosis. Its effects on the endocrine system are utilized in the treatments of hirsutism and acne but they can lead to adverse effects. Potassium-sparing Diuretics | Bioavailability Bioavailability Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics ↑ with fat | PB: > 90% | Extensive hepatic metabolism to multiple active metabolites |
|
| Finasteride | Bioavailability Bioavailability Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: approximately 60% | PB: 90% | Extensive hepatic metabolism via CYP3A4 CYP3A4 Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers) to active metabolites |
|
| Ketoconazole Ketoconazole Broad spectrum antifungal agent used for long periods at high doses, especially in immunosuppressed patients. Azoles | Bioavailability Bioavailability Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics ↑ in acidic environments (decreases with antacids) |
|
|
|
| Androgens | Antiandrogens | |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism |
|
Mechanisms include:
|
| Indications |
|
|
| Side effects |
|
|
| Contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation |
|
|