Androgen insensitivity syndrome ( AIS AIS Scoliosis) is an X-linked recessive X-Linked Recessive Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy condition in which a genetic mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations affects the function of androgen receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors, resulting in complete ( CAIS CAIs Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAIS) block the carbonic anhydrase enzymes in the proximal convoluted tubule, inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), which results in diuresis and metabolic acidosis. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors), partial (PAIS), or mild (MAIS) resistance Resistance Physiologically, the opposition to flow of air caused by the forces of friction. As a part of pulmonary function testing, it is the ratio of driving pressure to the rate of air flow. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing to testosterone Testosterone A potent androgenic steroid and major product secreted by the leydig cells of the testis. Its production is stimulated by luteinizing hormone from the pituitary gland. In turn, testosterone exerts feedback control of the pituitary LH and FSH secretion. Depending on the tissues, testosterone can be further converted to dihydrotestosterone or estradiol. Androgens and Antiandrogens. All individuals with AIS AIS Scoliosis have a 46,XY karyotype Karyotype The full set of chromosomes presented as a systematized array of metaphase chromosomes from a photomicrograph of a single cell nucleus arranged in pairs in descending order of size and according to the position of the centromere. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System; however, phenotypes vary and include phenotypic female, virilized female, undervirilized male, and phenotypic male individuals. Androgen insensitivity syndrome always leads to infertility Infertility Infertility is the inability to conceive in the context of regular intercourse. The most common causes of infertility in women are related to ovulatory dysfunction or tubal obstruction, whereas, in men, abnormal sperm is a common cause. Infertility. Hormone analysis, imaging, and genetic testing Genetic Testing Detection of a mutation; genotype; karyotype; or specific alleles associated with genetic traits, heritable diseases, or predisposition to a disease, or that may lead to the disease in descendants. It includes prenatal genetic testing. Myotonic Dystrophies help make the diagnosis. Management of AIS AIS Scoliosis varies depending on the degree of androgen sensitivity, phenotype Phenotype The complete genetic complement contained in the DNA of a set of chromosomes in a human. The length of the human genome is about 3 billion base pairs. Basic Terms of Genetics, and gender Gender Gender Dysphoria identity, and may involve hormone-replacement therapy and surgery to correct anatomical anomalies of the reproductive and genital structures.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
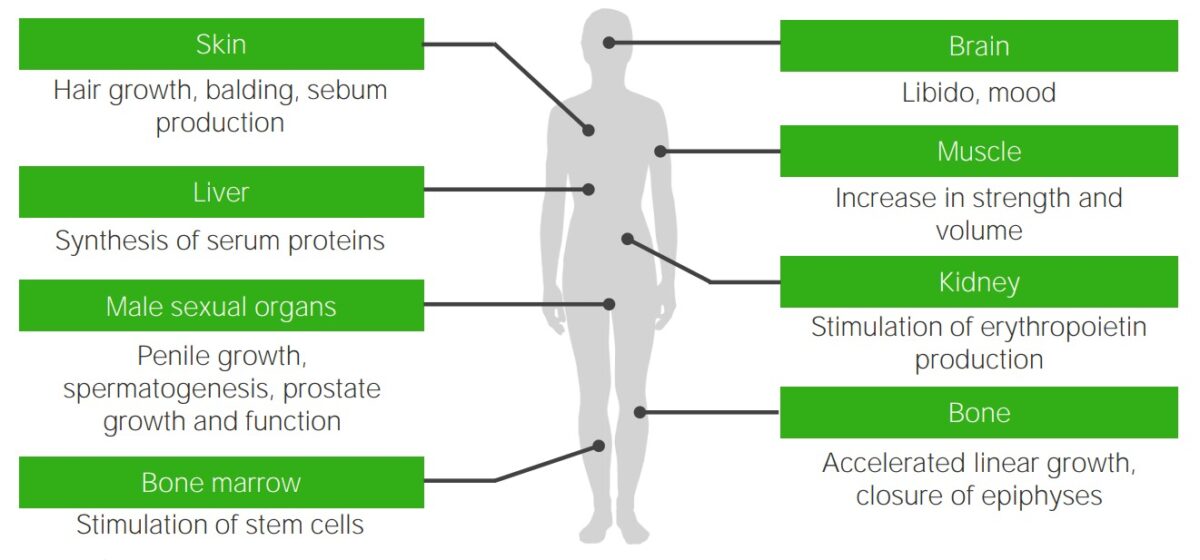
Effects of testosterone: target organs of testosterone and the typical androgenic effects that are missing or deficient in individuals with androgen insensitivity syndrome
Image by Lecturio.Sexual characteristics of affected individuals can vary and lead to 1 of the 3 classification types:
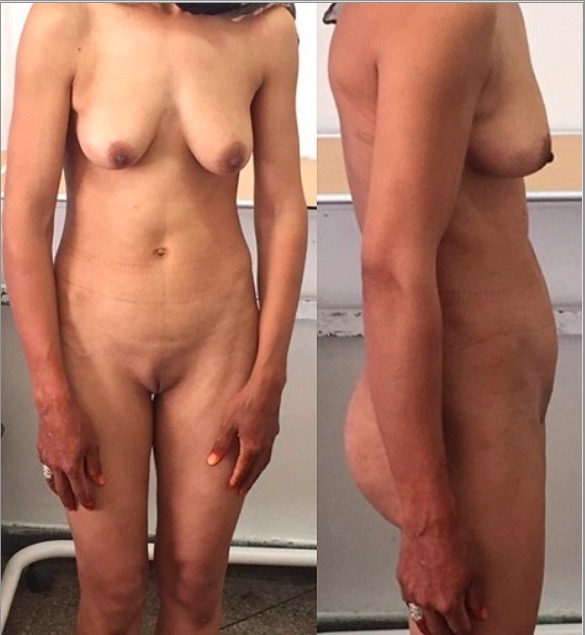
Complete androgen insensitivity syndrome: a 30-year-old patient presenting with primary amenorrhea. Note the scarce pubic hair.
Image: “Front and side view of the patient” by Regragui Souhail et al. License: CC BY 2.0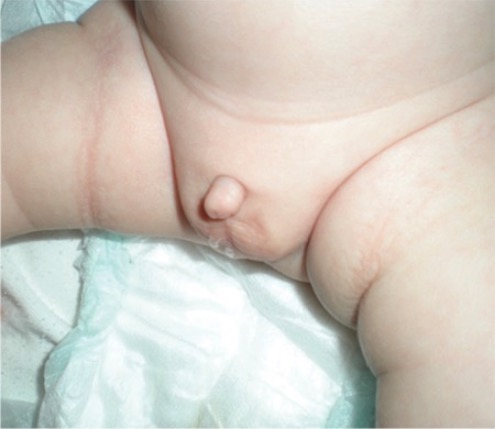
Infant born with a micropenis
Image: “Micropenis in a newborn” by Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Pediatric Endocrinology, Kayseri, Turkey. License: CC BY 2.5
Partial androgen insensitivity syndrome (PAIS)
A patient with PAIS who presented as a phenotypic male with gynecomastia
All disorders affecting sexual development must be considered. The following are select conditions that are part of the differential diagnoses for AIS AIS Scoliosis:
The following condition is related to AIS AIS Scoliosis in that it involves the AR AR Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders. Aortic Regurgitation gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics and impairs androgen receptivity:
Spinobulbar muscular atrophy Spinobulbar Muscular Atrophy Motor Neuron Lesions: an X-linked X-linked Genetic diseases that are linked to gene mutations on the X chromosome in humans or the X chromosome in other species. Included here are animal models of human X-linked diseases. Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) genetic condition, also known as Kennedy disease. Spinobulbar muscular atrophy Spinobulbar Muscular Atrophy Motor Neuron Lesions is caused by abnormal expansion repeat in the AR AR Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders. Aortic Regurgitation gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics, resulting in AR AR Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders. Aortic Regurgitation impairment. Spinobulbar muscular atrophy Spinobulbar Muscular Atrophy Motor Neuron Lesions is characterized by a progressive deterioration of anterior motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology and is associated with the development of gynecomastia Gynecomastia Gynecomastia is a benign proliferation of male breast glandular ductal tissue, usually bilateral, caused by increased estrogen activity, decreased testosterone activity, or medications. The condition is common and physiological in neonates, adolescent boys, and elderly men. Gynecomastia, infertility Infertility Infertility is the inability to conceive in the context of regular intercourse. The most common causes of infertility in women are related to ovulatory dysfunction or tubal obstruction, whereas, in men, abnormal sperm is a common cause. Infertility, and hormonal profiles, similar to that seen in AIS AIS Scoliosis.