Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Sclerosis A pathological process consisting of hardening or fibrosis of an anatomical structure, often a vessel or a nerve. Wilms Tumor (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, is a sporadic Sporadic Selective IgA Deficiency or inherited neurodegenerative disease of upper motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology (UMNs) and lower motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology (LMNs). Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Sclerosis A pathological process consisting of hardening or fibrosis of an anatomical structure, often a vessel or a nerve. Wilms Tumor is the most common progressive motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology neuron disease in North America, primarily affecting men and individuals of Caucasian ethnicity. This disease is characterized by the coexistence of UMN and LMN signs and symptoms. The diagnosis is made clinically. Management is supportive and symptomatic, progressing to end-of-life care.
Last updated: Jul 5, 2023
The cause of sporadic Sporadic Selective IgA Deficiency ALS is unknown. However, there are multiple contributing factors:
The exact pathogenic mechanism of ALS is unknown. There appear to be both molecular and genetic pathways that combine to cause UMN and LMN apoptosis Apoptosis A regulated cell death mechanism characterized by distinctive morphologic changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, including the endonucleolytic cleavage of genomic DNA, at regularly spaced, internucleosomal sites, I.e., DNA fragmentation. It is genetically-programmed and serves as a balance to mitosis in regulating the size of animal tissues and in mediating pathologic processes associated with tumor growth. Ischemic Cell Damage.
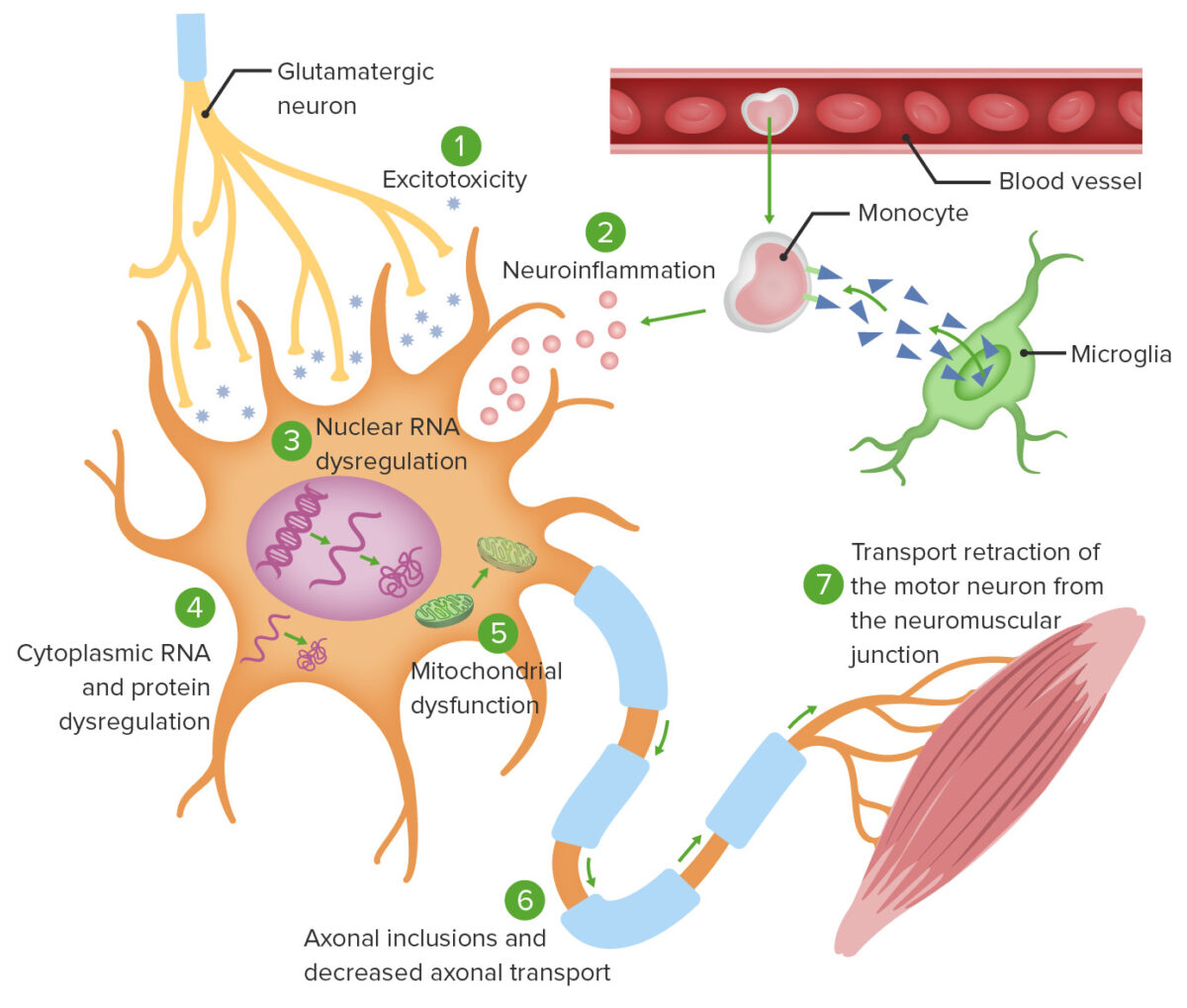
Theories of ALS cellular pathophysiology:
1. Excitotoxicity from glutamate induces intracellular neurodegenerative enzymatic processes.
2. Monocyte-mediated activation of microglia causes secretion of proinflammatory cytokines.
3. Specific gene mutations cause abnormal RNA translation, leading to intranuclear protein aggregation as well as cytoplasmic protein aggregation (4).
5. Mitochondrial dysfunction ensues, rendering neurons unable to adapt to oxidative stress.
6. Intracellular aggregates impair axonal transport.
7. Defective axonal transport leads to ineffective activation of the target neuromuscular junction.
During the usual natural course of the disease, more muscle groups are affected with time, starting with an asymmetrical distribution of weakness, later becoming symmetrical Symmetrical Dermatologic Examination.
| UMN sign | LMN signs |
|---|---|
| Asymmetrical weakness (earliest sign) can be attributed to either one. | |
|
|
Diagnosis is made with clinical presentation alone, but laboratory tests and imaging are typically performed to rule out other illnesses.
The specific criteria for the diagnosis of ALS are also known as the El Escorial World Federation of Neurology criteria.
Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Used to rule out other disorders and include:
Evidence of acute denervation, chronic denervation, and chronic reinnervation supports ALS diagnosis.
No definitive treatment. Current management is symptomatic and supportive.
Medical therapy is based on underlying conditions and clinical presentation.
Nutrition:
Physical therapy Physical Therapy Becker Muscular Dystrophy, occupational therapy Occupational Therapy Skilled treatment that helps individuals achieve independence in all facets of their lives. It assists in the development of skills needed for independent living. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder, and communication Communication The exchange or transmission of ideas, attitudes, or beliefs between individuals or groups. Decision-making Capacity and Legal Competence therapy:
The overall goal of these therapies is to improve the ability to carry out activities of daily living for as long as possible. Different tools are used to do so.
| Tool | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
|
Physical therapy
Physical Therapy
Becker Muscular Dystrophy and Occupational therapy Occupational Therapy Skilled treatment that helps individuals achieve independence in all facets of their lives. It assists in the development of skills needed for independent living. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cervical collar |
Prevent head drop |
|
|
|
|
| Communication Communication The exchange or transmission of ideas, attitudes, or beliefs between individuals or groups. Decision-making Capacity and Legal Competence therapy |
Writing |
Alternative to speaking as vocal quality Quality Activities and programs intended to assure or improve the quality of care in either a defined medical setting or a program. The concept includes the assessment or evaluation of the quality of care; identification of problems or shortcomings in the delivery of care; designing activities to overcome these deficiencies; and follow-up monitoring to ensure effectiveness of corrective steps. Quality Measurement and Improvement declines |
|
Alphabet boards |
Alternative to speaking as vocal quality Quality Activities and programs intended to assure or improve the quality of care in either a defined medical setting or a program. The concept includes the assessment or evaluation of the quality of care; identification of problems or shortcomings in the delivery of care; designing activities to overcome these deficiencies; and follow-up monitoring to ensure effectiveness of corrective steps. Quality Measurement and Improvement declines and writing becomes impaired |
|
|
Electronic assistive communication Communication The exchange or transmission of ideas, attitudes, or beliefs between individuals or groups. Decision-making Capacity and Legal Competence devices |
Voice-assist device as vocal quality Quality Activities and programs intended to assure or improve the quality of care in either a defined medical setting or a program. The concept includes the assessment or evaluation of the quality of care; identification of problems or shortcomings in the delivery of care; designing activities to overcome these deficiencies; and follow-up monitoring to ensure effectiveness of corrective steps. Quality Measurement and Improvement declines |