An amputation is the separation of a portion of the limb or the entire limb from the body, along with the bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types. Amputations are among the oldest recorded medical procedures and date back to 2000 BC in India, with significant advances made during wartime. Amputations are generally indicated for conditions that compromise the viability of the limb or promote the spread of a local process that could manifest systemically. Individuals who have undergone amputation are indicated a multidisciplinary rehabilitation process after the procedure to equip them with a prosthesis fitted to their needs.
Last updated: Jan 21, 2025
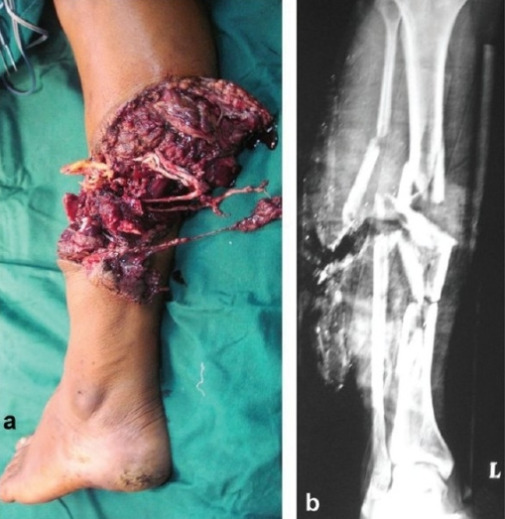
Partial traumatic amputation
Image: “Partial traumatic amputation” by Department of Orthopaedics and Spine Surgery, Ganga Hospital, Coimbatore 641043, India. License: CC BY 2.0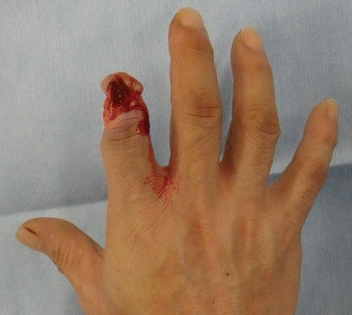
Complete traumatic amputation (crush injury)
Image: “Complete traumatic amputation (crush injury)” by Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, National Hospital Organization Nagasaki Medical Center. License: CC BY 4.0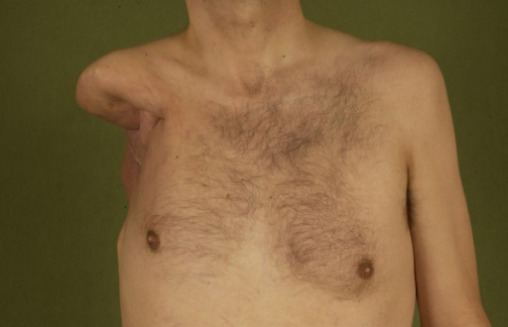
Surgical amputation (disarticulation of the shoulder)
Image: “Postoperative aspect after extended shoulder disarticulation for synovial sarcoma” by Department of Plastic Surgery, Burn Center, Hand surgery, Sarcoma Reference Center, BG-University Hospital Bergmannsheil, Ruhr-University Bochum. License: CC BY 2.0The surgeon should be familiar with the anatomical landmarks and important corresponding structures (nerves, vessels) of the amputation site to avoid injury. As an amputation can be performed at any point along the length of the limbs, a review of the anatomy depends on the site that is selected:
Upper limb amputation:
Lower limb amputation:
Therapeutic goals:
Selection Selection Lymphocyte activation by a specific antigen thus triggering clonal expansion of lymphocytes already capable of mounting an immune response to the antigen. B cells: Types and Functions of amputation type and level:
Emergency:
Elective:
General techniques to minimize tissue ischemia Ischemia A hypoperfusion of the blood through an organ or tissue caused by a pathologic constriction or obstruction of its blood vessels, or an absence of blood circulation. Ischemic Cell Damage and complications:
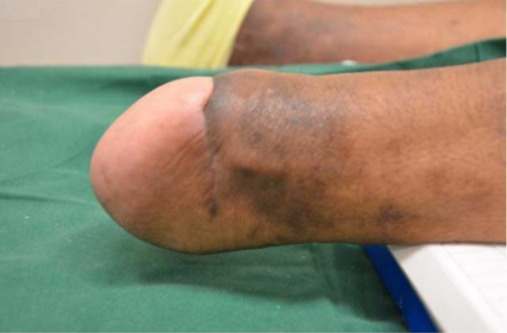
A well-healed stump (6 months postoperative) in an individual with diabetes
Image: “Clinical picture of a well-healed stump at 6-month follow-up” by Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University Orthopaedic, Hand and Reconstructive Microsurgery Cluster, National University Health System, Singapore. License: CC BY 2.0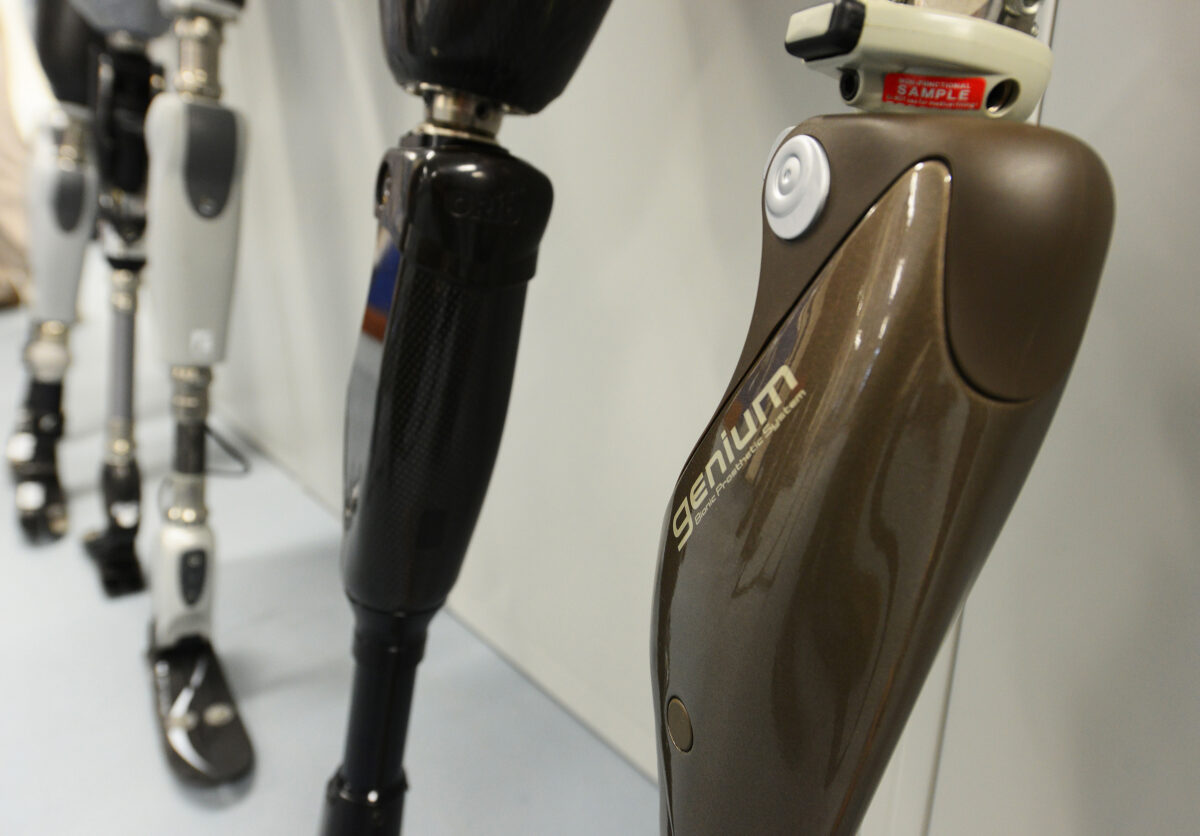
Examples of lower limb prosthesis
Image: “ Prosthetic limbs are lined up against a wall at the Defence Medical Rehabilitation Centre, Headley Court” by Cpl Richard Cave RLC. License: Open Government Licence version 1.0