Amebicides are drugs toxic to amebas such as Entamoeba Entamoeba A genus of ameboid protozoa characterized by the presence of beaded chromatin on the inner surface of the nuclear membrane. Its organisms are parasitic in invertebrates and vertebrates, including humans. Nitroimidazoles histolytica (the causative organism of amebiasis Amebiasis Amebiasis, or amoebic dysentery, is an infection caused by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Transmission is through the fecal-oral route or by consumption of contaminated food and water. Most patients infected with E. histolytica are asymptomatic, but about 10% may develop dysentery. Entamoeba spp./Amebiasis). Parasites enter the GI tract where trophozoites can penetrate the intestinal wall and cause an invasive infection. Amebicides are classified based on where the drug is most effective: intestinal lumen or tissues. Intestinal-lumen amebicides include iodoquinol and paromomycin. Tissue amebicides include the nitroimidazole drug class (e.g., metronidazole Metronidazole A nitroimidazole used to treat amebiasis; vaginitis; trichomonas infections; giardiasis; anaerobic bacteria; and treponemal infections. Pyogenic Liver Abscess, tinidazole Tinidazole A nitroimidazole alkylating agent that is used as an antitrichomonal agent against trichomonas vaginalis; entamoeba histolytica; and giardia lamblia infections. It also acts as an antibacterial agent for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis and anaerobic bacterial infections. Nitroimidazoles). Treatment of symptomatic disease usually requires a combination of both classes.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
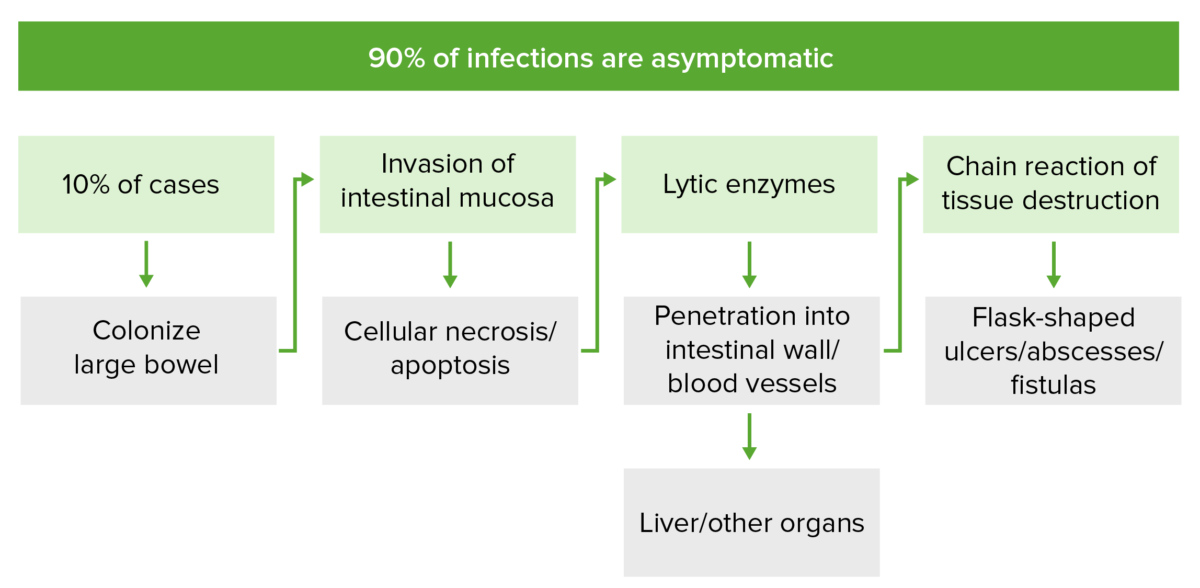
The pathogenesis of invasive Entamoeba histolytica infection:
In 10% of cases, E. histolytica colonizes the large intestine mucosa and invades via secretion of proteinases and lytic enzymes. This causes cellular necrosis and lysis of the membranes, respectively. This chain of events induces mucosal cell apoptosis and disrupts tight junctions between cells, allowing for flask-shaped ulcers, abscesses, and fistulas to form. Invasion may reach the portal venous system, through which E. histolytica can spread to other organs.
A combination of tissue and luminal amebicides are prescribed to treat amebiasis Amebiasis Amebiasis, or amoebic dysentery, is an infection caused by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Transmission is through the fecal-oral route or by consumption of contaminated food and water. Most patients infected with E. histolytica are asymptomatic, but about 10% may develop dysentery. Entamoeba spp./Amebiasis.
Luminal amebicides:
Tissue amebicides:
Iodoquinol was used to treat intestinal amebiasis Amebiasis Amebiasis, or amoebic dysentery, is an infection caused by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Transmission is through the fecal-oral route or by consumption of contaminated food and water. Most patients infected with E. histolytica are asymptomatic, but about 10% may develop dysentery. Entamoeba spp./Amebiasis. It’s no longer available in the United States as of 2025 due to FDA enforcement against unapproved products.
Iodoquinol is contraindicated in individuals with an allergy Allergy An abnormal adaptive immune response that may or may not involve antigen-specific IgE Type I Hypersensitivity Reaction or intolerance to iodine Iodine A nonmetallic element of the halogen group that is represented by the atomic symbol I, atomic number 53, and atomic weight of 126. 90. It is a nutritionally essential element, especially important in thyroid hormone synthesis. In solution, it has anti-infective properties and is used topically. Thyroid Hormones.
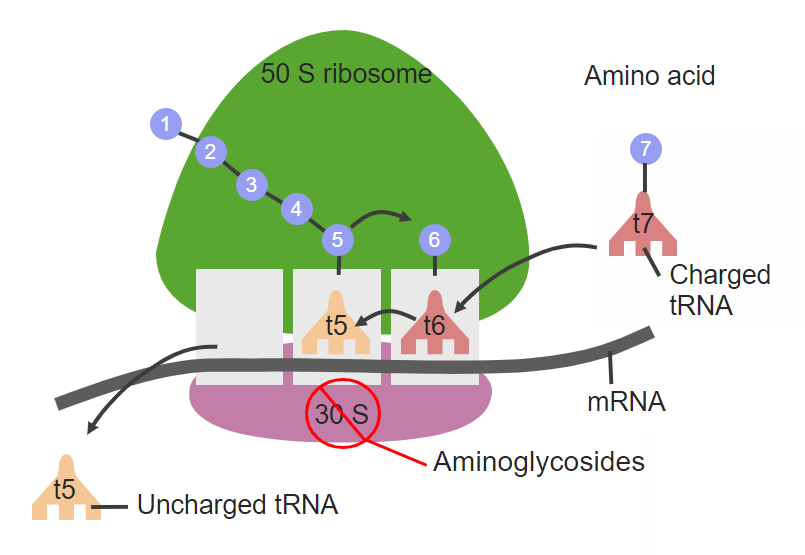
The site of action for aminoglycosides, which target the 30S ribosomal subunit
tRNA: transfer RNA
mRNA: messenger RNA
Caution should be used in individuals with:
In addition to anaerobic bacterial infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, nitroimidazoles Nitroimidazoles Nitroimidazoles are prodrugs composed of an imidazole ring with an attached nitro group. Nitroimidazoles are reduced within susceptible microorganisms, leading to free radical formation and disruption of DNA integrity. Nitroimidazoles can be used for: