Alport syndrome, also called hereditary nephritis, is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations in the genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure encoding for the alpha chains of type IV collagen Collagen A polypeptide substance comprising about one third of the total protein in mammalian organisms. It is the main constituent of skin; connective tissue; and the organic substance of bones (bone and bones) and teeth (tooth). Connective Tissue: Histology, resulting in the production of abnormal type IV collagen Collagen A polypeptide substance comprising about one third of the total protein in mammalian organisms. It is the main constituent of skin; connective tissue; and the organic substance of bones (bone and bones) and teeth (tooth). Connective Tissue: Histology strands. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship present with glomerulonephritis, hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension, edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema, hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma, and proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children, as well as with ocular ( cataract Cataract Partial or complete opacity on or in the lens or capsule of one or both eyes, impairing vision or causing blindness. The many kinds of cataract are classified by their morphology (size, shape, location) or etiology (cause and time of occurrence). Neurofibromatosis Type 2, retinopathy) and auditory ( sensorineural hearing loss Sensorineural hearing loss Hearing loss resulting from damage to the cochlea and the sensorineural elements which lie internally beyond the oval and round windows. These elements include the auditory nerve and its connections in the brainstem. Hearing Loss) findings. Diagnosis is established with urinalysis Urinalysis Examination of urine by chemical, physical, or microscopic means. Routine urinalysis usually includes performing chemical screening tests, determining specific gravity, observing any unusual color or odor, screening for bacteriuria, and examining the sediment microscopically. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) in Children, urine microscopy, and a renal function panel. A renal biopsy Renal Biopsy Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis showing characteristic glomerular basement membrane Basement membrane A darkly stained mat-like extracellular matrix (ecm) that separates cell layers, such as epithelium from endothelium or a layer of connective tissue. The ecm layer that supports an overlying epithelium or endothelium is called basal lamina. Basement membrane (bm) can be formed by the fusion of either two adjacent basal laminae or a basal lamina with an adjacent reticular lamina of connective tissue. Bm, composed mainly of type IV collagen; glycoprotein laminin; and proteoglycan, provides barriers as well as channels between interacting cell layers. Thin Basement Membrane Nephropathy (TBMN) splitting Splitting Defense Mechanisms may be used to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment for Alport syndrome is focused on limiting disease progression with angiotensin receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors A class of drugs whose main indications are the treatment of hypertension and heart failure. They exert their hemodynamic effect mainly by inhibiting the renin-angiotensin system. They also modulate sympathetic nervous system activity and increase prostaglandin synthesis. They cause mainly vasodilation and mild natriuresis without affecting heart rate and contractility. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors. Hearing aids are used for hearing loss Hearing loss Hearing loss, also known as hearing impairment, is any degree of impairment in the ability to apprehend sound as determined by audiometry to be below normal hearing thresholds. Clinical presentation may occur at birth or as a gradual loss of hearing with age, including a short-term or sudden loss at any point. Hearing Loss associated with Alport syndrome.
Last updated: Feb 25, 2025
Alport syndrome is a genetic disorder arising from a mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations in genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure encoding for the alpha chains of type IV collagen Collagen A polypeptide substance comprising about one third of the total protein in mammalian organisms. It is the main constituent of skin; connective tissue; and the organic substance of bones (bone and bones) and teeth (tooth). Connective Tissue: Histology, which is primarily located in the lens Lens A transparent, biconvex structure of the eye, enclosed in a capsule and situated behind the iris and in front of the vitreous humor (vitreous body). It is slightly overlapped at its margin by the ciliary processes. Adaptation by the ciliary body is crucial for ocular accommodation. Eye: Anatomy, cochlea Cochlea The part of the inner ear (labyrinth) that is concerned with hearing. It forms the anterior part of the labyrinth, as a snail-like structure that is situated almost horizontally anterior to the vestibular labyrinth. Ear: Anatomy, and kidneys Kidneys The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs located retroperitoneally against the posterior wall of the abdomen on either side of the spine. As part of the urinary tract, the kidneys are responsible for blood filtration and excretion of water-soluble waste in the urine. Kidneys: Anatomy (glomerulus).
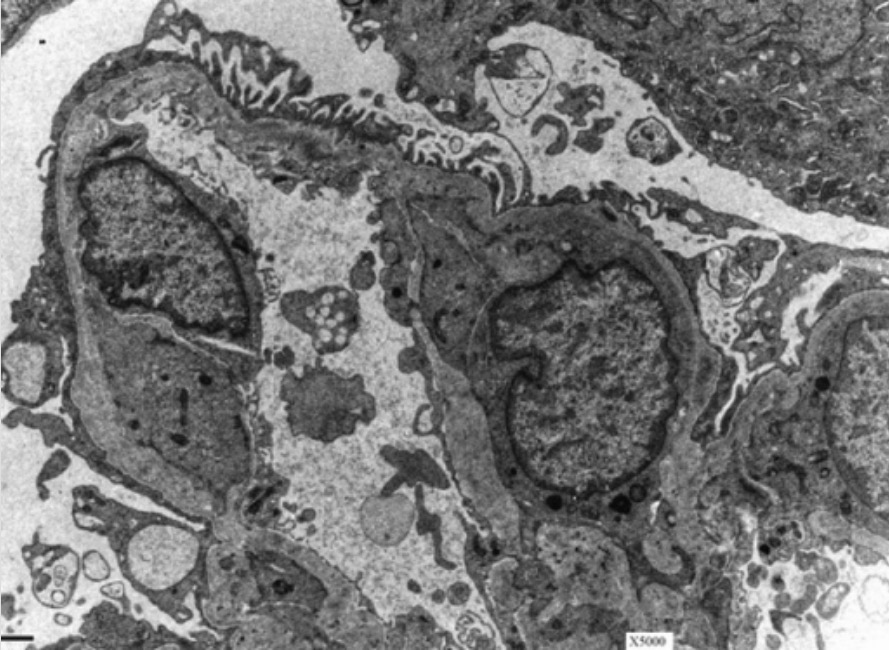
Glomerular basement membrane (GBM) in a patient with Alport syndrome:
Electron microscopy of a kidney shows the characteristic basket-weave appearance of the GBM in a patient with Alport syndrome.
Alport syndrome most often presents with renal, ocular, and auditory findings.
Sensorineural hearing loss Sensorineural hearing loss Hearing loss resulting from damage to the cochlea and the sensorineural elements which lie internally beyond the oval and round windows. These elements include the auditory nerve and its connections in the brainstem. Hearing Loss:
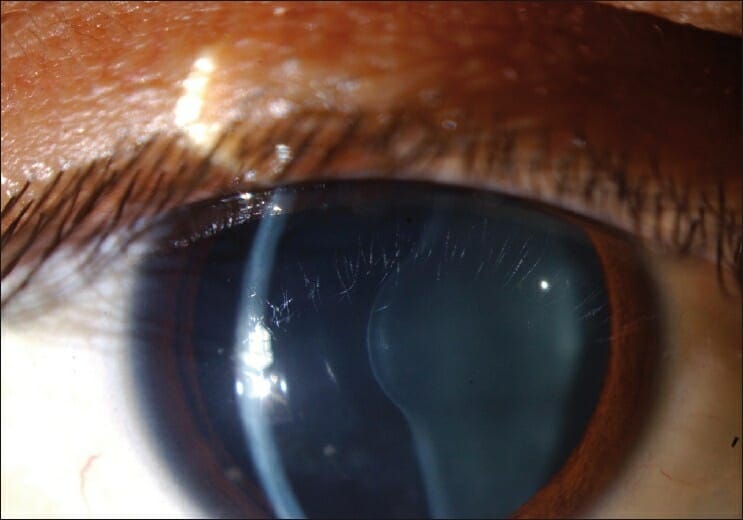
Anterior lenticonus in the eye of an individual with Alport syndrome
Image: “Figure 1 Anterior lenticonus in the right eye in a patient with Alport syndrome” by Ammar M Al-Mahmood, Samar A Al-Swailem, Abdulrahman Al-Khalaf, Ghada Y Al-Binali. License: CC BY 2.0A complete history, including family history Family History Adult Health Maintenance, and physical exam are required to make a diagnosis.
Treatment is focused on limiting the progression of kidney disease and proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children. No definitive treatment is currently available.