Alcoholic Alcoholic Persons who have a history of physical or psychological dependence on ethanol. Mallory-Weiss Syndrome (Mallory-Weiss Tear) liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy disease is a spectrum of disorders ranging from fatty liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy to cirrhosis Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a late stage of hepatic parenchymal necrosis and scarring (fibrosis) most commonly due to hepatitis C infection and alcoholic liver disease. Patients may present with jaundice, ascites, and hepatosplenomegaly. Cirrhosis can also cause complications such as hepatic encephalopathy, portal hypertension, portal vein thrombosis, and hepatorenal syndrome. Cirrhosis secondary to chronic alcohol use disorder Alcohol use disorder Alcohol is one of the most commonly used addictive substances in the world. Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is defined as pathologic consumption of alcohol leading to impaired daily functioning. Acute alcohol intoxication presents with impairment in speech and motor functions and can be managed in most cases with supportive care. Alcohol Use Disorder. Excessive and prolonged consumption of alcohol results in impairment of the lipolysis Lipolysis The metabolic process of breaking down lipids to release free fatty acids, the major oxidative fuel for the body. Lipolysis may involve dietary lipids in the digestive tract, circulating lipids in the blood, and stored lipids in the adipose tissue or the liver. A number of enzymes are involved in such lipid hydrolysis, such as lipase and lipoprotein lipase from various tissues. Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) pathway, causing inflammatory changes within the hepatocytes Hepatocytes The main structural component of the liver. They are specialized epithelial cells that are organized into interconnected plates called lobules. Liver: Anatomy. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship typically present during the hepatitis stage with jaundice Jaundice Jaundice is the abnormal yellowing of the skin and/or sclera caused by the accumulation of bilirubin. Hyperbilirubinemia is caused by either an increase in bilirubin production or a decrease in the hepatic uptake, conjugation, or excretion of bilirubin. Jaundice, fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, and abdominal pain Abdominal Pain Acute Abdomen. Diagnosis is based on a history of alcohol use disorder Alcohol use disorder Alcohol is one of the most commonly used addictive substances in the world. Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is defined as pathologic consumption of alcohol leading to impaired daily functioning. Acute alcohol intoxication presents with impairment in speech and motor functions and can be managed in most cases with supportive care. Alcohol Use Disorder and confirmed by laboratory derangement with an AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests/ ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests ratio > 2. Alcoholic Alcoholic Persons who have a history of physical or psychological dependence on ethanol. Mallory-Weiss Syndrome (Mallory-Weiss Tear) liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy disease carries a high mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status rate if patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship present with severe hepatitis. Management aims at alcohol abstinence for reversal (at certain stages) and addressing contributing factors (such as viral infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease or drugs) to minimize damage to the hepatocytes Hepatocytes The main structural component of the liver. They are specialized epithelial cells that are organized into interconnected plates called lobules. Liver: Anatomy. Approximately 10% of patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship regress with alcohol abstinence during the hepatitis stage. Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a late stage of hepatic parenchymal necrosis and scarring (fibrosis) most commonly due to hepatitis C infection and alcoholic liver disease. Patients may present with jaundice, ascites, and hepatosplenomegaly. Cirrhosis can also cause complications such as hepatic encephalopathy, portal hypertension, portal vein thrombosis, and hepatorenal syndrome. Cirrhosis is frequently irreversible.
Last updated: Dec 3, 2024
Alcoholic Alcoholic Persons who have a history of physical or psychological dependence on ethanol. Mallory-Weiss Syndrome (Mallory-Weiss Tear) liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy disease encompasses alcoholic Alcoholic Persons who have a history of physical or psychological dependence on ethanol. Mallory-Weiss Syndrome (Mallory-Weiss Tear) steatosis Steatosis Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) (fatty liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy, reversible), steatohepatitis Steatohepatitis Drug-Induced Liver Injury (can be reversible), and cirrhosis Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a late stage of hepatic parenchymal necrosis and scarring (fibrosis) most commonly due to hepatitis C infection and alcoholic liver disease. Patients may present with jaundice, ascites, and hepatosplenomegaly. Cirrhosis can also cause complications such as hepatic encephalopathy, portal hypertension, portal vein thrombosis, and hepatorenal syndrome. Cirrhosis (irreversible). All are secondary to alcohol use disorder Alcohol use disorder Alcohol is one of the most commonly used addictive substances in the world. Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is defined as pathologic consumption of alcohol leading to impaired daily functioning. Acute alcohol intoxication presents with impairment in speech and motor functions and can be managed in most cases with supportive care. Alcohol Use Disorder.
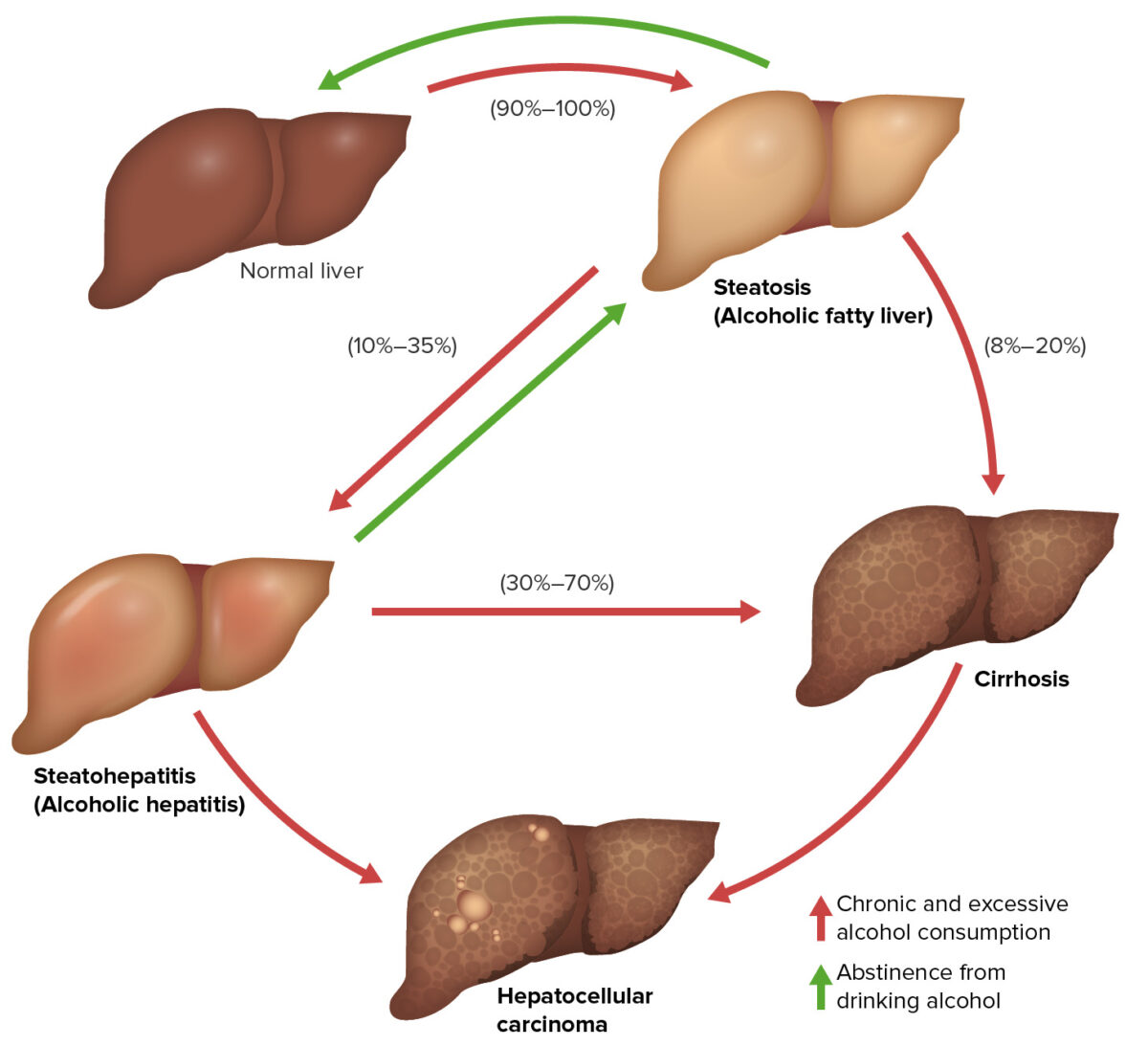
The 3 stages of alcoholic liver disease:
These 3 stages of alcoholic liver disease may overlap and do not necessarily occur in sequence: alcoholic fatty liver (reversible), alcoholic hepatitis (reversible if alcohol stopped), and alcohol-related cirrhosis (irreversible). They are also risk factors for developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
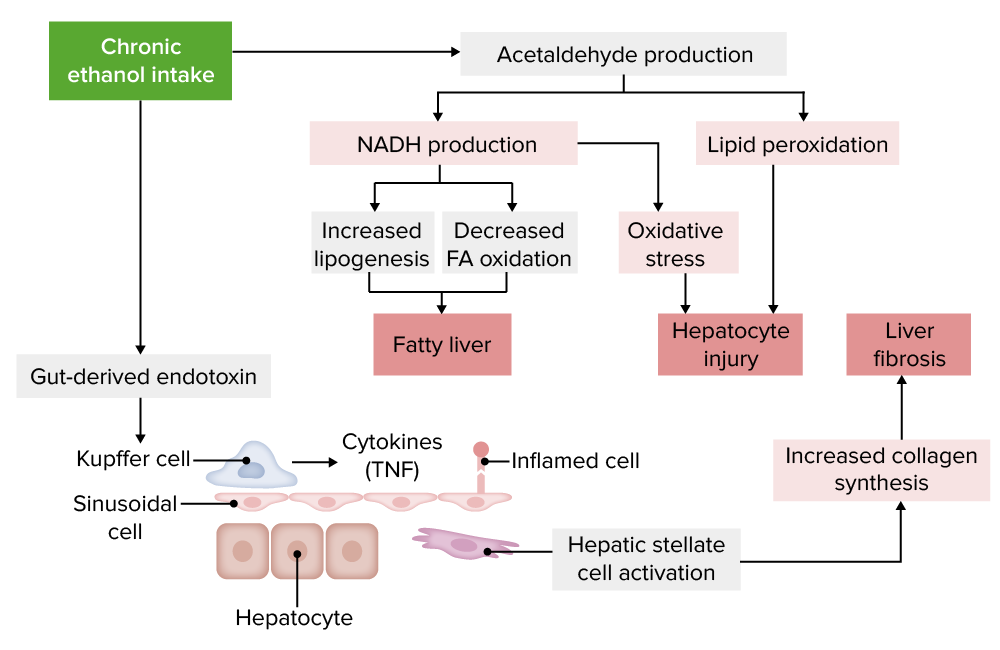
Pathophysiology of alcoholic liver disease:
FA: fatty acid; TNF: tumor necrosis factor
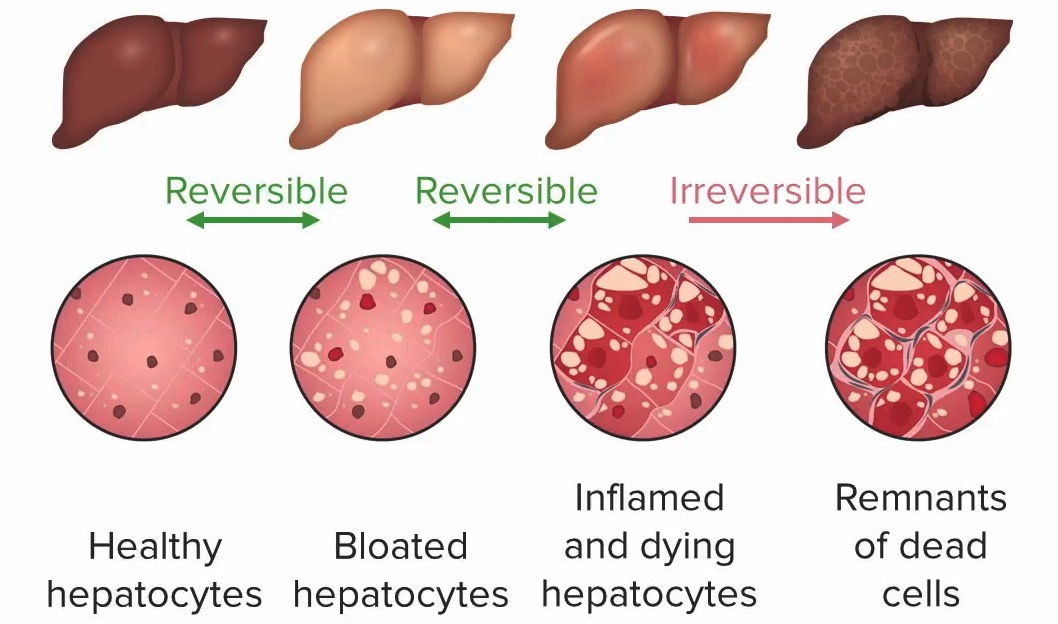
Progression of liver damage in alcoholic liver disease (left to right):
1. Healthy hepatocytes (no liver damage)
2. Bloated hepatocytes with steatosis (distended by fat droplets), no inflammation: steatosis (liver damage still reversible)
3. Inflamed and dying hepatocytes, possible fibrosis: hepatitis (liver damage still reversible)
4. Dead cells: cirrhosis (irreversible liver damage)
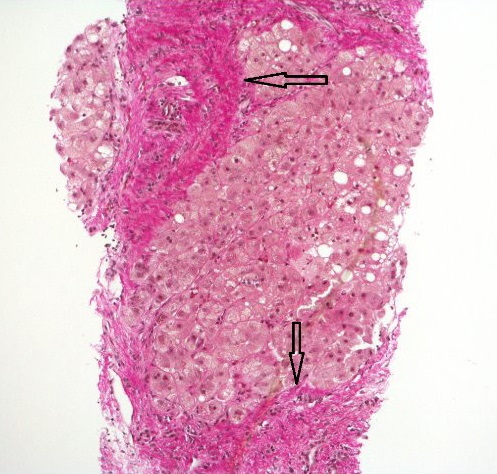
Steatohepatitis with established cirrhosis; thick bands of fibrosis (arrows) encircling a hepatocyte nodule
Image: “Hematoxylin and Van Gieson’s stain” by Alexander Boyd et al. License: CC BY 4.0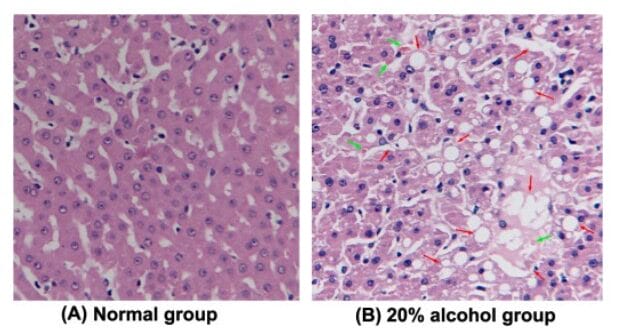
Alcohol-induced steatosis (histological features of liver sections):
(A): normal control group
(B): 20% alcohol-induced fatty liver with macrovesicles (indicated by red arrow) of hepatocytes graded as high in the alcoholic fatty liver disease group. The green arrow represents the formation of Mallory bodies.
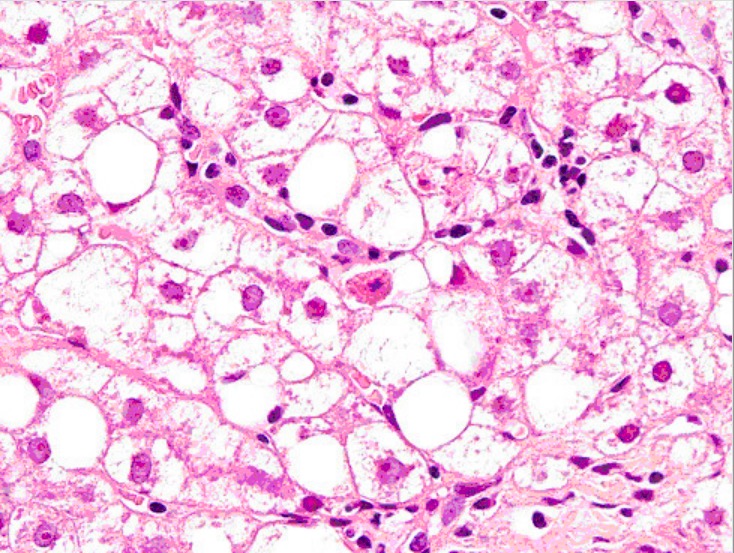
Liver biopsy showing Mallory bodies, large-droplet steatosis, and neutrophils
Image: “Liver biopsy” by Institute of Infectious and Tropical Diseases, University of Brescia, Italy. License: CC BY 2.0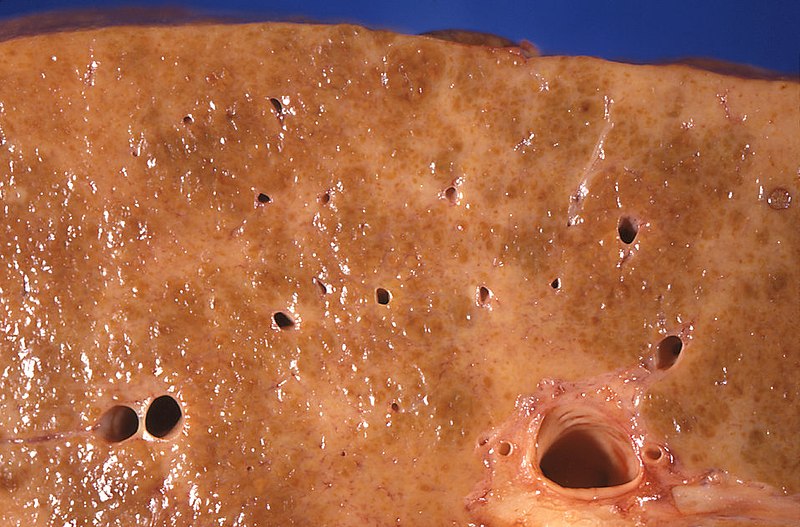
Gross pathology of alcoholic liver cirrhosis: The cut surface shows areas with diffuse pallor due to a dense network of scar tissue.
Image: “Gross pathology of alcoholic liver cirrhosis” by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Dr. Edwin P. Ewing, Jr. License: CC0 1.0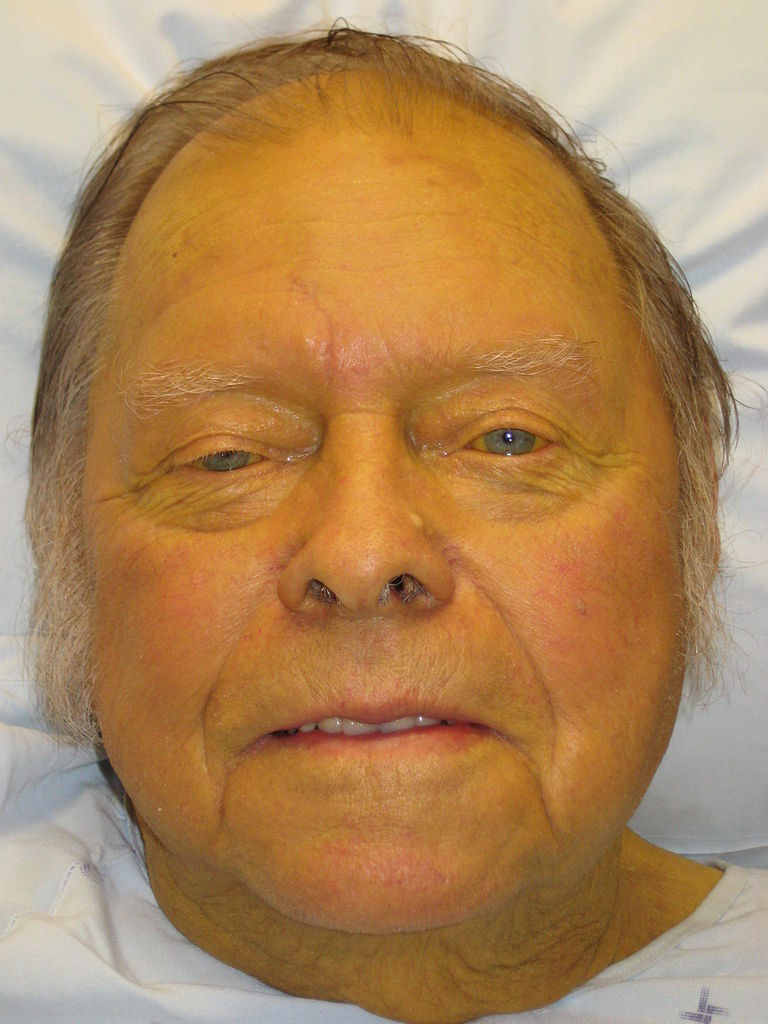
Jaundice: yellow discoloration of the skin due to bilirubin deposition
Image: “Jaundice08” by James Heilman, MD. License: CC BY 3.0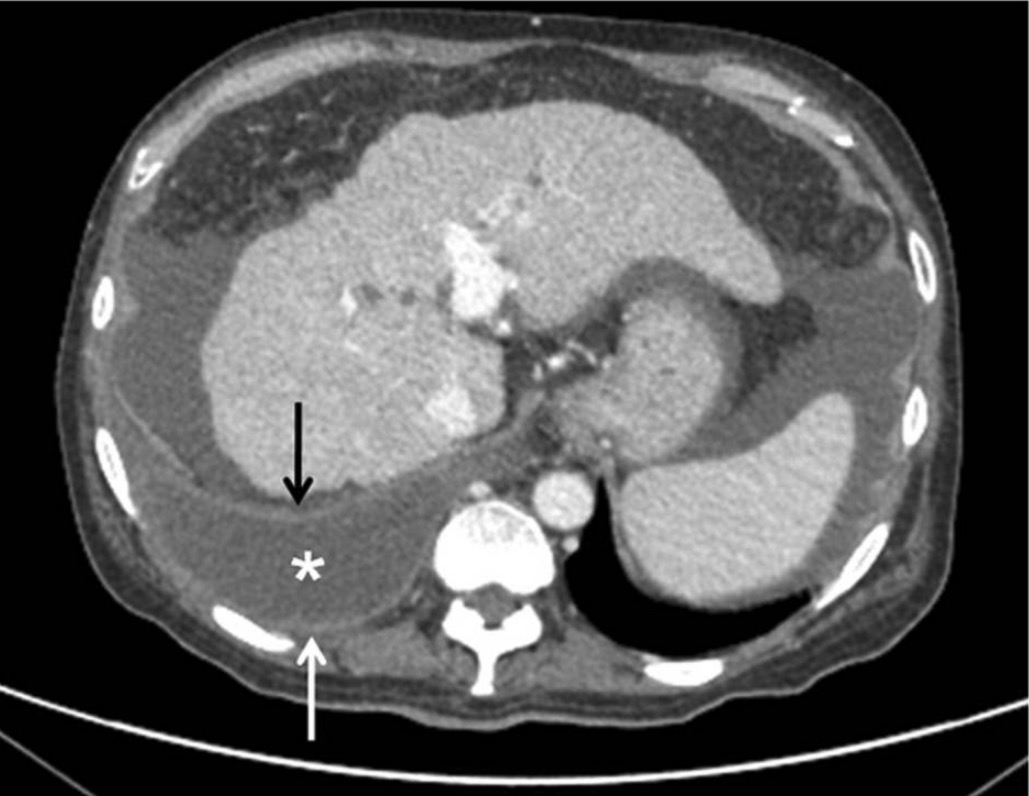
Liver cirrhosis with concomitant empyema (asterisk and arrows):
Liver appears nodular, irregular, and shrunken (notice abdominal ascites).
Maddrey discriminant function:
Glasgow alcoholic Alcoholic Persons who have a history of physical or psychological dependence on ethanol. Mallory-Weiss Syndrome (Mallory-Weiss Tear) hepatitis score:
Model for End-Stage Liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy Disease score:
Mild-to-moderate hepatitis:
Severe hepatitis:
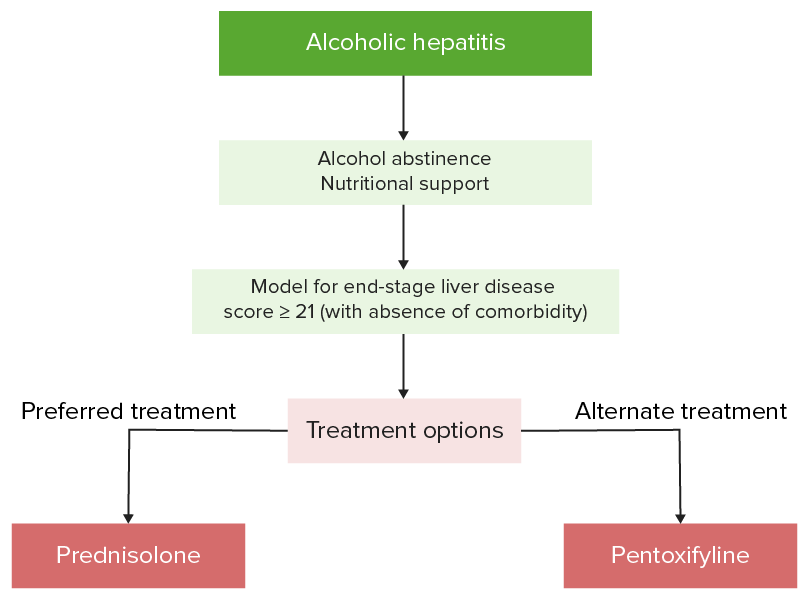
Management algorithm of alcoholic hepatitis
Image by Lecturio.