Albinism refers to a group of inherited disorders that result in the disruption of melanin Melanin Insoluble polymers of tyrosine derivatives found in and causing darkness in skin (skin pigmentation), hair, and feathers providing protection against sunburn induced by sunlight. Carotenes contribute yellow and red coloration. Seborrheic Keratosis production, causing hypopigmentation Hypopigmentation A condition caused by a deficiency or a loss of melanin pigmentation in the epidermis, also known as hypomelanosis. Hypopigmentation can be localized or generalized, and may result from genetic defects, trauma, inflammation, or infections. Malassezia Fungi and visual impairment. The condition is classified according to the clinical phenotype Phenotype The complete genetic complement contained in the DNA of a set of chromosomes in a human. The length of the human genome is about 3 billion base pairs. Basic Terms of Genetics. Oculocutaneous albinism results in hypopigmentation Hypopigmentation A condition caused by a deficiency or a loss of melanin pigmentation in the epidermis, also known as hypomelanosis. Hypopigmentation can be localized or generalized, and may result from genetic defects, trauma, inflammation, or infections. Malassezia Fungi of the skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions, eyes, and hair. Ocular albinism affects only the eyes. The diagnosis is clinical. Management is mainly supportive, with sun protection being a key component. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with albinism have an increased risk of skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions cancer and require frequent skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions examinations.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Albinism is a group of inherited disorders affecting the production of melanin Melanin Insoluble polymers of tyrosine derivatives found in and causing darkness in skin (skin pigmentation), hair, and feathers providing protection against sunburn induced by sunlight. Carotenes contribute yellow and red coloration. Seborrheic Keratosis and resulting in hypopigmentation Hypopigmentation A condition caused by a deficiency or a loss of melanin pigmentation in the epidermis, also known as hypomelanosis. Hypopigmentation can be localized or generalized, and may result from genetic defects, trauma, inflammation, or infections. Malassezia Fungi.
Albinism is classified according to its clinical phenotype Phenotype The complete genetic complement contained in the DNA of a set of chromosomes in a human. The length of the human genome is about 3 billion base pairs. Basic Terms of Genetics:
Albinism results from inherited genetic mutations Genetic Mutations Carcinogenesis.
The presentation can vary depending on the different genetic subtypes. However, the following are general signs and symptoms:
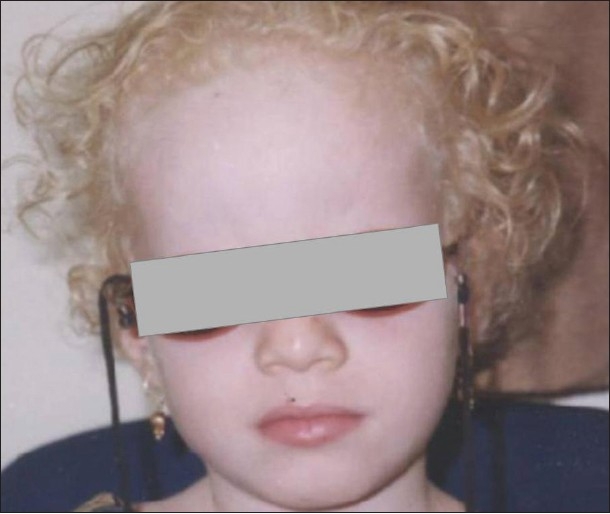
A child with albinism. Notice the very pale skin and light hair.
Image: “Albinism: Images in ophthalmology” by Sreelatha OK, Al-Harthy E, Vanrijen-Cooymans P, Al-Zuhaibi S, Ganesh A. License: CC BY 2.0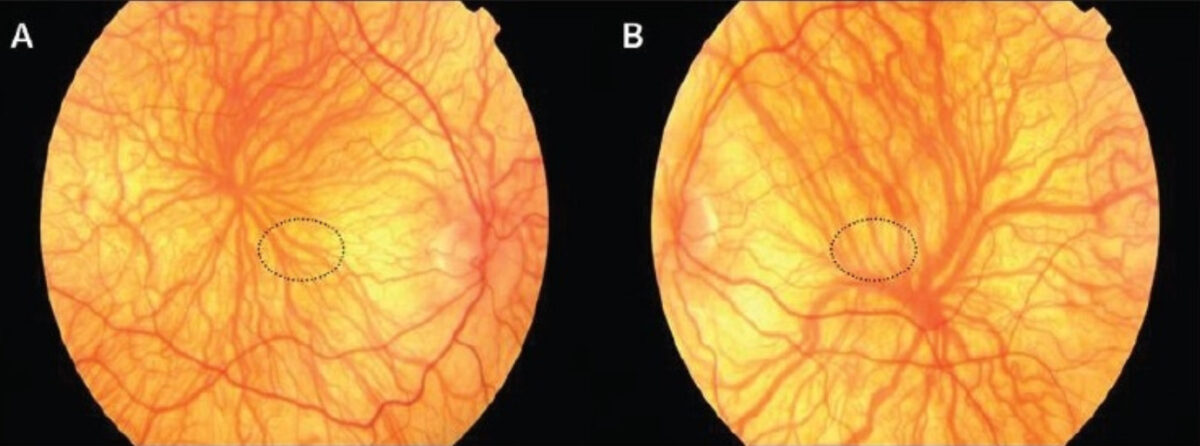
Fundoscopic findings in albinism:
These images demonstrate retinal hypopigmentation, prominent vasculature, foveal hypoplasia (should be located in the regions circled) with vessels coursing through the region, and indistinct optic disc margins.
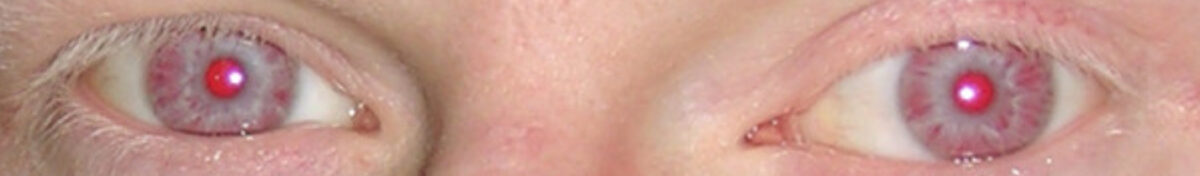
Hypopigmented eyes and eyelashes in a patient with oculocutaneous albinism
Image: “Oculocutaneous albinism” by Grønskov K, Ek J, Brondum-Nielsen K. License: CC BY 2.0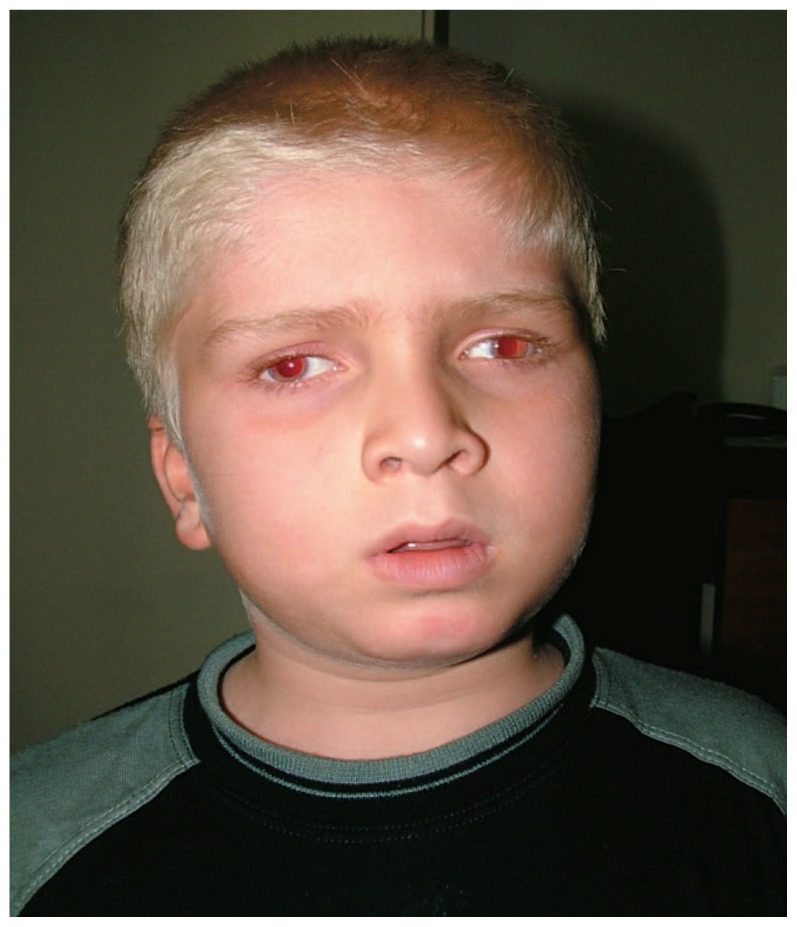
A patient with oculocutaneous albinism:
Notice the light hair, eyes, and exotropia (a form of strabismus).
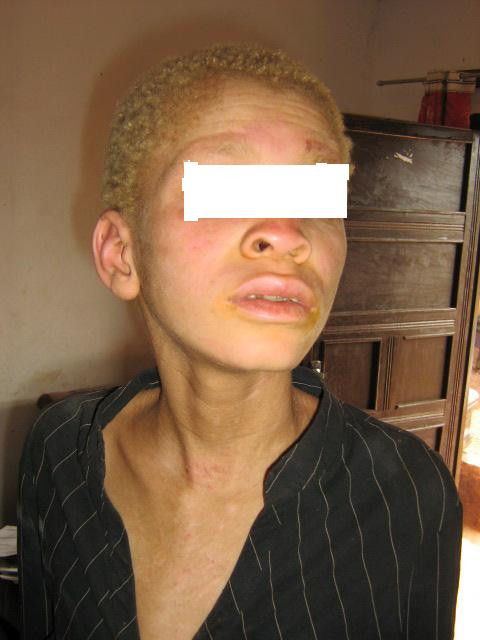
A patient with light skin, hair, and eyebrows due to albinism
Image: “Childhood autism in a 13 year old boy with oculocutaneous albinism: a case report” by Bakare MO, Ikegwuonu NN. License: CC BY 2.0There is no currently available cure, and management is mainly supportive.
Albinism is associated with an increased risk of skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions cancer, with squamous cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) is caused by malignant proliferation of atypical keratinocytes. This condition is the 2nd most common skin malignancy and usually affects sun-exposed areas of fair-skinned patients. The cancer presents as a firm, erythematous, keratotic plaque or papule. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) being the most common.
The following conditions are differential for OA OA Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis, and is due to cartilage destruction and changes of the subchondral bone. The risk of developing this disorder increases with age, obesity, and repetitive joint use or trauma. Patients develop gradual joint pain, stiffness lasting < 30 minutes, and decreased range of motion. Osteoarthritis:
The following conditions must be considered in the differential diagnosis for OCA OCA Primary Biliary Cholangitis: