Airway obstruction is a partial or complete blockage of the airways that impedes airflow. An airway obstruction can be classified as upper, central, or lower depending on location. Lower airway obstruction (LAO) is usually a manifestation of chronic disease, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Upper airway obstruction (UAO) and central airway obstruction (CAO) refer to a mechanical blockage of the large airways and are potentially life-threatening events that need to be recognized and managed promptly.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Airway Airway ABCDE Assessment obstruction is a blockage of the airways, which impedes air flow Flow Blood flows through the heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins in a closed, continuous circuit. Flow is the movement of volume per unit of time. Flow is affected by the pressure gradient and the resistance fluid encounters between 2 points. Vascular resistance is the opposition to flow, which is caused primarily by blood friction against vessel walls. Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure and effective respiration Respiration The act of breathing with the lungs, consisting of inhalation, or the taking into the lungs of the ambient air, and of exhalation, or the expelling of the modified air which contains more carbon dioxide than the air taken in. Nose Anatomy (External & Internal).
Upper airway Airway ABCDE Assessment obstruction and CAO (large airway Airway ABCDE Assessment obstruction):
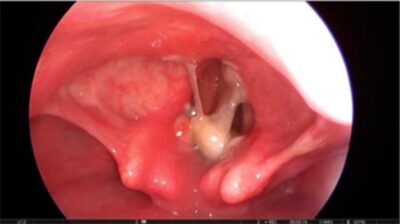
Foreign body stuck between vocal cords (bronchoscopic view)
Image: “Foreign body stuck between vocal cords” by Kamran Mottaghi et al. License: CC BY 3.0Lower airway Airway ABCDE Assessment obstruction (small airway Airway ABCDE Assessment obstruction):
History can be obtained from a responsive patient not in extremis.
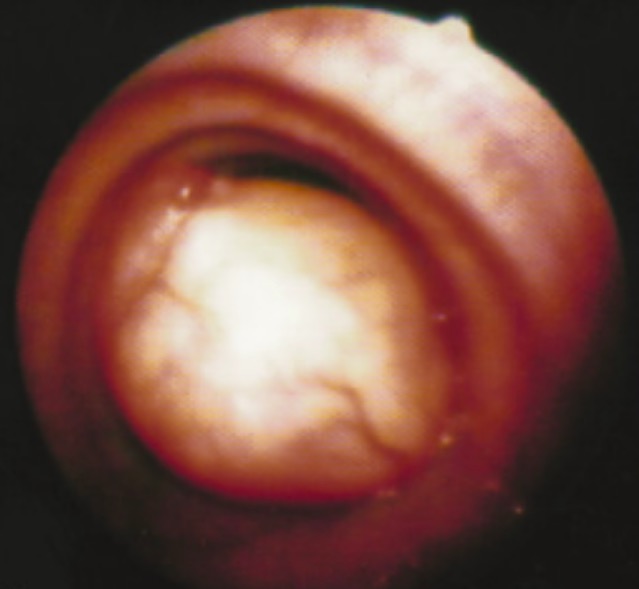
Bronchoscopic view of endoluminal tracheal tumor causing obstruction
Image: “Intraluminal tracheal tumor causing severe airway obstruction” by Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, School of Medicine, University of Patras, Greece. License: CC BY 2.0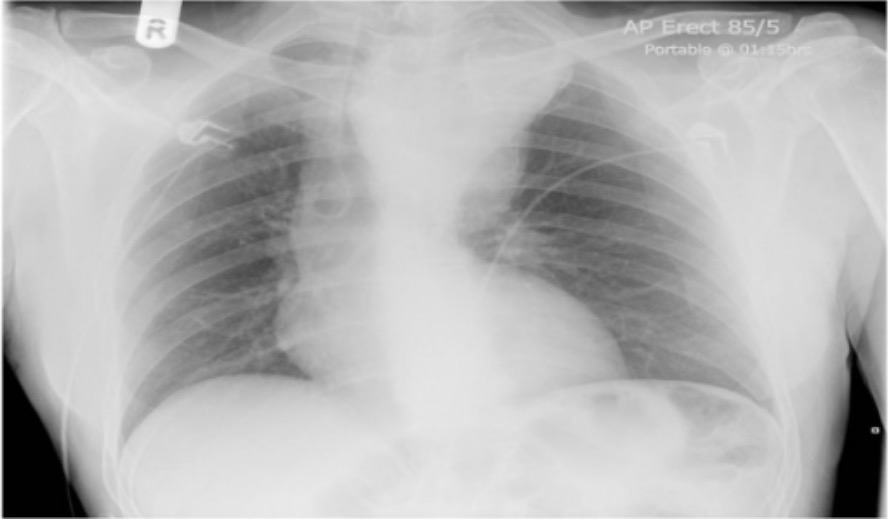
Chest X-ray showing tracheal deviation: a large superior mediastinal shadow suggestive of arch aneurysm extending well into neck and causing extrinsic compression of the trachea
Image: “Chest X-ray” by Leeds General Infirmary, Yorkshire Heart Centre, Great George Street, Leeds LS1 3EX, UK. License: CC BY 2.0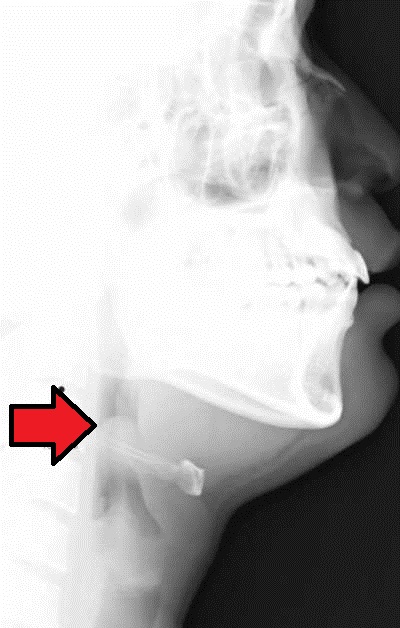
Acute epiglottitis presenting with the “thumb sign” in a lateral neck X-ray
Image: “Acute epiglottitis” by Med Chaos. License: CC0For chronic/subacute symptoms in the setting of suspected obstruction:
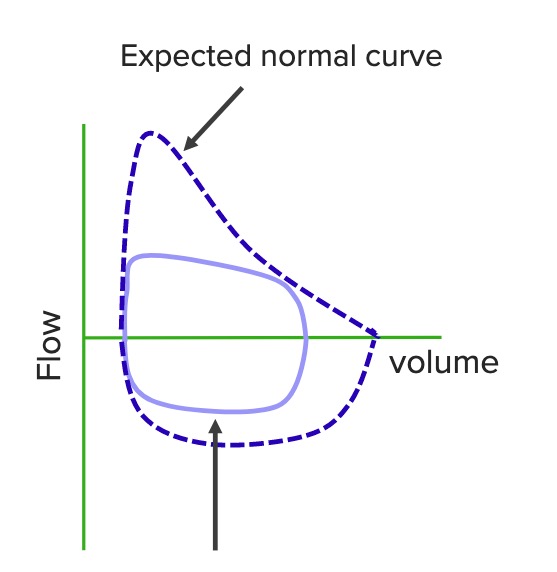
“Squared-off” flow-volume loop of tracheal obstruction
Image by Lecturio.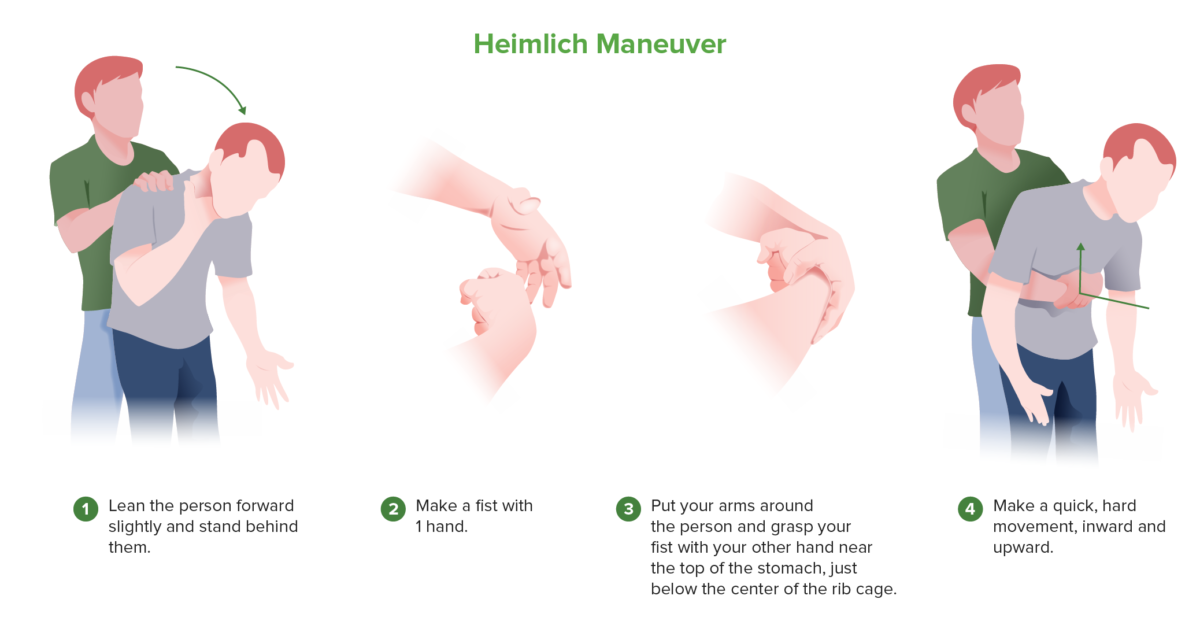
Abdominal thrusts, steps of Heimlich maneuver.
Image by Lecturio.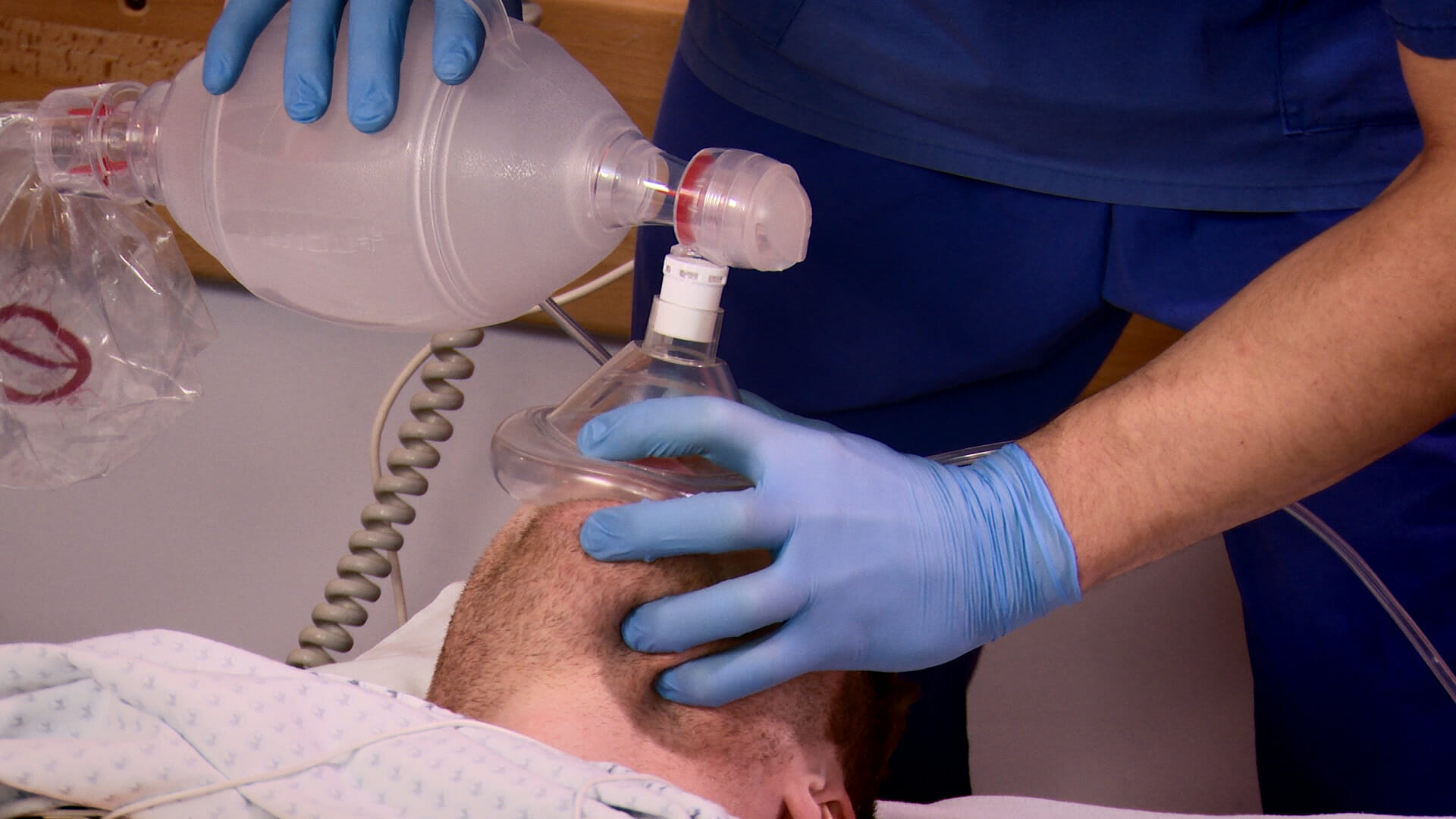
Bag-mask ventilation
Image by Lecturio.