Cell-mediated immunity Cell-mediated immunity Manifestations of the immune response which are mediated by antigen-sensitized T-lymphocytes via lymphokines or direct cytotoxicity. This takes place in the absence of circulating antibody or where antibody plays a subordinate role. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) is an integral part of the adaptive immune system Immune system The body's defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs, mounting a highly specific defense against pathogens. Cell-mediated immunity Cell-mediated immunity Manifestations of the immune response which are mediated by antigen-sensitized T-lymphocytes via lymphokines or direct cytotoxicity. This takes place in the absence of circulating antibody or where antibody plays a subordinate role. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) develops over a longer period of time than innate immunity Innate immunity The capacity of a normal organism to remain unaffected by microorganisms and their toxins. It results from the presence of naturally occurring anti-infective agents, constitutional factors such as body temperature and immediate acting immune cells such as natural killer cells. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation. Cell-mediated adaptive response occurs in cells/tissues (intracellular infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease or aberrant cells (e.g., tumors)) and involves the T cells T cells Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified - cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions or T lymphocytes T lymphocytes Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified - cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions. The cells, which arise from bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis, migrate to the thymus Thymus A single, unpaired primary lymphoid organ situated in the mediastinum, extending superiorly into the neck to the lower edge of the thyroid gland and inferiorly to the fourth costal cartilage. It is necessary for normal development of immunologic function early in life. By puberty, it begins to involute and much of the tissue is replaced by fat. Lymphatic Drainage System: Anatomy for further maturation. A T cell receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors is assembled and activation is facilitated by antigen-presenting cells Antigen-presenting cells A heterogeneous group of immunocompetent cells that mediate the cellular immune response by processing and presenting antigens to the T-cells. Traditional antigen-presenting cells include macrophages; dendritic cells; langerhans cells; and B-lymphocytes. Follicular dendritic cells are not traditional antigen-presenting cells, but because they hold antigen on their cell surface in the form of immune complexes for b-cell recognition they are considered so by some authors. Adaptive Immune Response in secondary lymphoid organs Lymphoid organs A system of organs and tissues that process and transport immune cells and lymph. Primary Lymphatic Organs. Influenced by cytokines Cytokines Non-antibody proteins secreted by inflammatory leukocytes and some non-leukocytic cells, that act as intercellular mediators. They differ from classical hormones in that they are produced by a number of tissue or cell types rather than by specialized glands. They generally act locally in a paracrine or autocrine rather than endocrine manner. Adaptive Immune Response, activated T cells T cells Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified - cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions can differentiate into subsets (e.g., CD4+ T helper cells, CD8+ cytotoxic Cytotoxic Parvovirus B19 T cells T cells Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified - cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions, memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment T cells T cells Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified - cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions). T helper cells aid in the eradication of pathogens by helping the partners of immune cells (e.g., macrophages Macrophages The relatively long-lived phagocytic cell of mammalian tissues that are derived from blood monocytes. Main types are peritoneal macrophages; alveolar macrophages; histiocytes; kupffer cells of the liver; and osteoclasts. They may further differentiate within chronic inflammatory lesions to epithelioid cells or may fuse to form foreign body giant cells or langhans giant cells. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation and granulocytes Granulocytes Leukocytes with abundant granules in the cytoplasm. They are divided into three groups according to the staining properties of the granules: neutrophilic, eosinophilic, and basophilic. Mature granulocytes are the neutrophils; eosinophils; and basophils. White Myeloid Cells: Histology). With mechanisms activating the caspase pathway, cytotoxic Cytotoxic Parvovirus B19 T cells T cells Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified - cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions have the capacity to kill microbes. Memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment T cells T cells Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified - cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions develop after initial exposure to the antigen Antigen Substances that are recognized by the immune system and induce an immune reaction. Vaccination and become effector T cells T cells Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified - cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions on reinfection. T cells T cells Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified - cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions also activate B cells B cells Lymphoid cells concerned with humoral immunity. They are short-lived cells resembling bursa-derived lymphocytes of birds in their production of immunoglobulin upon appropriate stimulation. B cells: Types and Functions (a major component in humoral immunity), which enhance the ability to eliminate pathogens.
Last updated: Sep 8, 2022
The immune system Immune system The body’s defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs provides defense (immunity) against invading pathogens ranging from viruses Viruses Minute infectious agents whose genomes are composed of DNA or RNA, but not both. They are characterized by a lack of independent metabolism and the inability to replicate outside living host cells. Virology to parasites. Components are interconnected by blood and the lymphatic circulation Circulation The movement of the blood as it is pumped through the cardiovascular system. ABCDE Assessment.
Two lines of overlapping defense:
| Innate immunity Innate immunity The capacity of a normal organism to remain unaffected by microorganisms and their toxins. It results from the presence of naturally occurring anti-infective agents, constitutional factors such as body temperature and immediate acting immune cells such as natural killer cells. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation | Adaptive immunity | |
|---|---|---|
| Genetics Genetics Genetics is the study of genes and their functions and behaviors. Basic Terms of Genetics | Germline encoded | Gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics rearrangements involved in lymphocyte development |
| Immune response | Nonspecific | Highly specific |
| Timing of response | Immediate (minutes to hours) | Develops over a longer period of time |
| Memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment response | None | Responds quickly upon recognition of antigen Antigen Substances that are recognized by the immune system and induce an immune reaction. Vaccination with memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment response |
| Recognition of pathogen | Pattern recognition receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors (PRRs) such as toll-like receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors (TLRs) recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns Sepsis and Septic Shock ( PAMPs PAMPs Sepsis and Septic Shock) |
|
| Components |
|
|
Responding to microbial invaders is the responsibility of the immune system Immune system The body’s defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs. Often the innate immune system Immune system The body’s defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs has the capability to contain the pathogens, but invaders may evolve to evade innate immunity Innate immunity The capacity of a normal organism to remain unaffected by microorganisms and their toxins. It results from the presence of naturally occurring anti-infective agents, constitutional factors such as body temperature and immediate acting immune cells such as natural killer cells. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation. The next line of defense is the adaptive immune system Immune system The body’s defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs.
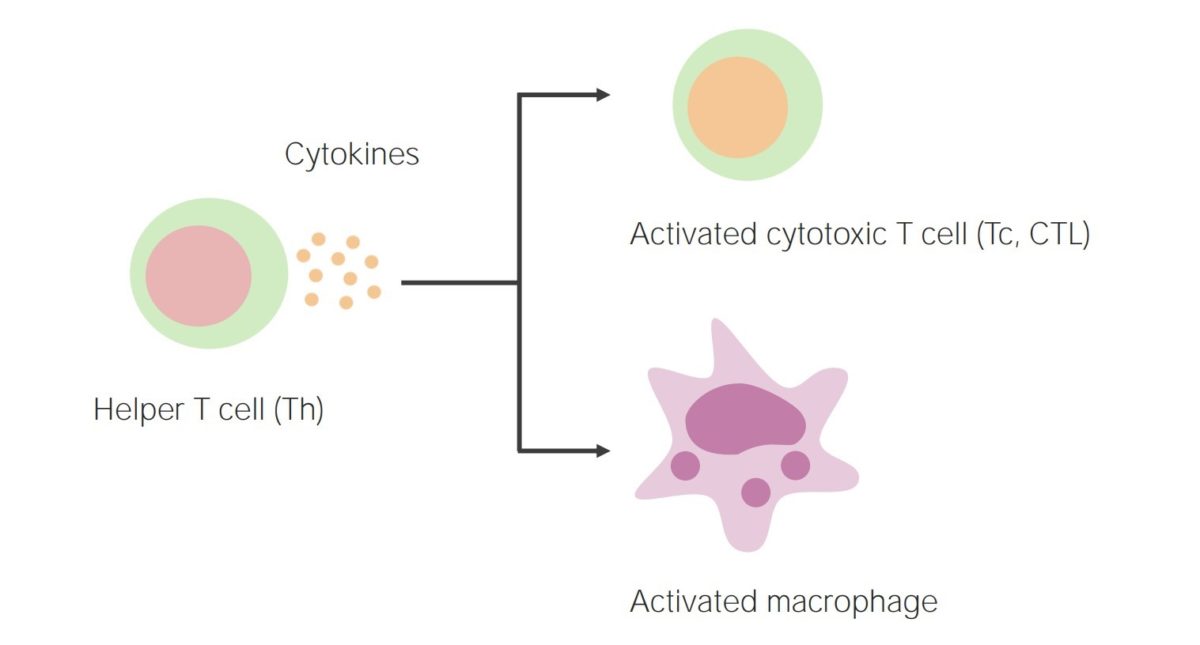
Cell-mediated immunity:
Activation of helper T cells results in the release of cytokines, thereby activating cytotoxic T cells and phagocytes (such as macrophages).
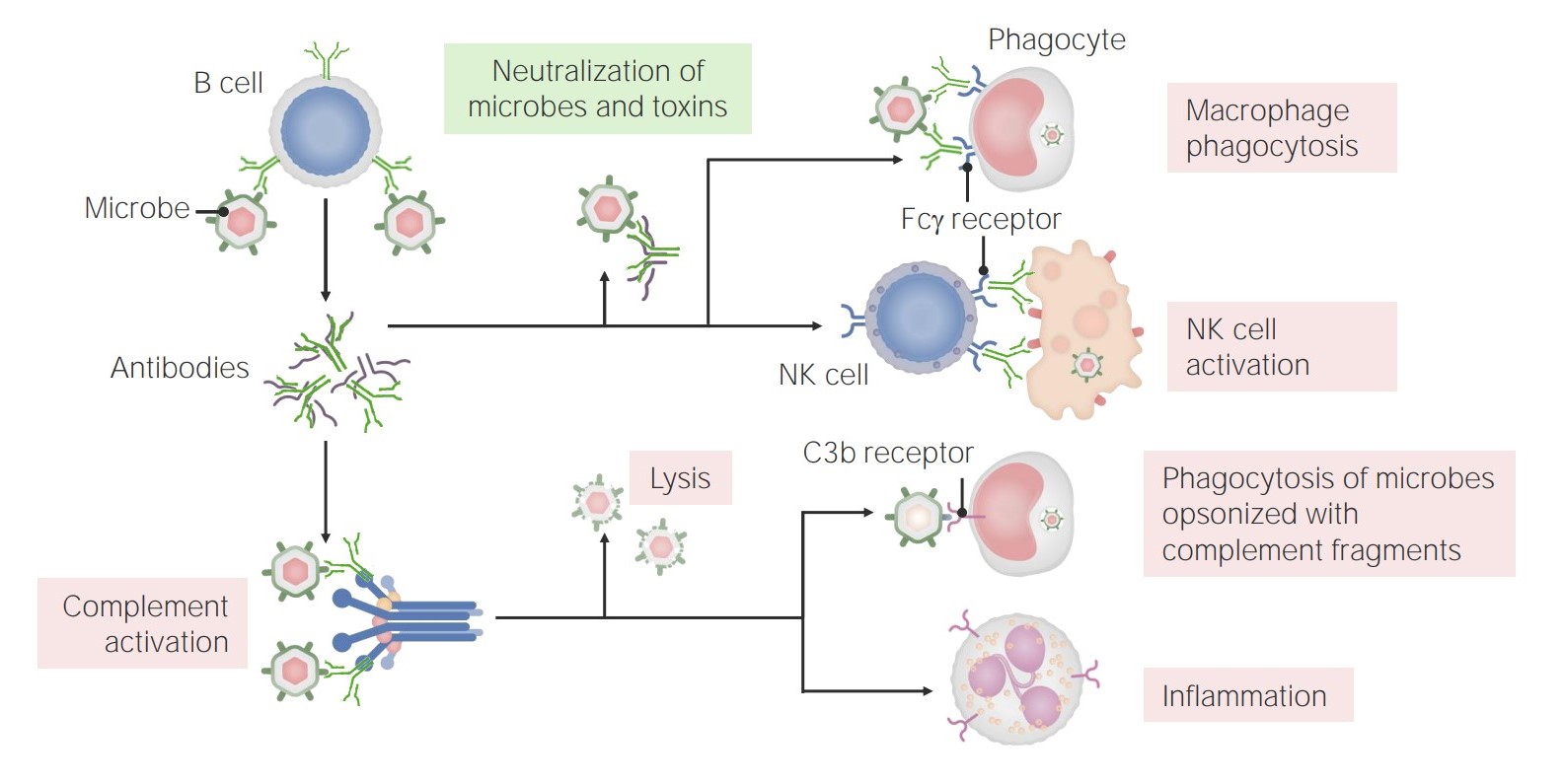
The functions of antibodies:
Antibodies have multiple roles in immunity, including neutralization (of microbes and toxins), promotion of phagocytosis, and NK cell activation. In addition, antibodies have a role in complement activation, which can lead to direct microbe lysis, opsonization and phagocytosis, and recruitment/activation of neutrophils.
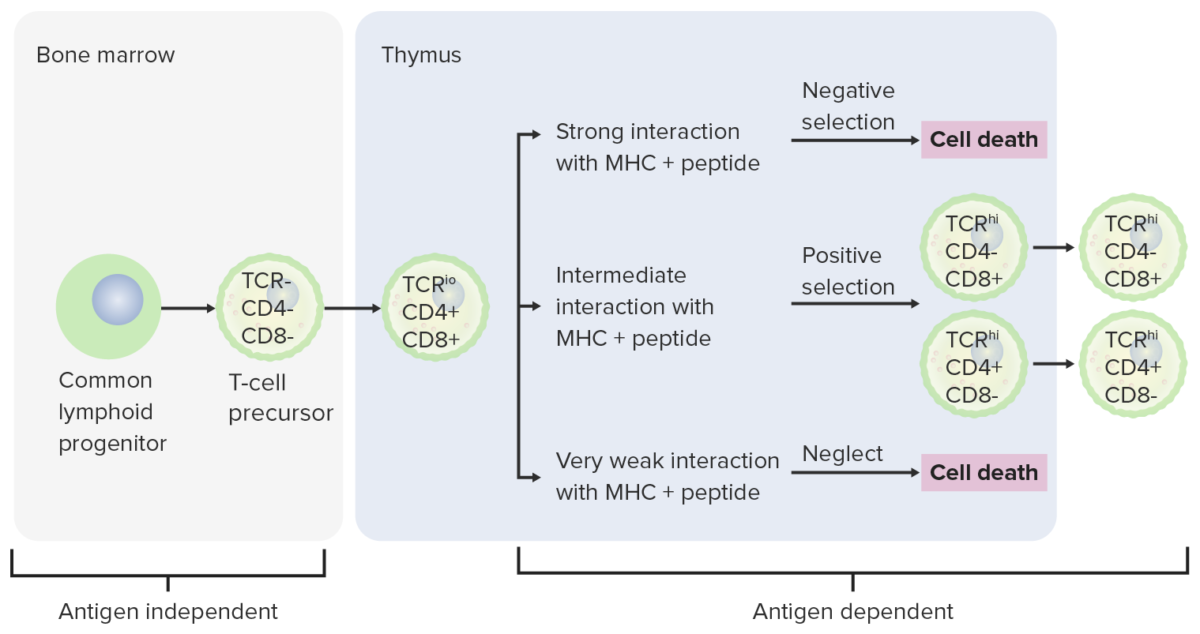
Differentiation stages of T cell:
From the bone marrow, progenitor cells go to the thymus for further maturation. The DN cells (no expression of CD4/CD8 or CD4–/CD8–) have not developed the TCR. The DN cells undergo rearrangement of the TCR gene and become pro-T cells, then pre-T cells. Through the series, CD4 and CD8 are expressed, and the TCR becomes assembled through gene rearrangements (DP cells). The thymus then presents MHC molecules to the developing T cells. Some cells undergo positive selection (intermediate interaction between MHC and TCR takes place) and produce functional cells. Some cells undergo negative selection (strong interaction between MHC and TCR), which results in cell death. The release of dysfunctional T cells, which can activate autoimmunity, is prevented. Some T cells fail to interact, leading to apoptosis. Mature T cells express either CD4 (T helper cells) or CD8 (cytotoxic T cells), not both.
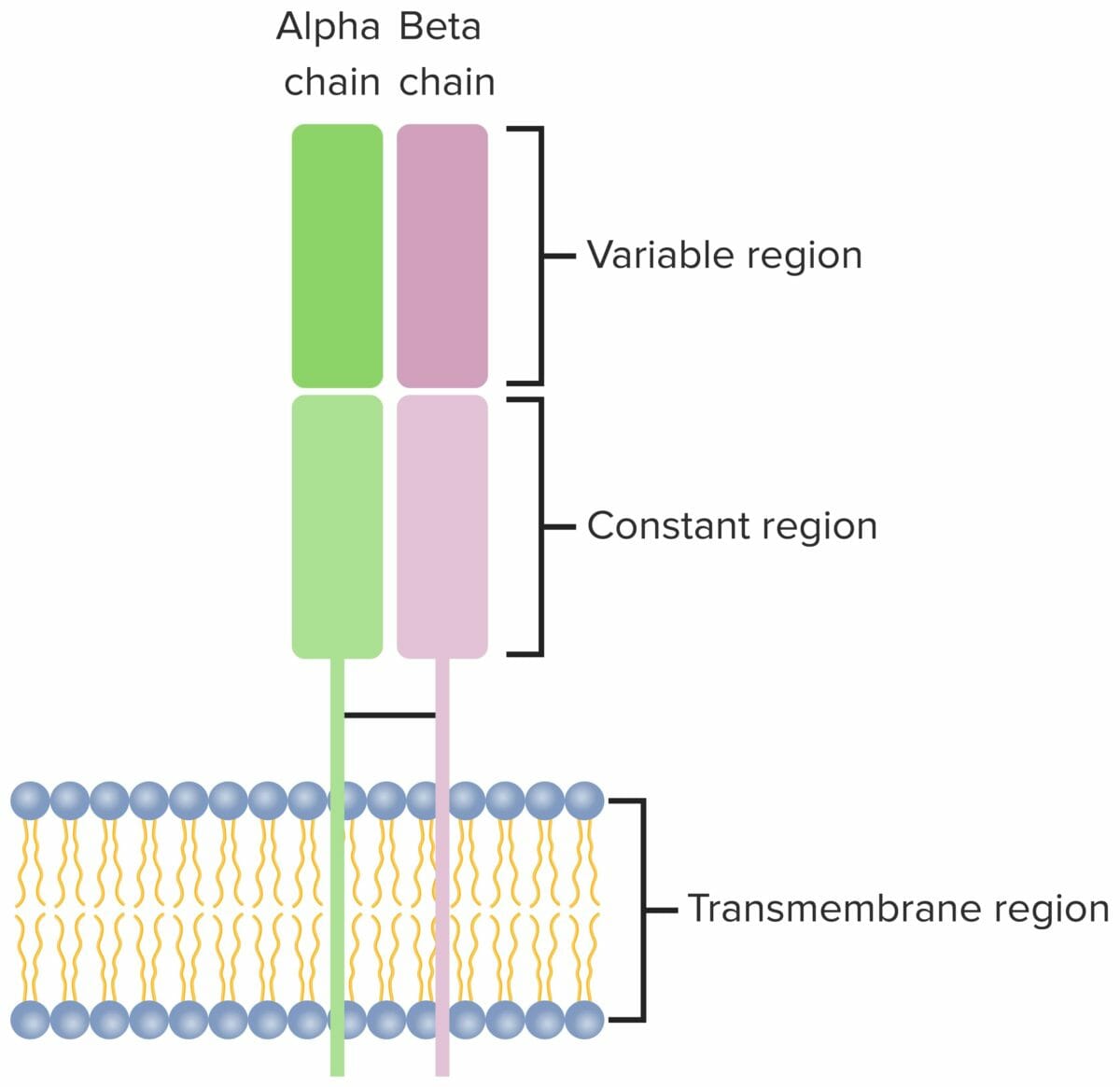
T cell receptor:
Heterodimer that consists of 2 transmembrane polypeptide chains, with α and β chains found in the majority of T cells. Both chains have a variable, constant, transmembrane and a short cytoplasmic region.
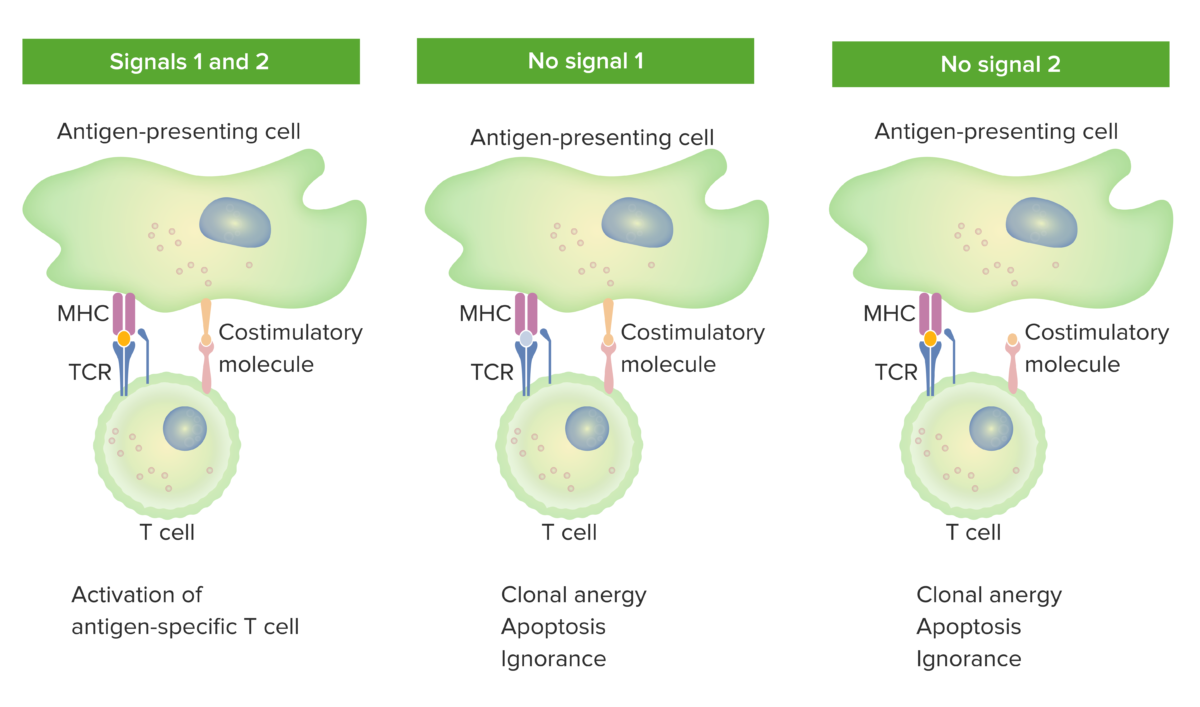
2-signal model of T-cell dependence on costimulation:
When both signal 1 (TCR binding the cognate antigen presented by the MHC molecule in the antigen-presenting cell) and signal 2 (costimulatory molecule interaction between the antigen-presenting cell and the T cell) are present, the mature T cell is fully activated.
The orange spot in the left panel indicates proper binding between antigen and TCR. However, when either signal 1 (middle image shows no antigen and TCR binding) or signal 2 (right image shows no costimulation) is missing, the T cell will not be fully activated.
Outcomes would be anergy (state of unresponsiveness), apoptosis (cell death), or ignorance (T cell does not notice or does not get affected by the antigen).
TCR: T-cell receptor
| CD4+ T cells T cells Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified – cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions | Stimulated by | Cytokines Cytokines Non-antibody proteins secreted by inflammatory leukocytes and some non-leukocytic cells, that act as intercellular mediators. They differ from classical hormones in that they are produced by a number of tissue or cell types rather than by specialized glands. They generally act locally in a paracrine or autocrine rather than endocrine manner. Adaptive Immune Response produced | Functions | Role in disease |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th1 Th1 A subset of helper-inducer T-lymphocytes which synthesize and secrete interleukin-2; interferon-gamma; and interleukin-12. Due to their ability to kill antigen-presenting cells and their lymphokine-mediated effector activity, th1 cells are associated with vigorous delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. T cells: Types and Functions | IL-12, IFN-γ | IFN-γ, TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF), IL-2 |
|
|
| Th2 Th2 A subset of helper-inducer T-lymphocytes which synthesize and secrete the interleukins il-4; il-5; il-6; and il-10. These cytokines influence b-cell development and antibody production as well as augmenting humoral responses. T cells: Types and Functions | IL-2, IL-4 | IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-9, IL-10, IL-13 |
|
|
| Th17 Th17 A subset of helper-effector T-lymphocytes which synthesize and secrete interleukins il-17; il-17f; and il-22. These cytokines are involved in host defenses and tissue inflammation in autoimmune diseases. T cells: Types and Functions | IL-1, IL-6, IL-23, TGF-β | IL-17, IL-21, IL-22 | Promote neutrophilic inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation |
|
| Tfh | IL-6 | IL-4, IL-21 | Facilitate B cell activation B cell activation Humoral Adaptive Immunity and maturation | Antibody production |
| Treg | TGF-β, IL-2 | TGF-β, IL-10, IL-35 |
|
↓ Autoimmunity Autoimmunity Autoimmunity is a pathologic immune response toward self-antigens, resulting from a combination of factors: immunologic, genetic, and environmental. The immune system is equipped with self-tolerance, allowing immune cells such as T cells and B cells to recognize self-antigens and to not mount a reaction against them. Defects in this mechanism, along with environmental triggers (such as infections) and genetic susceptibility factors (most notable of which are the HLA genes) can lead to autoimmune diseases. Autoimmunity, allergy Allergy An abnormal adaptive immune response that may or may not involve antigen-specific IgE Type I Hypersensitivity Reaction, inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation |
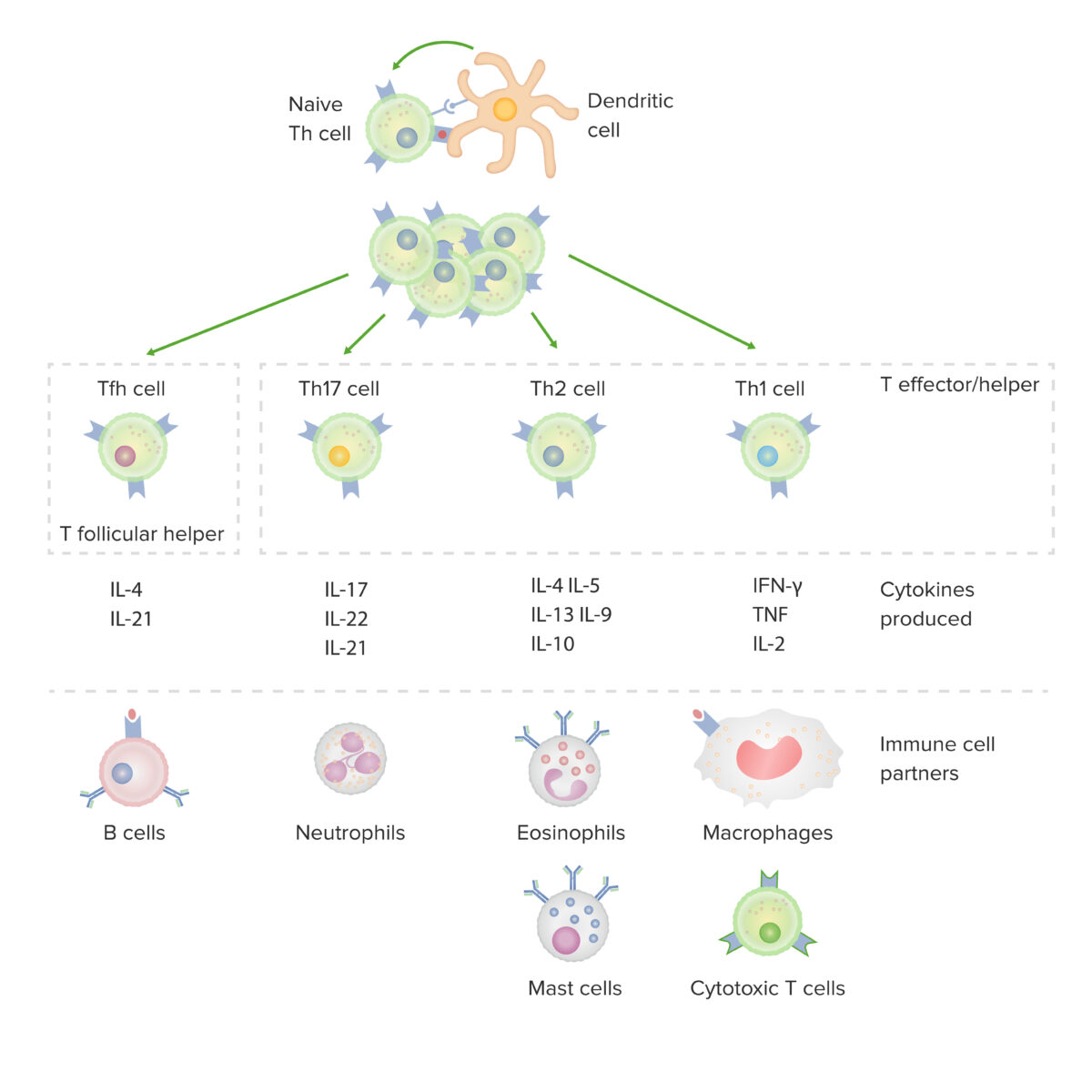
Subsets of CD4-positive helper T cells:
After activation by a dendritic cell, in the presence of particular cytokines, a naive CD4-positive T cell divides and differentiates into effector/helper (Th1, Th2 or Th17) or follicular helper (Tfh) subsets. Each type of cell produces cytokines that facilitate activation of other immune-cell partners.
IFN: interferon
TNF: tumor necrosis factor
| Cytokine | Function and activity |
|---|---|
| IL-2 |
|
| IL-4 |
|
| IL-5 |
|
| IL-10 |
|
| IL-13 |
|
| IL-17 | Inflammatory cytokine release Release Release of a virus from the host cell following virus assembly and maturation. Egress can occur by host cell lysis, exocytosis, or budding through the plasma membrane. Virology (including IL-6, IL-1, TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF), which mediate fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever and sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock) |
| IL-21 | B cell and T cell differentiation |
| IL-22 |
|
| IFN-ɣ |
|
| TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) |
|
| Cytokine inhibition | Drug name | Conditions treated |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-TNF |
|
|
| Anti-interleukin-1 | Anakinra Anakinra Immunosuppressants | Rheumatoid arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis |
| Anti-interleukin-1b | Canakinumab Canakinumab Immunosuppressants |
|
| Anti-interleukin-6 | Tocilizumab Tocilizumab Immunosuppressants |
|
| Therapeutic cytokine | Conditions treated |
|---|---|
| Interferon-α |
|
| Interferon-β | Multiple sclerosis Sclerosis A pathological process consisting of hardening or fibrosis of an anatomical structure, often a vessel or a nerve. Wilms Tumor |
| Interferon-γ |
|
| Interleukin-2 Interleukin-2 A soluble substance elaborated by antigen- or mitogen-stimulated T-lymphocytes which induces DNA synthesis in naive lymphocytes. Interleukins |
|