Acute otitis media is an infection in the middle ear characterized by mucosal inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation and retention of fluid. The most common pathogens are Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae Haemophilus Influenzae A species of Haemophilus found on the mucous membranes of humans and a variety of animals. The species is further divided into biotypes I through viii. Haemophilus, and Moraxella catarrhalis Moraxella catarrhalis Gram-negative aerobic cocci of low virulence that colonize the nasopharynx and occasionally cause meningitis; bacteremia; empyema; pericarditis; and pneumonia. Moraxella. The condition can present with fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, otalgia, and diminished hearing. Diagnosis is made by history and otoscopic exam showing a bulging tympanic membrane Tympanic membrane An oval semitransparent membrane separating the external ear canal from the tympanic cavity. It contains three layers: the skin of the external ear canal; the core of radially and circularly arranged collagen fibers; and the mucosa of the middle ear. Ear: Anatomy with reduced mobility. Observation or antibiotics are the usual management approaches, but surgery for tympanostomy tubes may be required if there are recurrent infections Recurrent infections Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID). Potential complications include hearing loss Hearing loss Hearing loss, also known as hearing impairment, is any degree of impairment in the ability to apprehend sound as determined by audiometry to be below normal hearing thresholds. Clinical presentation may occur at birth or as a gradual loss of hearing with age, including a short-term or sudden loss at any point. Hearing Loss, tympanic membrane Tympanic membrane An oval semitransparent membrane separating the external ear canal from the tympanic cavity. It contains three layers: the skin of the external ear canal; the core of radially and circularly arranged collagen fibers; and the mucosa of the middle ear. Ear: Anatomy perforation Perforation A pathological hole in an organ, blood vessel or other soft part of the body, occurring in the absence of external force. Esophagitis, and mastoiditis Mastoiditis Inflammation of the honeycomb-like mastoid bone in the skull just behind the ear. It is usually a complication of otitis media. Mumps Virus/Mumps.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Acute otitis media is an infection characterized by the accumulation of fluid and inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation within the middle ear.
Acute otitis media is an inflammatory condition of the middle ear with an infectious etiology that may be bacterial (most common) or viral. Causes include:
Bacterial:
Viral:
The middle ear is lined with respiratory mucosa, and the cascade of events affecting adjacent areas is usually reflected in similar changes in the ear.
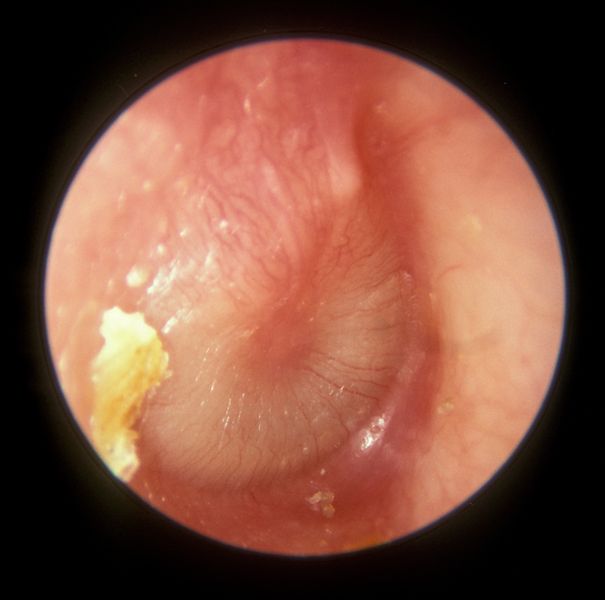
Endoscopic view of early otitis media of the left middle ear:
The typical aspect of beginning radial vascular drawing, injection of the vessels of the malleus handle, effusion with reddening and beginning protrusion of the tympanic membrane, as well as cloudiness of the surface of the eardrum are found.
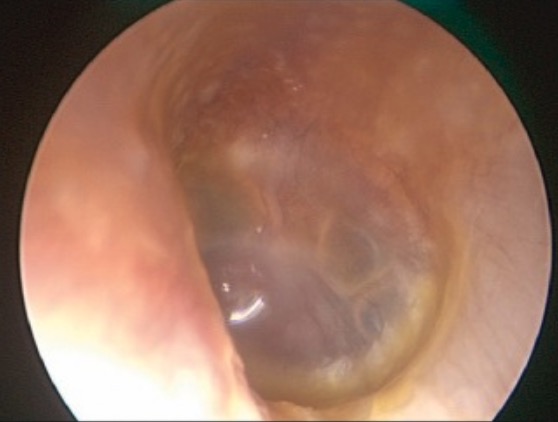
Endoscopic view of acute otitis media:
The middle ear is filled with a creamy-white mucopurulent exudate, which is causing the tympanic membrane to bulge laterally. Note the dilatation of the radial blood vessels of the tympanic membrane, which appear like the “spokes of a wheel.”
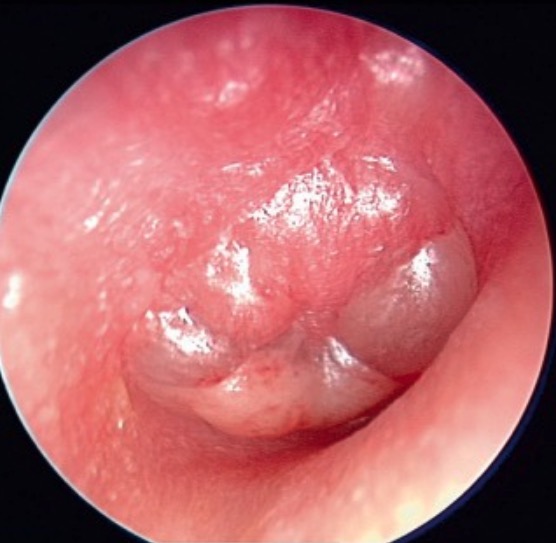
Endoscopic view of an advanced acute otitis media of the right middle ear:
Severe inflammatory reaction and protrusion of the eardrum are found.
The diagnosis of acute otitis media is primarily based on clinical presentation and otoscopic exam. No lab tests or imaging are needed unless there are special circumstances.
Observation:
Pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways control:
Antibiotics:
Two types of complications can occur.
Intratemporal complications:
Intracranial complications: