Acute bronchiolitis Bronchiolitis Inflammation of the bronchioles. Pediatric Chest Abnormalities is primarily a pediatric respiratory condition caused by inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation of the bronchioles Bronchioles The small airways branching off the tertiary bronchi. Terminal bronchioles lead into several orders of respiratory bronchioles which in turn lead into alveolar ducts and then into pulmonary alveoli. Bronchial Tree: Anatomy in response to a viral infection. The condition is a common cause of hospitalization Hospitalization The confinement of a patient in a hospital. Delirium in children in the United States, with the majority of cases caused by respiratory syncytial virus Respiratory Syncytial Virus Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is an enveloped, single-stranded, linear, negative-sense RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae and the genus Orthopneumovirus. Two subtypes (A and B) are present in outbreaks, but type A causes more severe disease. Respiratory syncytial virus causes infections of the lungs and respiratory tract. Respiratory Syncytial Virus ( RSV RSV Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is an enveloped, single-stranded, linear, negative-sense RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae and the genus Orthopneumovirus. Two subtypes (A and B) are present in outbreaks, but type A causes more severe disease. Respiratory syncytial virus causes infections of the lungs and respiratory tract. Respiratory Syncytial Virus). Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship usually present with upper respiratory symptoms, such as cough and congestion, and later develop lower respiratory signs, including dyspnea Dyspnea Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea, wheezing Wheezing Wheezing is an abnormal breath sound characterized by a whistling noise that can be relatively high-pitched and shrill (more common) or coarse. Wheezing is produced by the movement of air through narrowed or compressed small (intrathoracic) airways. Wheezing, crackles, and hypoxia Hypoxia Sub-optimal oxygen levels in the ambient air of living organisms. Ischemic Cell Damage, for up to 10 days. Diagnosis is clinical and treatment is directed at improving oxygenation and hydration. As the disease course is self-limiting Self-Limiting Meningitis in Children, acute bronchiolitis Bronchiolitis Inflammation of the bronchioles. Pediatric Chest Abnormalities has good prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas with appropriate management.
Last updated: Jan 24, 2025
Acute bronchiolitis Bronchiolitis Inflammation of the bronchioles. Pediatric Chest Abnormalities is a clinical constellation of respiratory symptoms (increased work of breathing Work of breathing Respiratory muscle contraction during inhalation. The work is accomplished in three phases: lung compliance work, that required to expand the lungs against its elastic forces; tissue resistance work, that required to overcome the viscosity of the lung and chest wall structures; and airway resistance work, that required to overcome airway resistance during the movement of air into the lungs. Work of breathing does not refer to expiration, which is entirely a passive process caused by elastic recoil of the lung and chest cage. Pulmonary Examination, wheezing Wheezing Wheezing is an abnormal breath sound characterized by a whistling noise that can be relatively high-pitched and shrill (more common) or coarse. Wheezing is produced by the movement of air through narrowed or compressed small (intrathoracic) airways. Wheezing, and crackles) caused by acute inflammation Acute Inflammation Inflammation of the small airways (small bronchi Bronchi The larger air passages of the lungs arising from the terminal bifurcation of the trachea. They include the largest two primary bronchi which branch out into secondary bronchi, and tertiary bronchi which extend into bronchioles and pulmonary alveoli. Bronchial Tree: Anatomy and bronchioles Bronchioles The small airways branching off the tertiary bronchi. Terminal bronchioles lead into several orders of respiratory bronchioles which in turn lead into alveolar ducts and then into pulmonary alveoli. Bronchial Tree: Anatomy), typically secondary to viral infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease.
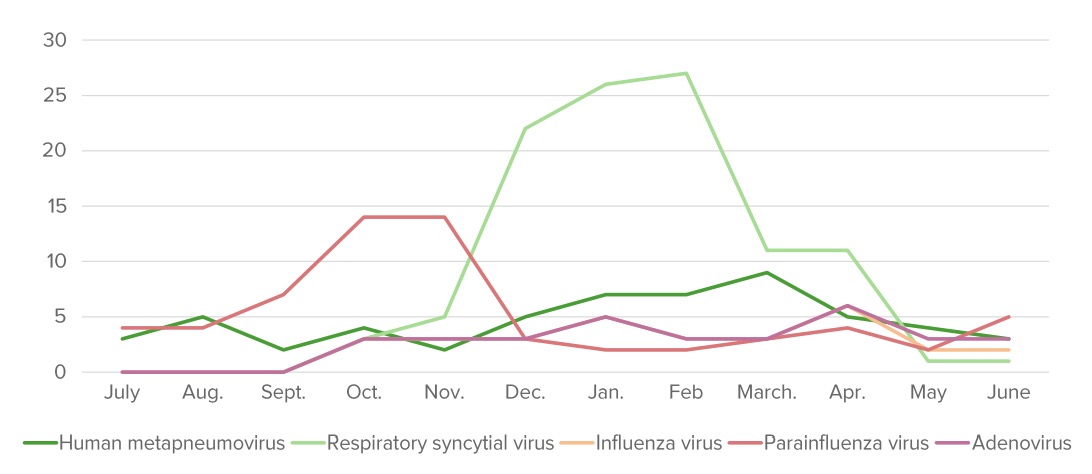
The annual distribution (%) of pathogens that cause bronchiolitis. “Bronchiolitis season” starts around October and finishes around May in the Northern Hemisphere.
Image by Lecturio.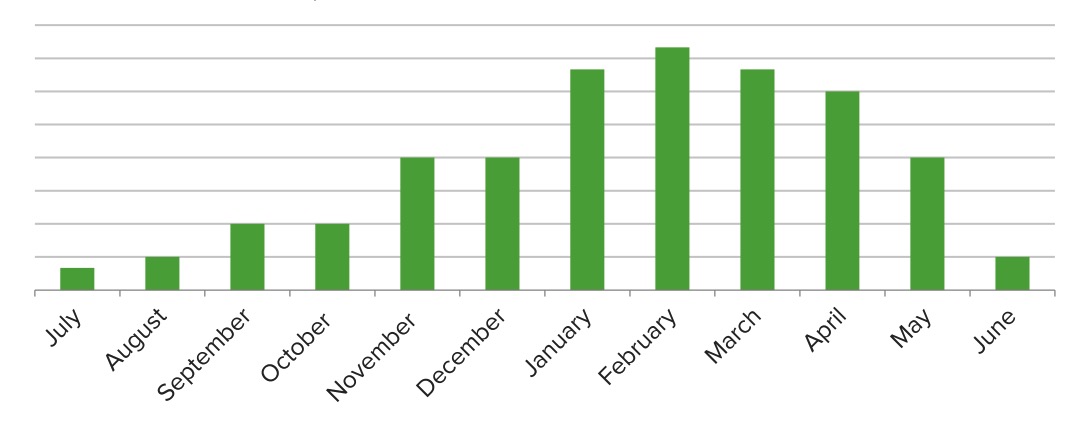
Seasonal variations in the number of cases that can be attributed to the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV): At its peak, RSV accounts for about 1/3 of bronchiolitis cases.
Image by Lecturio.Pathologic changes are noted within 24 hours of contact with a pathogen:
Symptoms are on a spectrum based on the severity of the disease:
Management depends on severity: