Actinic keratosis (AK) is a precancerous Precancerous Pathological conditions that tend eventually to become malignant. Barrett Esophagus skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions lesion that affects sun-exposed areas. The condition presents as small, non-tender macules/papules with a characteristic sandpaper-like texture Texture Dermatologic Examination that can become erythematous scaly plaques. Actinic keratosis is usually diagnosed clinically but suspicious features warrant a biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma to rule out invasive squamous cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) is caused by malignant proliferation of atypical keratinocytes. This condition is the 2nd most common skin malignancy and usually affects sun-exposed areas of fair-skinned patients. The cancer presents as a firm, erythematous, keratotic plaque or papule. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC). The majority of AK lesions remain non-malignant, but it is difficult to distinguish those that will resolve from those that will become cancerous. Actinic keratosis has multiple types of treatment, including cryotherapy Cryotherapy A form of therapy consisting in the local or general use of cold. The selective destruction of tissue by extreme cold or freezing is cryosurgery. Chondrosarcoma, shave removal, excision, topical medications, and photodynamic therapy. Lesions with features that are suggestive of cancer warrant removal and pathologic evaluation.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
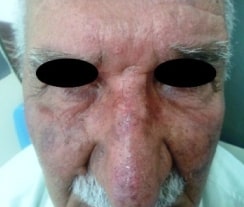
Large actinic keratoses on the nose.
Image: “Large AKs on the nose of a participant in the colchicine group” by Advances in Medicine. License: CC BY 4.0, edited by Lecturio.
Patient with albinism showing actinic keratoses lesions over the chest.
Image: “Albino showing actinic keratoses lesions over the chest” by Ramalingam VS, Sinnakirouchenan R, Thappa DM – Indian journal of dermatology (2009). License: CC BY 2.0.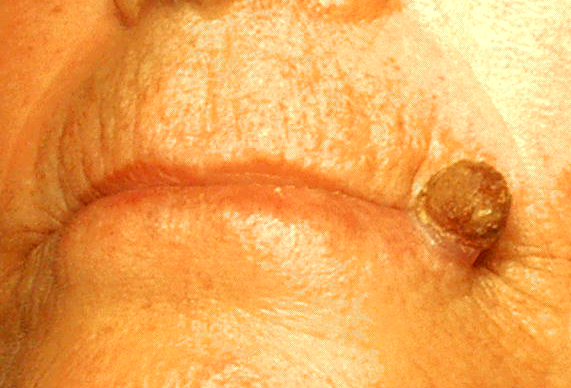
Actinic keratosis on the lip (actinic cheilitis) with a cutaneous horn.
Image: “Actinic keratosis on the lip ” by Eray Copcu1, Nazan Sivrioglu1m and Nil Culhaci. License: Public DomainDiagnosis is usually made clinically by inspection Inspection Dermatologic Examination and palpation Palpation Application of fingers with light pressure to the surface of the body to determine consistency of parts beneath in physical diagnosis; includes palpation for determining the outlines of organs. Dermatologic Examination.
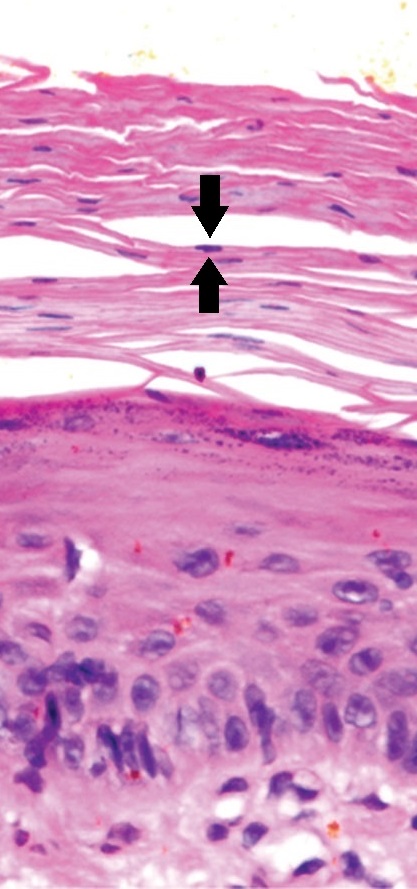
Actinic keratosis with atypical keratinocytes confined to the lower 3rd of the epidermis. There is parakeratosis, as indicated by black arrows pointing to 1 of the multiple retained nuclei in the stratum corneum.
Image: “Example of an early actinic keratosis with keratinocyte dysplasia confined to the lower third of the epidermis” by Mikael Häggström, M.D.. License: CC BY 4.0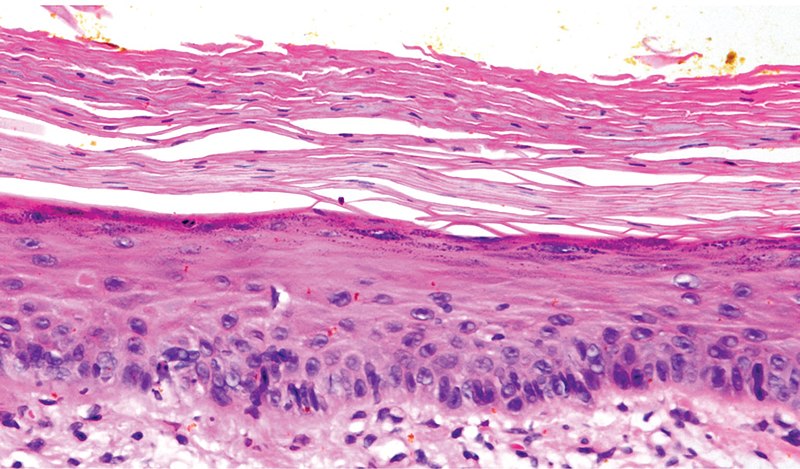
Example of an early actinic keratosis with keratinocyte dysplasia confined to the lower 3rd of the epidermis.
Image: “Micrograph of early actinic keratosis” by Valerie R. Yanofsky, Stephen E.Mercer, and Robert G. Phelps. License: CC BY 4.0Prevention consists of the use of sunscreen Sunscreen Chemical or physical agents that protect the skin from sunburn and erythema by absorbing or blocking ultraviolet radiation. Melanoma and sun protection.