Acoustic neuroma, also referred to as vestibular schwannoma Schwannoma Schwannomas (also known as neurilemmomas) are benign nerve sheath tumors in the peripheral nervous system (PNS), arising from Schwann cells that encase the peripheral nerves. Schwannomas are the most common tumors in the PNS. Schwannoma, is a benign Benign Fibroadenoma tumor Tumor Inflammation arising from Schwann cells of the vestibular component of the cranial nerve VIII. Acoustic neuroma forms within the internal auditory meatus and extends into the cerebellopontine angle. Vestibular schwannoma Schwannoma Schwannomas (also known as neurilemmomas) are benign nerve sheath tumors in the peripheral nervous system (PNS), arising from Schwann cells that encase the peripheral nerves. Schwannomas are the most common tumors in the PNS. Schwannoma is mostly unilateral. Bilateral vestibular schwannomas Vestibular schwannomas A benign schwannoma of the eighth cranial nerve (vestibulocochlear nerve), mostly arising from the vestibular branch (vestibular nerve) during the fifth or sixth decade of life. Clinical manifestations include hearing loss; headache; vertigo; tinnitus; and facial pain. Bilateral acoustic neuromas are associated with neurofibromatosis 2. Neurofibromatosis Type 2 are associated with neurofibromatosis type II. Symptoms arise due to compression Compression Blunt Chest Trauma of the cranial nerves Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves (CNs), which run from the brain to various parts of the head, neck, and trunk. The CNs can be sensory or motor or both. The CNs are named and numbered in Roman numerals according to their location, from the front to the back of the brain. The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions V, VII, and VIII, and the cerebellum Cerebellum The cerebellum, Latin for "little brain," is located in the posterior cranial fossa, dorsal to the pons and midbrain, and its principal role is in the coordination of movements. The cerebellum consists of 3 lobes on either side of its 2 hemispheres and is connected in the middle by the vermis. Cerebellum: Anatomy. The most common complaint is unilateral hearing loss Unilateral hearing loss Partial or complete hearing loss in one ear. Hearing Loss but acoustic neuroma can also present with vertigo Vertigo Vertigo is defined as the perceived sensation of rotational motion while remaining still. A very common complaint in primary care and the ER, vertigo is more frequently experienced by women and its prevalence increases with age. Vertigo is classified into peripheral or central based on its etiology. Vertigo, decreased facial sensation, Bell palsy Palsy paralysis of an area of the body, thus incapable of voluntary movement Cranial Nerve Palsies, and ataxia Ataxia Impairment of the ability to perform smoothly coordinated voluntary movements. This condition may affect the limbs, trunk, eyes, pharynx, larynx, and other structures. Ataxia may result from impaired sensory or motor function. Sensory ataxia may result from posterior column injury or peripheral nerve diseases. Motor ataxia may be associated with cerebellar diseases; cerebral cortex diseases; thalamic diseases; basal ganglia diseases; injury to the red nucleus; and other conditions. Ataxia-telangiectasia. Diagnosis of vestibular schwannoma Schwannoma Schwannomas (also known as neurilemmomas) are benign nerve sheath tumors in the peripheral nervous system (PNS), arising from Schwann cells that encase the peripheral nerves. Schwannomas are the most common tumors in the PNS. Schwannoma is made with an MRI of the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification with contrast. Treatment depends on the size of the tumor Tumor Inflammation and symptom severity. Large tumors with severe hearing loss Hearing loss Hearing loss, also known as hearing impairment, is any degree of impairment in the ability to apprehend sound as determined by audiometry to be below normal hearing thresholds. Clinical presentation may occur at birth or as a gradual loss of hearing with age, including a short-term or sudden loss at any point. Hearing Loss are treated with surgical excision or radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma therapy, while small tumors with mild symptoms can be observed over time.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
An acoustic neuroma is a benign Benign Fibroadenoma tumor Tumor Inflammation of Schwann cells that is most commonly found on cranial nerve VIII ( vestibulocochlear nerve Vestibulocochlear nerve The 8th cranial nerve. The vestibulocochlear nerve has a cochlear part (cochlear nerve) which is concerned with hearing and a vestibular part (vestibular nerve) which mediates the sense of balance and head position. The fibers of the cochlear nerve originate from neurons of the spiral ganglion and project to the cochlear nuclei (cochlear nucleus). The fibers of the vestibular nerve arise from neurons of scarpa’s ganglion and project to the vestibular nuclei. The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions).
| Categories | Specific tumors |
|---|---|
| Neuroepithelial tumors in the CNS |
|
| Meningeal tumors |
|
| Sellar region tumors |
|
| Primary CNS lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum | Primary CNS lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum |
| Metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis to the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification (5x more common than primary brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification tumors) | Most commonly arising from: |
| Peripheral tumors |
|
Symptoms of acoustic neuroma are divided into early and late phases.
Tumor Tumor Inflammation expansion in the internal auditory meatus exerting pressure on vestibulocochlear nerve Vestibulocochlear nerve The 8th cranial nerve. The vestibulocochlear nerve has a cochlear part (cochlear nerve) which is concerned with hearing and a vestibular part (vestibular nerve) which mediates the sense of balance and head position. The fibers of the cochlear nerve originate from neurons of the spiral ganglion and project to the cochlear nuclei (cochlear nucleus). The fibers of the vestibular nerve arise from neurons of scarpa’s ganglion and project to the vestibular nuclei. The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions (CN VIII):
Compression Compression Blunt Chest Trauma of adjacent structures in the cerebellopontine angle:
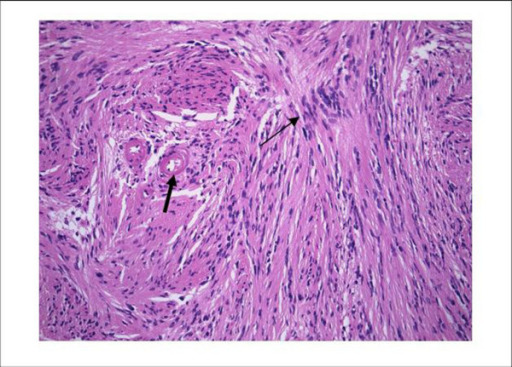
Schwannoma histology:
Low-power view of schwannoma illustrating the nuclear palisading (thin arrow) and the hyaline vessel walls (thick arrow). H&E stain ×300
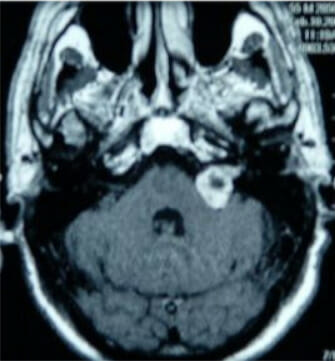
Gadolinium contrast MRI showing an acoustic neuroma of the left cerebellopontine angle
Image: “Figure 1” by Sean P Collins et al. License: CC BY 2.0Serial monitoring: