Acne vulgaris, also known as acne, is a common disorder of the pilosebaceous units Pilosebaceous Units Hidradenitis Suppurativa in adolescents and young adults. The condition occurs due to follicular hyperkeratinization, excess sebum Sebum The oily substance secreted by sebaceous glands. It is composed of keratin, fat, and cellular debris. Infectious Folliculitis production, follicular colonization Colonization Bacteriology by Cutibacterium acnes, and inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation. Acne can present as open or closed comedones, papules, pustules, nodules, or cysts Cysts Any fluid-filled closed cavity or sac that is lined by an epithelium. Cysts can be of normal, abnormal, non-neoplastic, or neoplastic tissues. Fibrocystic Change. The diagnosis is based on clinical exam. Management depends on the severity, but includes skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions care techniques, topical therapies, antibiotics, and retinoids Retinoids Retinol and derivatives of retinol that play an essential role in metabolic functioning of the retina, the growth of and differentiation of epithelial tissue, the growth of bone, reproduction, and the immune response. Dietary vitamin A is derived from a variety of carotenoids found in plants. It is enriched in the liver, egg yolks, and the fat component of dairy products. Fat-soluble Vitamins and their Deficiencies.
Last updated: Apr 10, 2025
Acne vulgaris is a disorder of the pilosebaceous unit (which includes the hair follicle Hair follicle A tube-like invagination of the epidermis from which the hair shaft develops and into which sebaceous glands open. The hair follicle is lined by a cellular inner and outer root sheath of epidermal origin and is invested with a fibrous sheath derived from the dermis. Follicles of very long hairs extend into the subcutaneous layer of tissue under the skin. Cowden Syndrome and sebaceous gland Sebaceous Gland Small, sacculated organs found within the dermis. Each gland has a single duct that emerges from a cluster of oval alveoli. Each alveolus consists of a transparent basement membrane enclosing epithelial cells. The ducts from most sebaceous glands open into a hair follicle, but some open on the general surface of the skin. Sebaceous glands secrete sebum. Hordeolum (Stye)) and is characterized by 4 pathogenic factors:
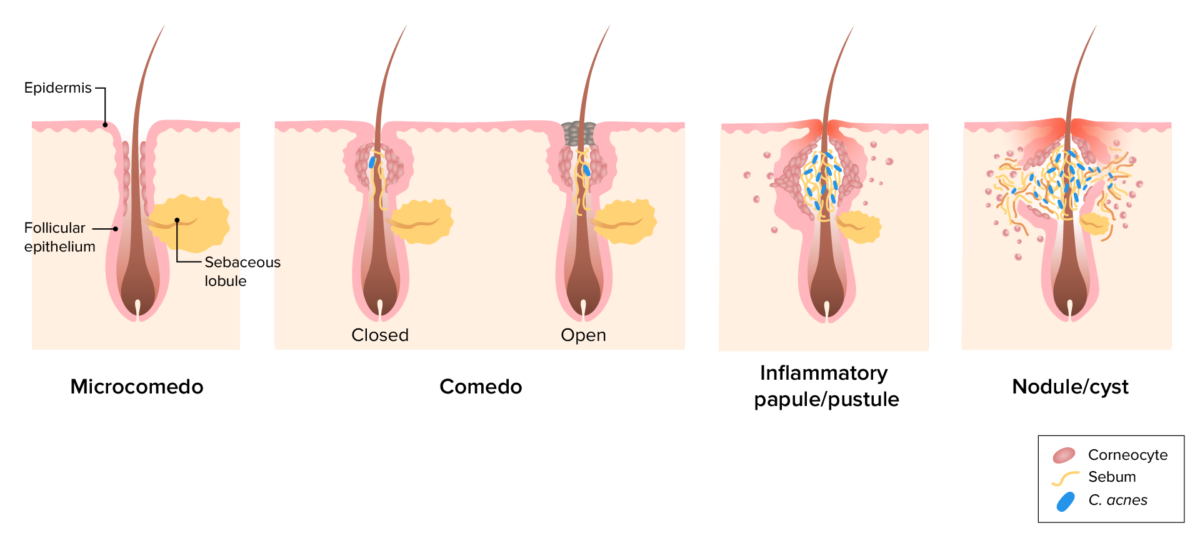
Pathogenesis of acne vulgaris:
Image depicting the pathogenic factors leading to comedo, pustule, and nodule development. Plugging of the follicle by corneocytes results in sebum accumulation. C. acnes colonization triggers an inflammatory response, which may lead to follicular rupture.
Noninflammatory acne (comedones):
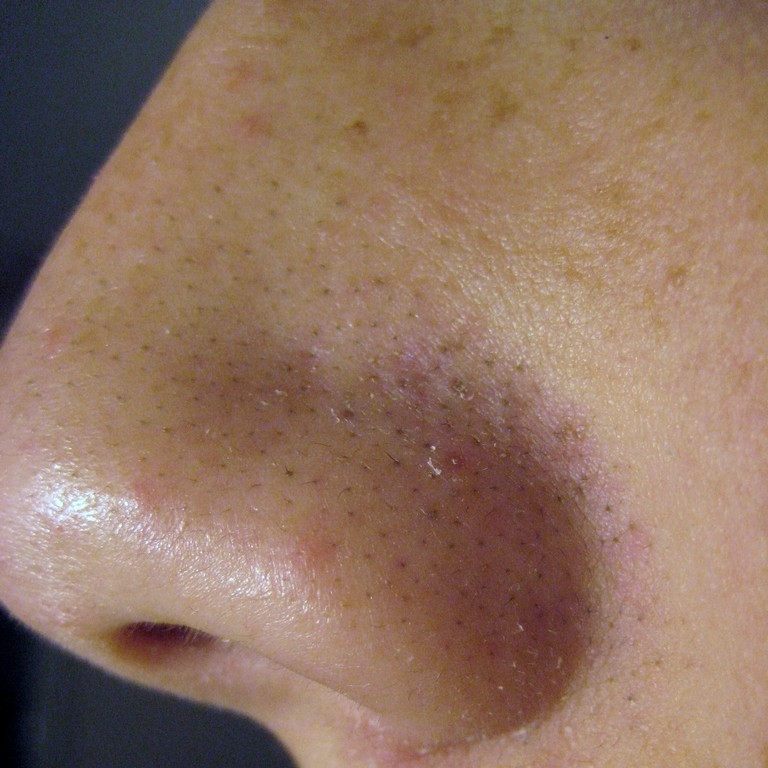
Open comedones on the nose
Image: “Blackheads” by Elecbullet. License: Public Domain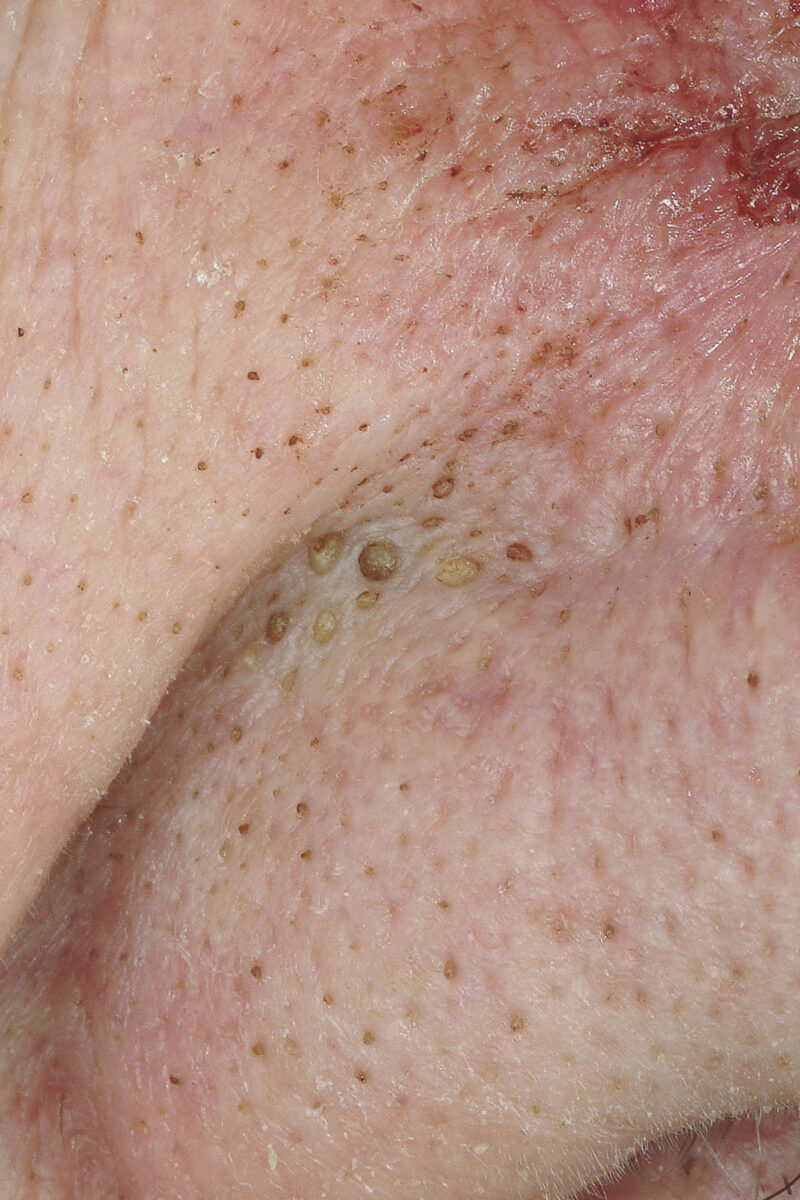
Closed comedones at the nasolabial folds
Image: “Comedos Nose 01” by M. Sand, D. Sand, C. Thrandorf, V. Paech, P. Altmeyer, F. G. Bechara. License: CC BY 2.0Inflammatory acne:
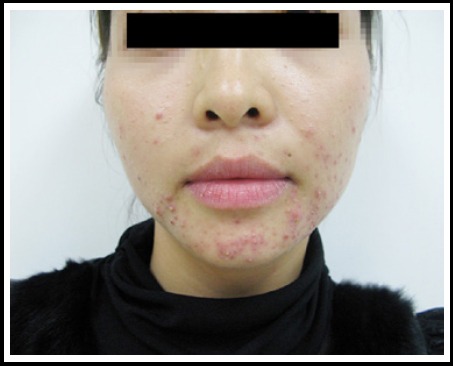
Acne vulgaris with typical lesions, such as comedones, papules, and pustules on the face
Image: “Clinical characteristics and epidermal barrier function of papulopustular rosacea: A comparison study with acne vulgaris” by Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences. License: CC BY 3.0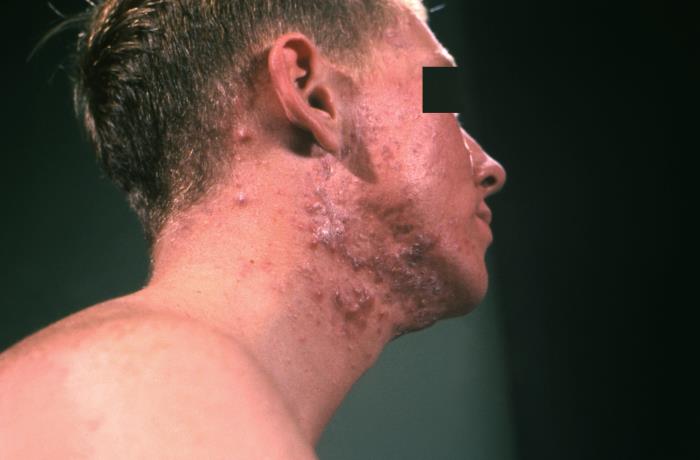
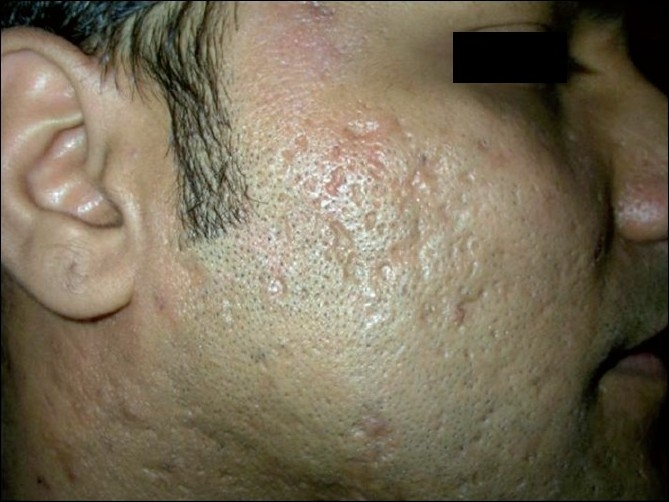
Severe acne vulgaris:
A cutaneous papular outbreak over the neck and lower jaw, with a coalescence of numerous inflamed papules
Atrophic acne scarring in a patient with severe acne vulgaris
Image: “Novel Technology in the Treatment of Acne Scars: The Matrix-tunable Radiofrequency Technology” by Ramesh M, Gopal M, Kumar S, Talwar A. License: CC BY 2.0The following variants are rare forms of acne that more often affect adolescent boys and men.
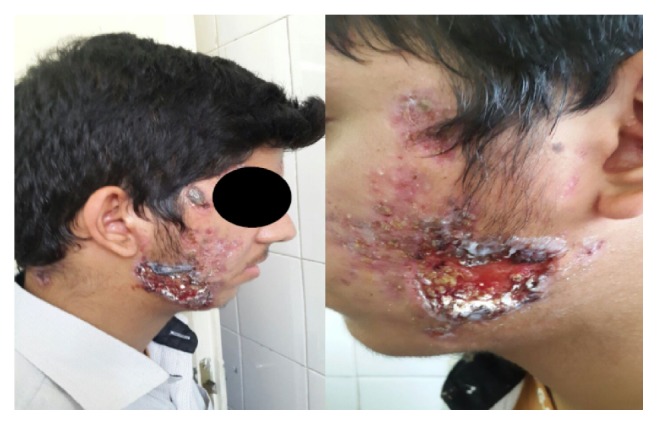
Large, hemorrhagic ulcerations on the face of a patient with acne fulminans
Image: “Successful Treatment of Facial Acne Fulminans: Antimicrobial Agents and Oral Prednisolone as Promising Regimes” by Case Reports in Dermatological Medicine. License: CC BY 4.0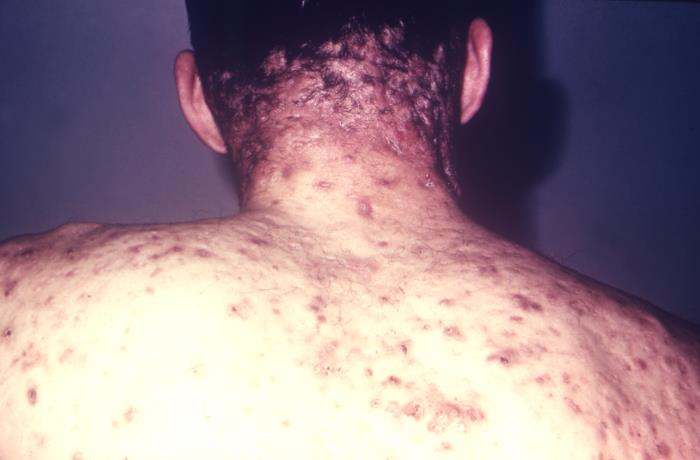
Acne conglobata:
A rare form of acne vulgaris that causes extensive scarring, and a coalescence of developing inflammatory cutaneous nodules.
The diagnosis is clinical and based on the physical examination. No laboratory or skin biopsy Skin Biopsy Secondary Skin Lesions is required.
These treatments are indicated for all patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with inflammatory disease in order to prevent sequelae and complications.
In addition to the above measures, the following may be added: