Acetaminophen (APAP), or paracetamol, is an over-the-counter nonopioid analgesic and antipyretic medication. It is the most commonly used analgesic worldwide. Likewise, APAP overdose is one of the most common causes of medication poisoning and death. Acetaminophen is primarily metabolized by the liver; therefore, overdose can lead to life threatening hepatotoxicity. In adults, limitation of total APAP dose (from all sources and routes) to < 4000 mg per day is recommended. During evaluation, a thorough history and measurement of serum APAP are important, as the initial clinical signs of APAP overdose can be nonspecific. Management of overdose includes drug serum concentration, stabilization, decontamination, and administration of N-acetylcysteine (NAC). Use of NAC within 8 hours of ingestion is associated with good case outcomes. Without treatment, however, cases are at significant risk of severe hepatotoxicity and potentially death.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
The clinical course of APAP APAP Acetaminophen (APAP) is an over-the-counter nonopioid analgesic and antipyretic medication. Acetaminophen is the most commonly used analgesic worldwide. Acetaminophen overdose is also one of the most common causes of medication poisoning and death. Acetaminophen Overdose poisoning is often divided into 4 stages, which are classified according to duration since time of ingestion.[12]
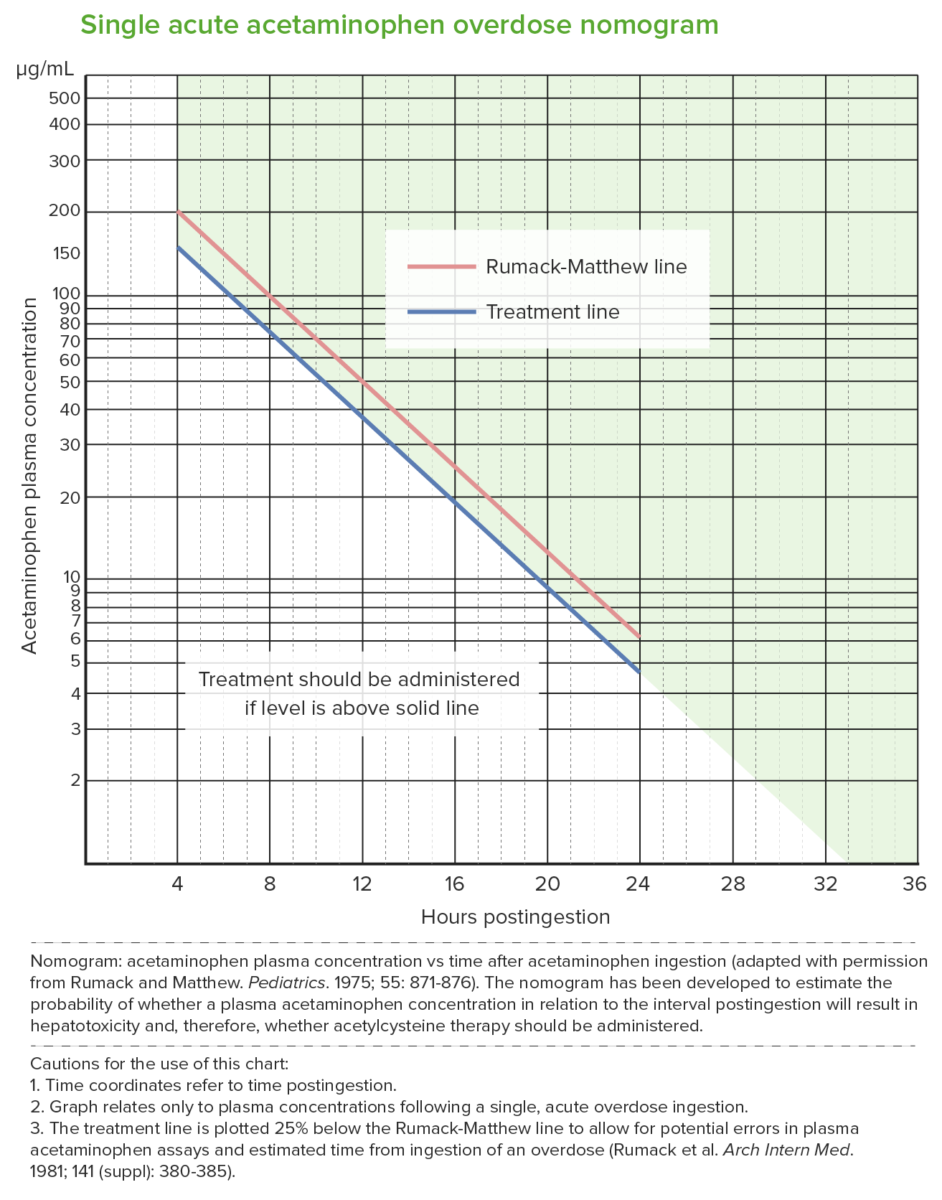
Rumack-Matthew nomogram (acetaminophen toxicity nomogram):
Used after a single acute acetaminophen ingestion.
The nomogram predicts potential hepatotoxicity beginning at 4 hours after ingestion. Levels measured earlier than 4 hours may not be reliable.
The nomogram cannot be used for ingestions that occurred > 24 hours prior to presentation.
The upper (red) line is the Rumack-Matthew line; values above this line develop toxicity (noted in 60%).
The lower (blue) line is the treatment line (U.S. Food and Drug Administration required treatment line to be 25% below the original line).
NAC treatment is given when the acetaminophen level is at the treatment line 4 hours post ingestion (which is below the toxicity threshold).
Entails supportive care, limiting drug absorption Absorption Absorption involves the uptake of nutrient molecules and their transfer from the lumen of the GI tract across the enterocytes and into the interstitial space, where they can be taken up in the venous or lymphatic circulation. Digestion and Absorption, and treatment of toxic effects:
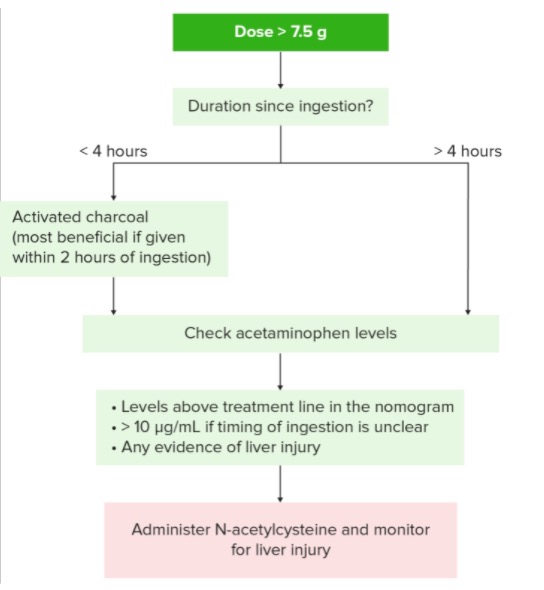
Overview of the treatment algorithm for acetaminophen toxicity
Image by Lecturio.Diagnosis Codes:
These codes are used to document an acetaminophen Acetaminophen Acetaminophen is an over-the-counter nonopioid analgesic and antipyretic medication and the most commonly used analgesic worldwide. Despite the widespread use of acetaminophen, its mechanism of action is not entirely understood. Acetaminophen ( paracetamol paracetamol Acetaminophen is an over-the-counter nonopioid analgesic and antipyretic medication and the most commonly used analgesic worldwide. Despite the widespread use of acetaminophen, its mechanism of action is not entirely understood. Acetaminophen) overdose. It is crucial to specify the intent (accidental, intentional self-harm Self-harm Psychiatric Assessment) and the encounter type (initial, subsequent).
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | T39.1X1A | Poisoning by 4-aminophenol derivatives, accidental (unintentional), initial encounter |
| ICD-10-CM | T39.1X2A | Poisoning by 4-aminophenol derivatives, intentional self-harm Self-harm Psychiatric Assessment, initial encounter |
Evaluation & Workup:
These codes are for the essential laboratory tests following a suspected acetaminophen overdose Acetaminophen Overdose Acetaminophen (APAP) is an over-the-counter nonopioid analgesic and antipyretic medication. Acetaminophen is the most commonly used analgesic worldwide. Acetaminophen overdose is also one of the most common causes of medication poisoning and death. Acetaminophen Overdose. An acetaminophen Acetaminophen Acetaminophen is an over-the-counter nonopioid analgesic and antipyretic medication and the most commonly used analgesic worldwide. Despite the widespread use of acetaminophen, its mechanism of action is not entirely understood. Acetaminophen level is used with the Rumack-Matthew nomogram Rumack-Matthew nomogram Guides the use of the antidote n-acetylcysteine (NAC) based on sapap and hours since ingestion in relation to probability of hepatotoxicity. Acetaminophen Overdose to determine the risk of liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy toxicity Toxicity Dosage Calculation, and liver function tests Liver function tests Liver function tests, also known as hepatic function panels, are one of the most commonly performed screening blood tests. Such tests are also used to detect, evaluate, and monitor acute and chronic liver diseases. Liver Function Tests (LFTs) monitor for liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy injury.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CPT | 82003 | Acetaminophen Acetaminophen Acetaminophen is an over-the-counter nonopioid analgesic and antipyretic medication and the most commonly used analgesic worldwide. Despite the widespread use of acetaminophen, its mechanism of action is not entirely understood. Acetaminophen; quantitative |
| CPT | 84450 | Transferase; aspartate Aspartate One of the non-essential amino acids commonly occurring in the l-form. It is found in animals and plants, especially in sugar cane and sugar beets. It may be a neurotransmitter. Synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids amino ( AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests) (SGOT) |
| CPT | 84460 | Transferase; alanine Alanine A non-essential amino acid that occurs in high levels in its free state in plasma. It is produced from pyruvate by transamination. It is involved in sugar and acid metabolism, increases immunity, and provides energy for muscle tissue, brain, and the central nervous system. Synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids amino ( ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests) (SGPT) |
Medications:
This code is used to bill for the administration of N-acetylcysteine N-Acetylcysteine Acetaminophen Overdose ( NAC NAC Acetaminophen Overdose), the specific antidote Antidote An antidote is a substance that counteracts poisoning or toxicity. Substances that can cause poisoning include heavy metals (from occupation, treatments, or diet), alcohols, environmental toxins, and medications. Antidotes of Common Poisonings for acetaminophen Acetaminophen Acetaminophen is an over-the-counter nonopioid analgesic and antipyretic medication and the most commonly used analgesic worldwide. Despite the widespread use of acetaminophen, its mechanism of action is not entirely understood. Acetaminophen poisoning, which works by replenishing glutathione stores in the liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy to prevent toxic metabolite injury.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| HCPCS | J0132 | Injection, acetylcysteine, 100 mg |
| RxNorm | 196 | Acetylcysteine (ingredient) |
Complications:
This code is used to document the most severe consequence of an untreated or massive acetaminophen overdose Acetaminophen Overdose Acetaminophen (APAP) is an over-the-counter nonopioid analgesic and antipyretic medication. Acetaminophen is the most commonly used analgesic worldwide. Acetaminophen overdose is also one of the most common causes of medication poisoning and death. Acetaminophen Overdose: acute liver failure Liver failure Severe inability of the liver to perform its normal metabolic functions, as evidenced by severe jaundice and abnormal serum levels of ammonia; bilirubin; alkaline phosphatase; aspartate aminotransferase; lactate dehydrogenases; and albumin/globulin ratio. Autoimmune Hepatitis, which can be fatal without a liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy transplant.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | K72.00 | Acute and subacute hepatic failure Hepatic failure Severe inability of the liver to perform its normal metabolic functions, as evidenced by severe jaundice and abnormal serum levels of ammonia; bilirubin; alkaline phosphatase; aspartate aminotransferase; lactate dehydrogenases; and albumin/globulin ratio. Autoimmune Hepatitis without coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma |