Abnormal uterine bleeding is the medical term for abnormalities in the frequency, volume, duration, and regularity of the menstrual cycle Menstrual cycle The menstrual cycle is the cyclic pattern of hormonal and tissular activity that prepares a suitable uterine environment for the fertilization and implantation of an ovum. The menstrual cycle involves both an endometrial and ovarian cycle that are dependent on one another for proper functioning. There are 2 phases of the ovarian cycle and 3 phases of the endometrial cycle. Menstrual Cycle. Abnormal uterine bleeding is classified using the acronym PALM-COEIN, with PALM representing the structural causes and COEIN indicating the non-structural causes. Etiologies include polyp (P), adenomyosis Adenomyosis Adenomyosis is a benign uterine condition characterized by the presence of ectopic endometrial glands and stroma within the myometrium. Adenomyosis is a common condition, affecting 20%-35% of women, and typically presents with heavy menstrual bleeding and dysmenorrhea. Adenomyosis (A), leiomyoma Leiomyoma A benign tumor derived from smooth muscle tissue, also known as a fibroid tumor. They rarely occur outside of the uterus and the gastrointestinal tract but can occur in the skin and subcutaneous tissue, probably arising from the smooth muscle of small blood vessels in these tissues. Infertility (L), malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax/ hyperplasia Hyperplasia An increase in the number of cells in a tissue or organ without tumor formation. It differs from hypertrophy, which is an increase in bulk without an increase in the number of cells. Cellular Adaptation (M), coagulopathy (C), ovulatory dysfunction (O); endometrial pathology including endometritis Endometritis Endometritis is an inflammation of the endometrium, the inner layer of the uterus. The most common subtype is postpartum endometritis, resulting from the ascension of normal vaginal flora to the previously aseptic uterus. Postpartum Endometritis and atrophy Atrophy Decrease in the size of a cell, tissue, organ, or multiple organs, associated with a variety of pathological conditions such as abnormal cellular changes, ischemia, malnutrition, or hormonal changes. Cellular Adaptation (E), iatrogenic Iatrogenic Any adverse condition in a patient occurring as the result of treatment by a physician, surgeon, or other health professional, especially infections acquired by a patient during the course of treatment. Anterior Cord Syndrome causes (I), and etiologies not otherwise classified (N). Diagnosis usually requires careful history-taking and examination, basic laboratory work, transvaginal ultrasound Transvaginal Ultrasound Obstetric Imaging, and endometrial biopsy Endometrial Biopsy Diagnostic Procedures in Gynecology based on age and risk factors. Management depends on the underlying etiology, but often includes oral contraceptive Oral contraceptive Compounds, usually hormonal, taken orally in order to block ovulation and prevent the occurrence of pregnancy. The hormones are generally estrogen or progesterone or both. Benign Liver Tumors pills, levonorgestrel-containing intrauterine devices Intrauterine devices Contraceptive devices placed high in the uterine fundus. Hormonal Contraceptives, and surgery.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB):
Owing to the previous lack of consistency Consistency Dermatologic Examination in terminologies surrounding AUB, a new system was developed in 2011 to describe and classify AUB.
| Old term | New preferred term |
|---|---|
| Oligomenorrhea Oligomenorrhea Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome | Infrequent uterine bleeding |
| Polymenorrhea | Frequent uterine bleeding |
| Menorrhagia | Abnormal uterine bleeding/heavy menstrual bleeding (AUB/HMB) |
| Metrorrhagia | Abnormal uterine bleeding/intermenstrual bleeding (AUB/IMB) |
| Amenorrhea Amenorrhea Absence of menstruation. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System | Amenorrhea Amenorrhea Absence of menstruation. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System (no change) |
| Dysfunctional uterine bleeding | Use specific disorders (or the new terms) |
The causes of AUB are classified according to the PALM-COEIN system, which is an acronym.
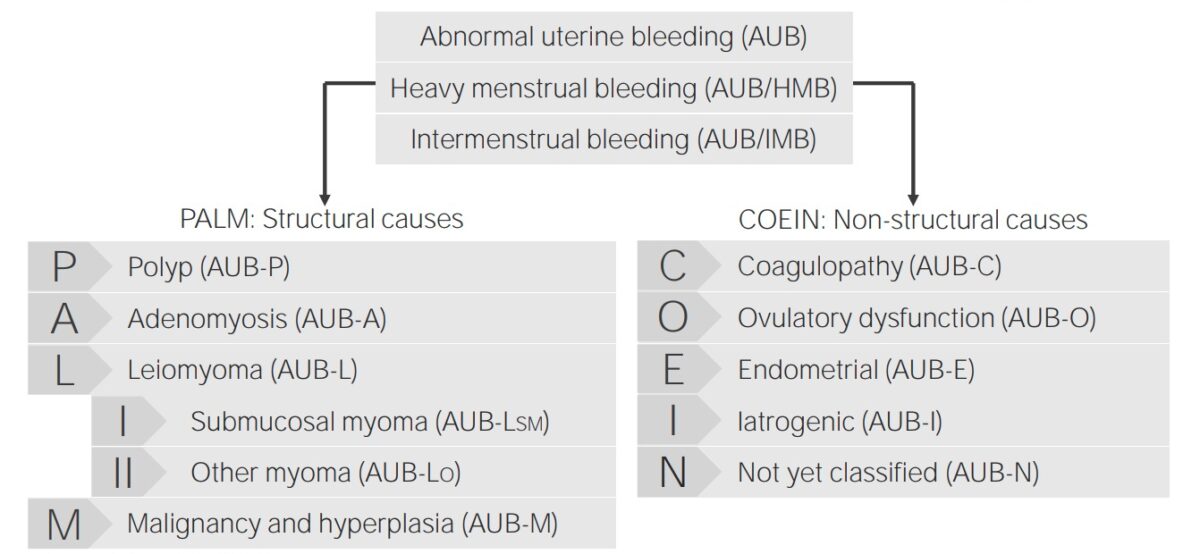
Classification of abnormal uterine bleeding and its causes
Image by Lecturio.
Uterine fibroids (location):
| Etiology | Bleeding presentation | Other clinical findings |
|---|---|---|
| Polyp (AUB-P) | HMB, IMB, and/or prolonged uterine bleeding |
|
| Adenomyosis Adenomyosis Adenomyosis is a benign uterine condition characterized by the presence of ectopic endometrial glands and stroma within the myometrium. Adenomyosis is a common condition, affecting 20%-35% of women, and typically presents with heavy menstrual bleeding and dysmenorrhea. Adenomyosis (AUB-A) | HMB, IMB, and/or prolonged uterine bleeding |
|
| Leiomyoma Leiomyoma A benign tumor derived from smooth muscle tissue, also known as a fibroid tumor. They rarely occur outside of the uterus and the gastrointestinal tract but can occur in the skin and subcutaneous tissue, probably arising from the smooth muscle of small blood vessels in these tissues. Infertility (AUB-L) | HMB, IMB, and/or prolonged uterine bleeding |
|
| Malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax and hyperplasia Hyperplasia An increase in the number of cells in a tissue or organ without tumor formation. It differs from hypertrophy, which is an increase in bulk without an increase in the number of cells. Cellular Adaptation (AUB-M) |
|
|
| Etiology | Bleeding presentation | Other clinical findings |
|---|---|---|
| Coagulopathy (AUB-C) | AUB/HMB since menarche Menarche The first menstrual cycle marked by the initiation of menstruation. Menstrual Cycle | History of easy bleeding (e.g., dental bleeding, postpartum hemorrhage Postpartum hemorrhage Postpartum hemorrhage is one of the most common and deadly obstetric complications. Since 2017, postpartum hemorrhage has been defined as blood loss greater than 1,000 mL for both cesarean and vaginal deliveries, or excessive blood loss with signs of hemodynamic instability. Postpartum Hemorrhage) |
| Ovulatory dysfunction (AUB-O) | Infrequent bleeding | Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea Functional Hypothalamic Amenorrhea Secondary Amenorrhea (eating disorder): weight loss Weight loss Decrease in existing body weight. Bariatric Surgery |
|
Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea Functional Hypothalamic Amenorrhea Secondary Amenorrhea (stress): psychological factors | |
|
Polycystic ovary syndrome (
PCOS
PCOS
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, affecting nearly 5%-10% of women in the age group. It is characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic anovulation leading to oligomenorrhea (or amenorrhea), and metabolic dysfunction.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome):
|
|
| Amenorrhea Amenorrhea Absence of menstruation. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System |
Primary ovarian insufficiency
Primary ovarian insufficiency
Cessation of ovarian function after menarche but before the age of 40, without or with ovarian follicle depletion. It is characterized by the presence of oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea, elevated gonadotropins, and low estradiol levels. It is a state of female hypergonadotropic hypogonadism. Etiologies include genetic defects, autoimmune processes, chemotherapy, radiation, and infections. The most commonly known genetic cause is the expansion of a cgg repeat to 55 to 199 copies in the 5′ untranslated region in the X-linked fmr1 gene.
Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (POI):
|
|
|
Signs and symptoms of other endocrine disorders affecting ovulation Ovulation The discharge of an ovum from a rupturing follicle in the ovary. Menstrual Cycle (e.g., hyperthyroidism Hyperthyroidism Hypersecretion of thyroid hormones from the thyroid gland. Elevated levels of thyroid hormones increase basal metabolic rate. Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism Hypothyroidism Hypothyroidism is a condition characterized by a deficiency of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency is the most common cause worldwide, but Hashimoto’s disease (autoimmune thyroiditis) is the leading cause in non-iodine-deficient regions. Hypothyroidism, hyperprolactinemia Hyperprolactinemia Hyperprolactinemia is defined as a condition of elevated levels of prolactin (PRL) hormone in the blood. The PRL hormone is secreted by the anterior pituitary gland and is responsible for breast development and lactation. The most common cause is PRL-secreting pituitary adenomas (prolactinomas). Hyperprolactinemia) | |
| Irregular bleeding | Age-related anovulation Anovulation Suspension or cessation of ovulation in animals or humans with follicle-containing ovaries (ovarian follicle). Depending on the etiology, ovulation may be induced with appropriate therapy. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome near menarche Menarche The first menstrual cycle marked by the initiation of menstruation. Menstrual Cycle or menopause Menopause Menopause is a physiologic process in women characterized by the permanent cessation of menstruation that occurs after the loss of ovarian activity. Menopause can only be diagnosed retrospectively, after 12 months without menstrual bleeding. Menopause | |
| Endometrial (AUB-E) | HMB, IMB, or prolonged bleeding |
PID
PID
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is defined as a polymicrobial infection of the upper female reproductive system. The disease can affect the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and adjacent structures. Pelvic inflammatory disease is closely linked with sexually transmitted diseases, most commonly caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and gardnerella vaginalis.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease:
|
| IMB | Endometrial atrophy Atrophy Decrease in the size of a cell, tissue, organ, or multiple organs, associated with a variety of pathological conditions such as abnormal cellular changes, ischemia, malnutrition, or hormonal changes. Cellular Adaptation: accompanied by vaginal atrophy Atrophy Decrease in the size of a cell, tissue, organ, or multiple organs, associated with a variety of pathological conditions such as abnormal cellular changes, ischemia, malnutrition, or hormonal changes. Cellular Adaptation | |
| Iatrogenic Iatrogenic Any adverse condition in a patient occurring as the result of treatment by a physician, surgeon, or other health professional, especially infections acquired by a patient during the course of treatment. Anterior Cord Syndrome (AUB-I) | AUB/IMB | Dependent on agent(s) |
| Not otherwise classified (AUB-N) | Poorly defined or extremely rare (e.g., arteriovenous malformation Arteriovenous malformation Abnormal formation of blood vessels that shunt arterial blood directly into veins without passing through the capillaries. They usually are crooked, dilated, and with thick vessel walls. A common type is the congenital arteriovenous fistula. The lack of blood flow and oxygen in the capillaries can lead to tissue damage in the affected areas. Erysipelas, isthmocele) | |
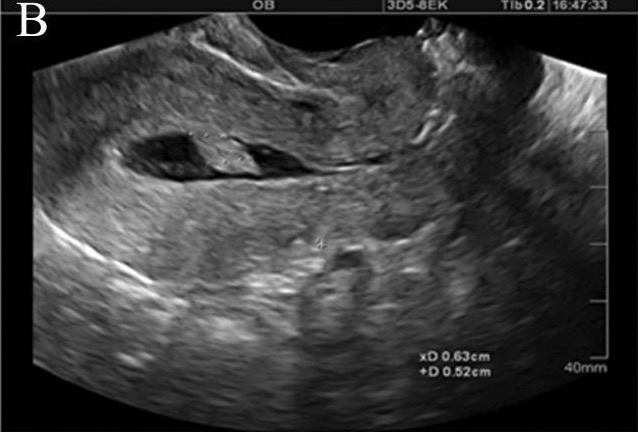
Saline infusion sonogram demonstrating a pedunculated intracavitary lesion, likely an endometrial polyp:
Injection of sterile fluid into the endometrial cavity distends the cavity and allows for assessment of structural endometrial pathology, including polyps, submucosal fibroids, and synechiae.