The airway, breathing, and circulation, disability and exposure (ABCDE) assessment is the mainstay management approach used in managing critically ill patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship. The ABCDEs are the essential 1st steps to perform in many situations including unresponsive patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship, cardiac arrests, and critical medical or trauma patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship. For the trauma patient, ABCDE is included in the primary survey Primary Survey Thoracic Trauma in Children, the initial evaluation, and management of injuries.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
A primary survey Primary Survey Thoracic Trauma in Children is the initial evaluation used to identify and manage life-threatening injuries in a trauma patient.
The components of the primary survey Primary Survey Thoracic Trauma in Children are:
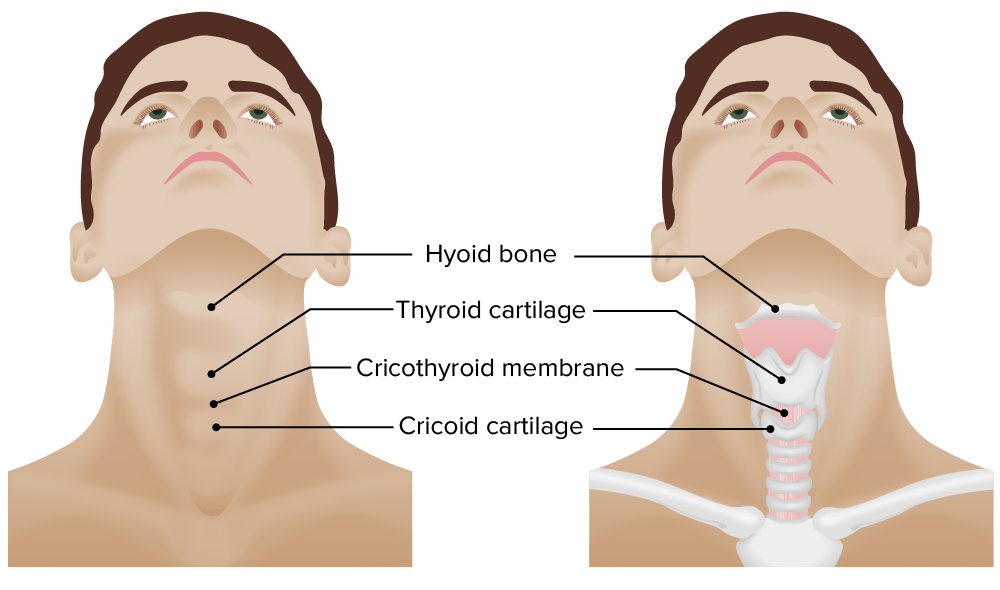
Tracheal anatomy and external landmarks: a cricothyrotomy is performed by creating an incision in the crocothyroid membrane (between the thyroid cartilage and cricoid cartilage). A tube can then be inserted, providing a definitive airway.
Image by Lecturio.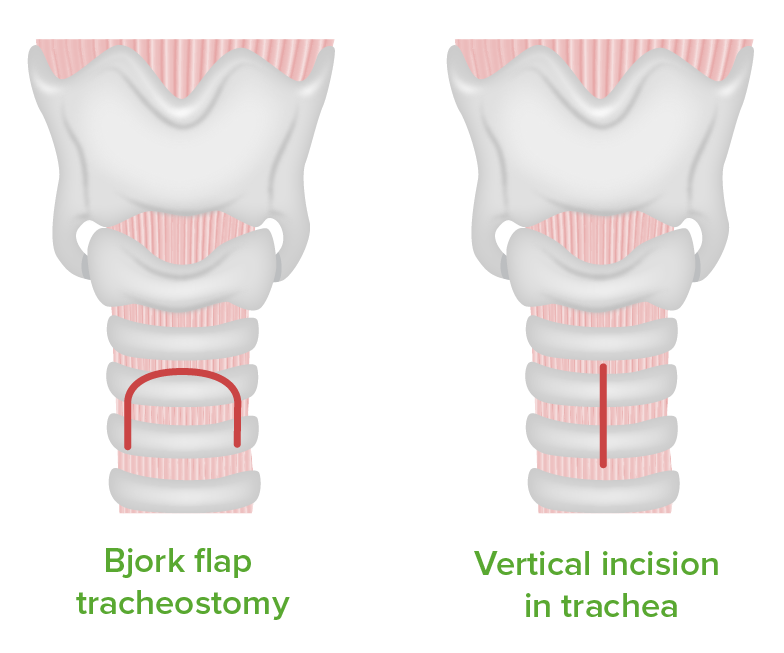
Types of tracheotomy incisions
Image by Lecturio.Breathing is the next step after the airway has been deemed adequate.
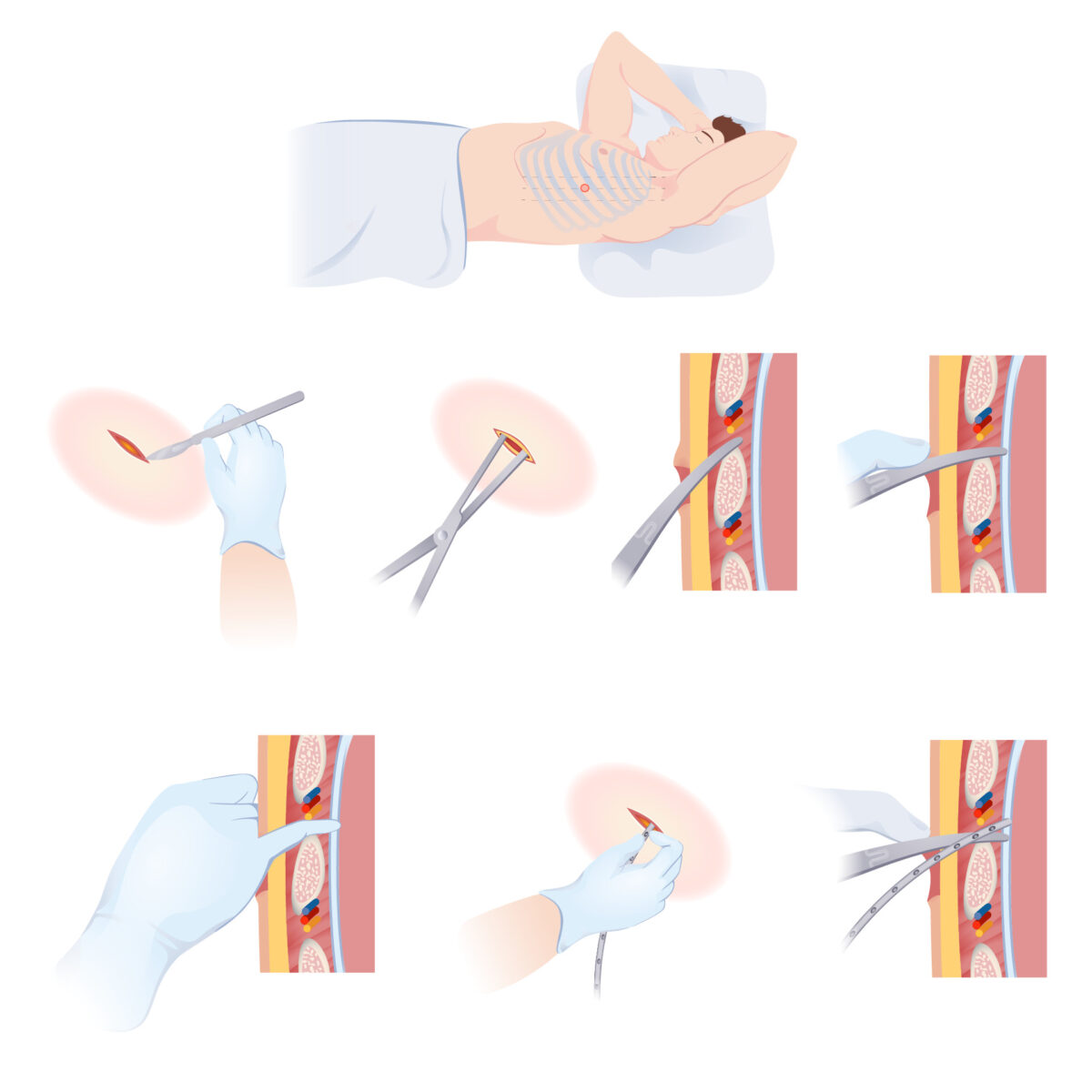
Thoracostomy:
A primary skin incision is made superiorly to the rib to avoid the neurovascular supply that runs inferiorly to the rib. The surgeon tunnels through the subcutaneous tissue and muscle to enter the pleural cavity. Entrance into the pleural cavity is confirmed and the chest tube is placed.
Performed after the airway and breathing have been judged as normal and adequate.
The goal of disability assessment Disability Assessment Multitrauma is to determine and manage the presence of neurologic injury.
| Feature | Response | Score |
|---|---|---|
| Eye opening | Open spontaneously | 4 |
| Open to verbal command | 3 | |
| Open to pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways | 2 | |
| No eye opening | 1 | |
| Verbal response | Oriented and appropriate | 5 |
| Disoriented but conversant | 4 | |
| Nonsensical words | 3 | |
| Moaning | 2 | |
| Silent | 1 | |
| Motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology response | Follows commands | 6 |
| Localizes pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways | 5 | |
| Withdraws to pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways | 4 | |
| Flexor posturing | 3 | |
| Extensor posturing Extensor posturing A condition characterized by abnormal posturing of the limbs that is associated with injury to the brainstem. This may occur as a clinical manifestation or induced experimentally in animals. The extensor reflexes are exaggerated leading to rigid extension of the limbs accompanied by hyperreflexia and opisthotonus. This condition is usually caused by lesions which occur in the region of the brainstem that lies between the red nuclei and the vestibular nuclei. In contrast, decorticate rigidity is characterized by flexion of the elbows and wrists with extension of the legs and feet. The causative lesion for this condition is located above the red nuclei and usually consists of diffuse cerebral damage. Increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP) | 2 | |
| Flaccid | 1 |
The goal of this step is to evaluate and manage negative environmental effects:
The goal of the secondary survey is to rapidly and thoroughly examine the patient from head to toe to identify all potentially significant injuries.
The following are conditions that can cause acutely and severely impaired cardiovascular function in a patient: