Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy
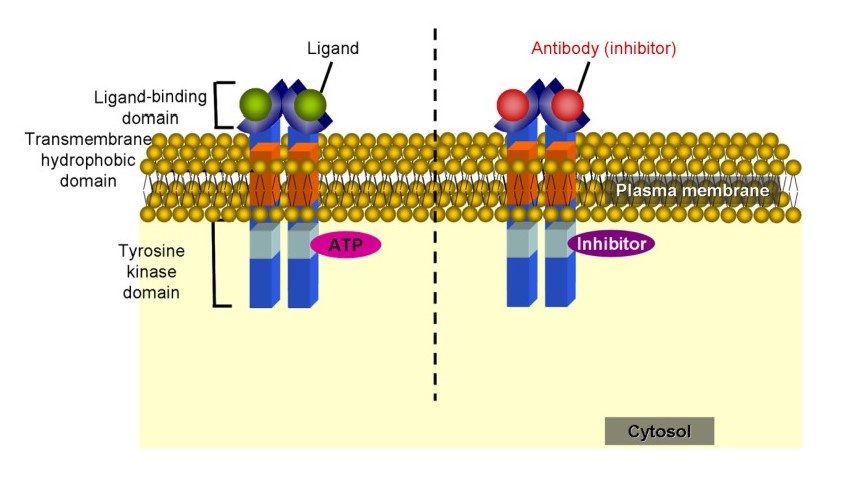
Overview Cancer therapy development Targeted cancer therapy Protein Kinase Inhibitors Protein kinases BCR-ABL kinase inhibitors Table: BCR-ABL kinase inhibitors Imatinib Dasatinib Nilotinib Pharmacodynamics Inhibit BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase (causing apoptosis of BCR-ABL positive cell lines) Inhibit c-KIT, PDGFR Imatinib: also inhibits stem-cell factor Pharmacokinetics Oral Hepatic metabolism Excretion: mostly in feces Indications CML Imatinib, dasatinib: ALL […]
Thrombolytics
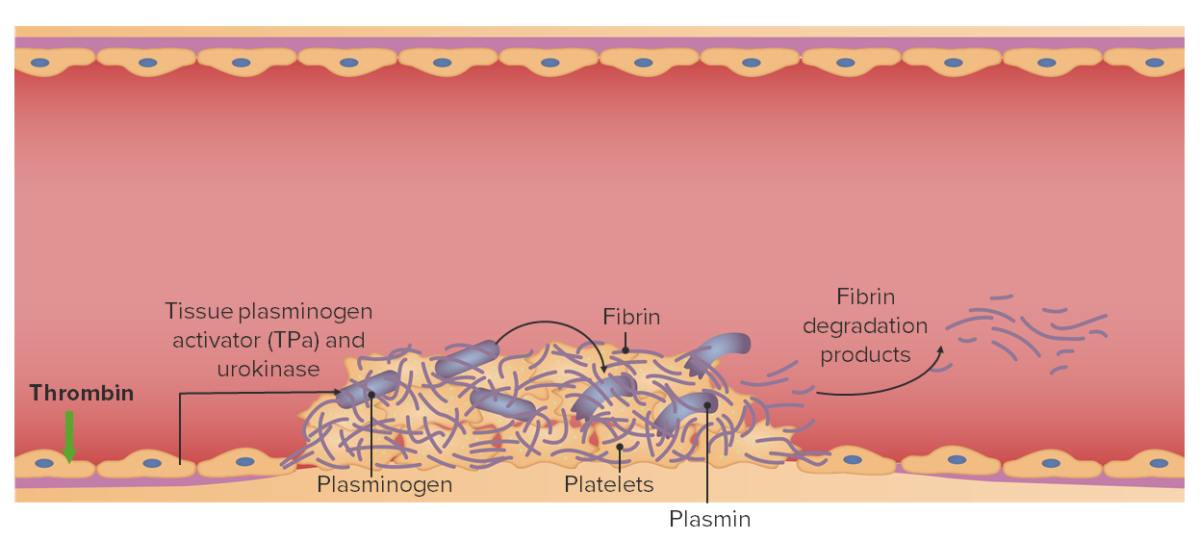
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemistry Mechanism of action Normal physiology: Thrombolytics (also known as fibrinolytics): Indications Administration Indications ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI): Acute ischemic stroke: Pulmonary embolism (PE): Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): Additional indications: Adverse Effects and Contraindications Use thrombolytics cautiously. The medications have a significant risk of bleeding, which can be life threatening or […]
Gout Drugs
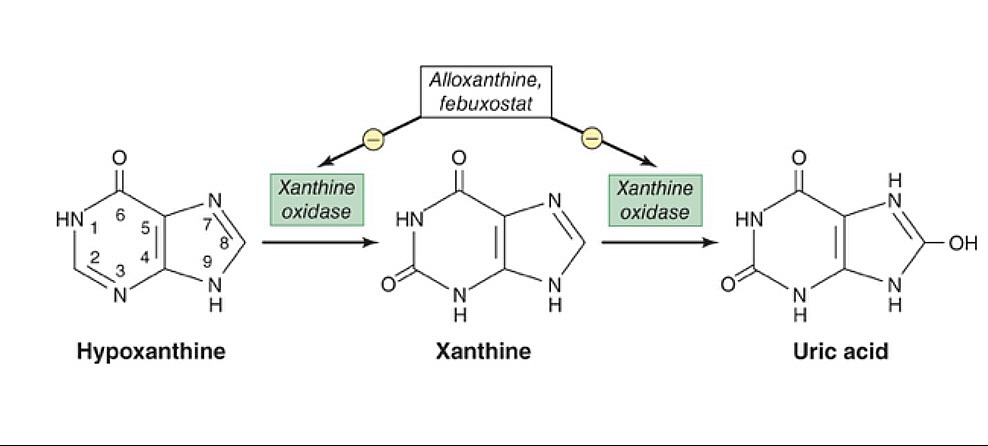
Overview Gout pathophysiology Management options Colchicine Chemistry Colchicine is an alkaloid extracted from Colchicum autumnale (autumn crocus). Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Absorption: Distribution: Metabolism: Excretion: Indications Gout: Other indications include: Adverse effects Precautions Caution should be used in individuals with: Drug interactions The following could lead to increased levels of colchicine: Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors Chemistry […]
Antihistamines
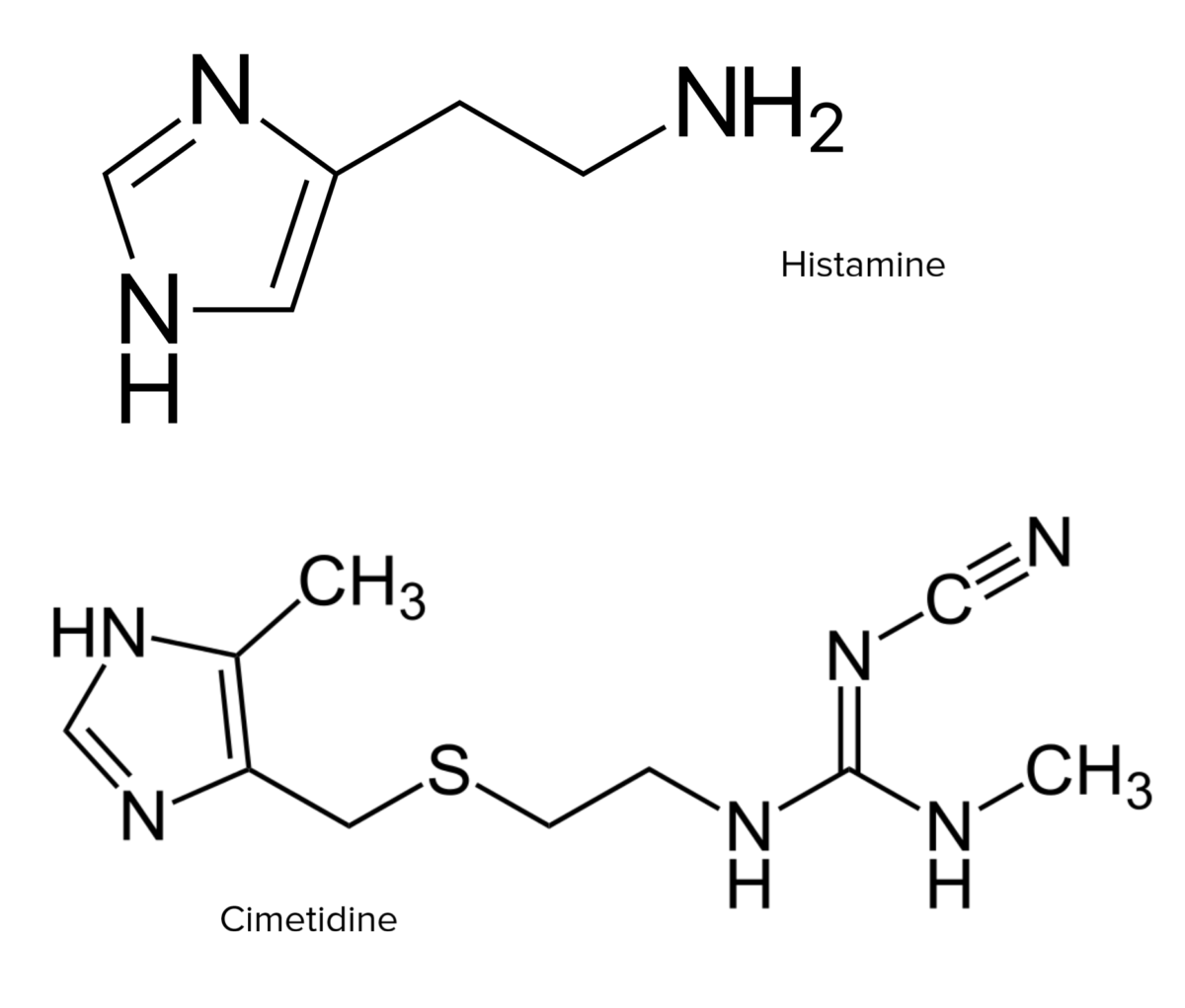
Overview Histamine Antihistamines H1 Antagonists Medications Table: H1 antagonists 1st generation 2nd generation Carbinoxamine Chlorpheniramine Clemastine Dexchlorpheniramine Dimenhydrinate Diphenhydramine Doxylamine Hydroxyzine Meclizine Promethazine Triprolidine Alcaftadine Azelastine Bepotastine Bilastine Cetirizine Desloratadine Emedastine Epinastine Fexofenadine Ketotifen Levocetirizine Loratadine Olopatadine Rupatadine Chemistry and pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics Table: Pharmacokinetics of representative H1 antagonists Type Drug Pharmacokinetics 1st generation Chlorpheniramine Oral […]
Second-Generation Anticonvulsant Drugs
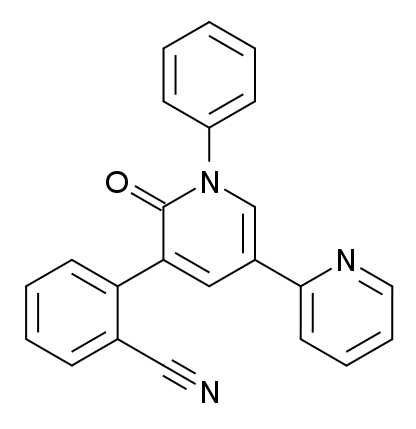
Overview Definitions Antiseizure drugs (ASDs) are used to suppress abnormal electrical activity in the brain through various mechanisms. Pathophysiology of seizures The hyperexcitable state of neurons results from 3 steps: Second-generation antiseizure drugs Felbamate Chemistry and pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics Indications Adverse effects and contraindications Gabapentin and Pregabalin Chemistry and pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics and indications Table: Gabapentin and […]
Intravenous Anesthetics
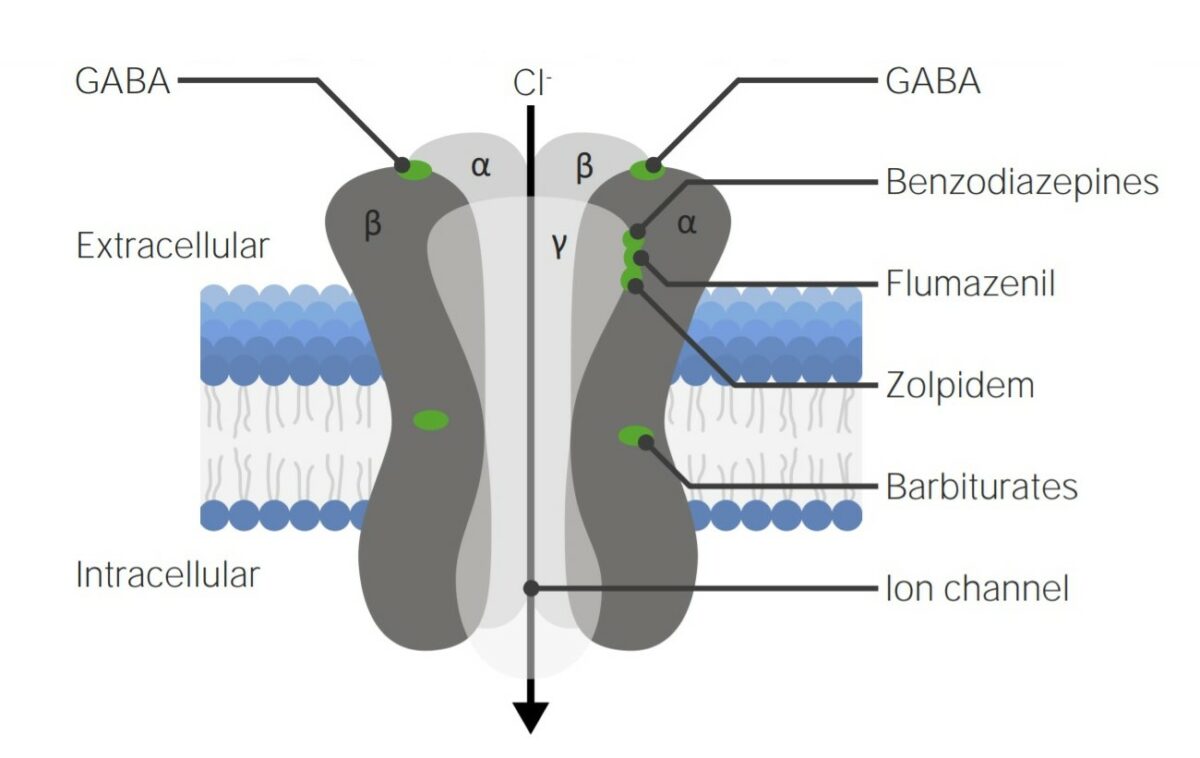
Overview Continuum of sedation and anesthesia Anesthetic agents The intravenous anesthetics include: Barbiturates Agents in the class Chemistry Mechanism of action Physiologic effects Pharmacokinetics Indications Barbiturates are a group of sedative-hypnotic medications with the following indications: Adverse effects and contraindications Adverse effects: Drug interactions: Contraindications: Benzodiazepines Overview Chemistry Mechanism of action Occupation/activation of the GABAA […]
Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors
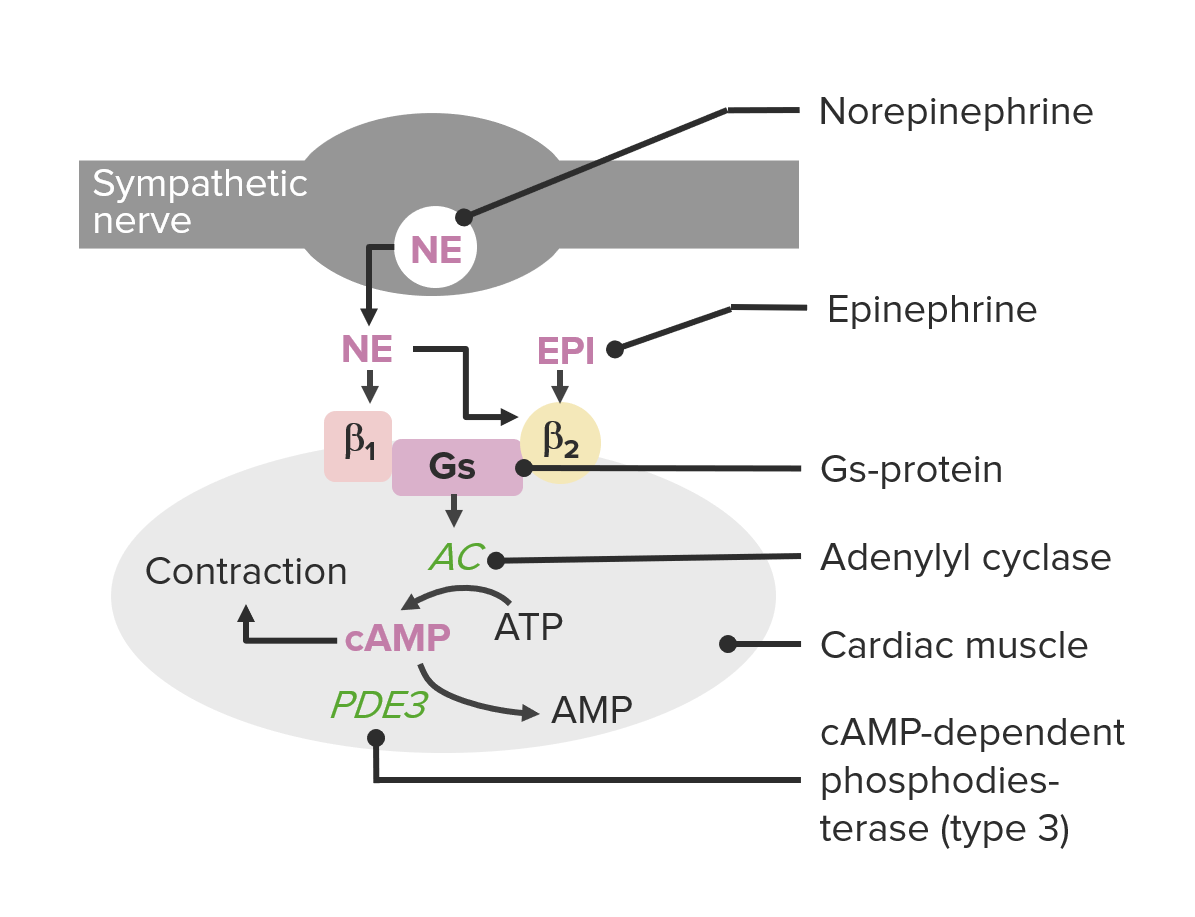
Overview Phosphodiesterase enzymes General mechanism of action The common mechanisms of phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors are: Classification The PDE inhibitors are classified based on the subtype(s) affected: Phosphodiesterase-3 Inhibitors Medications in this class Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics The following table summarizes the pharmacokinetics of the PDE3 inhibitors: Table: Pharmacokinetics of the PDE3 inhibitors Medication Formulation Distribution […]
Other Antidepressants
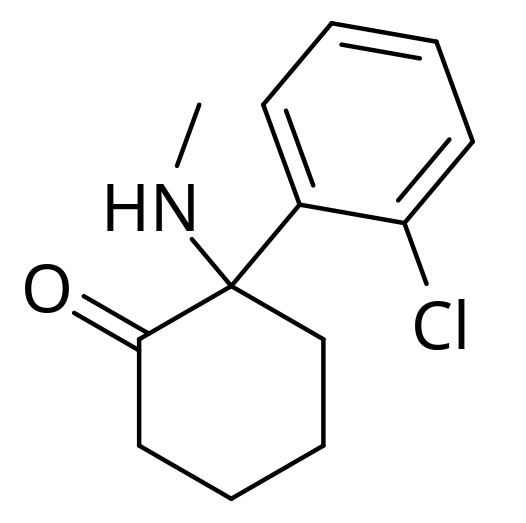
Overview Depression is a unipolar mood disorder characterized by persistent low mood and loss of interest in association with somatic symptoms for a duration of at least 2 weeks. Depression is managed via pharmacotherapy, psychotherapy, and neuromodulation. Bupropion Chemistry Mechanism of action Norepinephrine dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI): Heterocyclic structure Inhibits norepinephrine (NE) transporter (NET) and […]
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
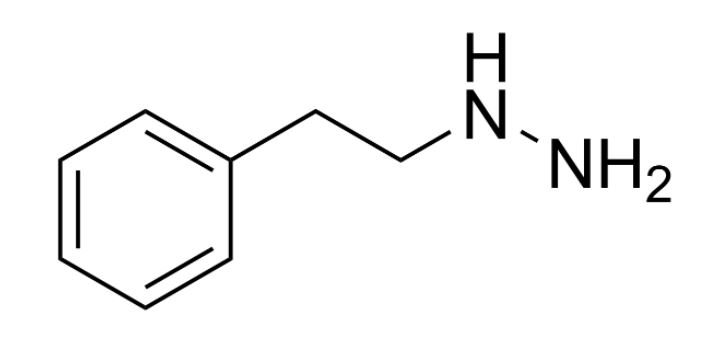
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemical structure The monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) have variable chemical structures. Mechanism of action Monoamine oxidase (MAO): MAOIs: Classification MAOIs are classified based on their selectivity for MAO-A and MAO-B. Pharmacokinetics Absorption and distribution Metabolism and excretion Indications Adverse Effects and Contraindications Adverse effects Contraindications Drug interactions Overdose Clinical presentation Management References
Cholinomimetic Drugs
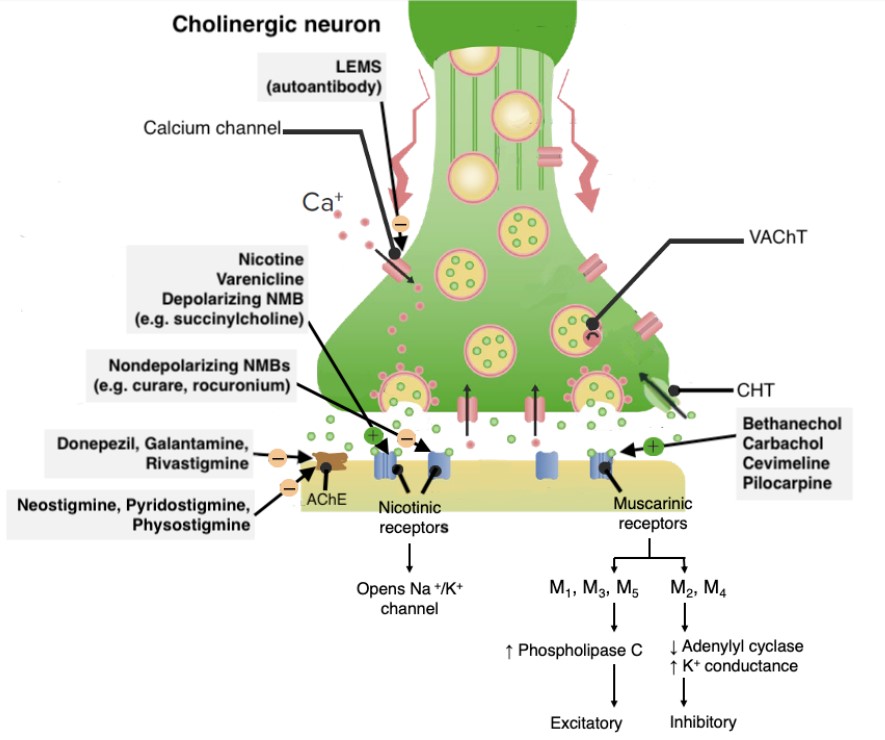
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Acetylcholine (ACh) is a prototype direct-acting cholinergic drug. Cholinomimetics are direct activators of both the muscarinic and nicotinic cholinergic receptors. Overview Mechanism of action and physiologic effects Classification and Pharmacokinetics Cholinomimetic drugs either act directly on cholinergic receptors or inhibit AChE (the enzyme breaking down ACh). Important points about the pharmacokinetic properties […]