Antiemetics

Overview Definition Antiemetics are medications used to treat nausea and vomiting. Classification The following classes of drugs are used either alone or in combination for the prevention and treatment of nausea and vomiting: General indications Physiology Nausea and vomiting Control of nausea and vomiting Specific causes Serotonin-Receptor Antagonists Agents Mechanism of action 2nd-generation serotonin-receptor antagonist, […]
Anticholinergic Drugs
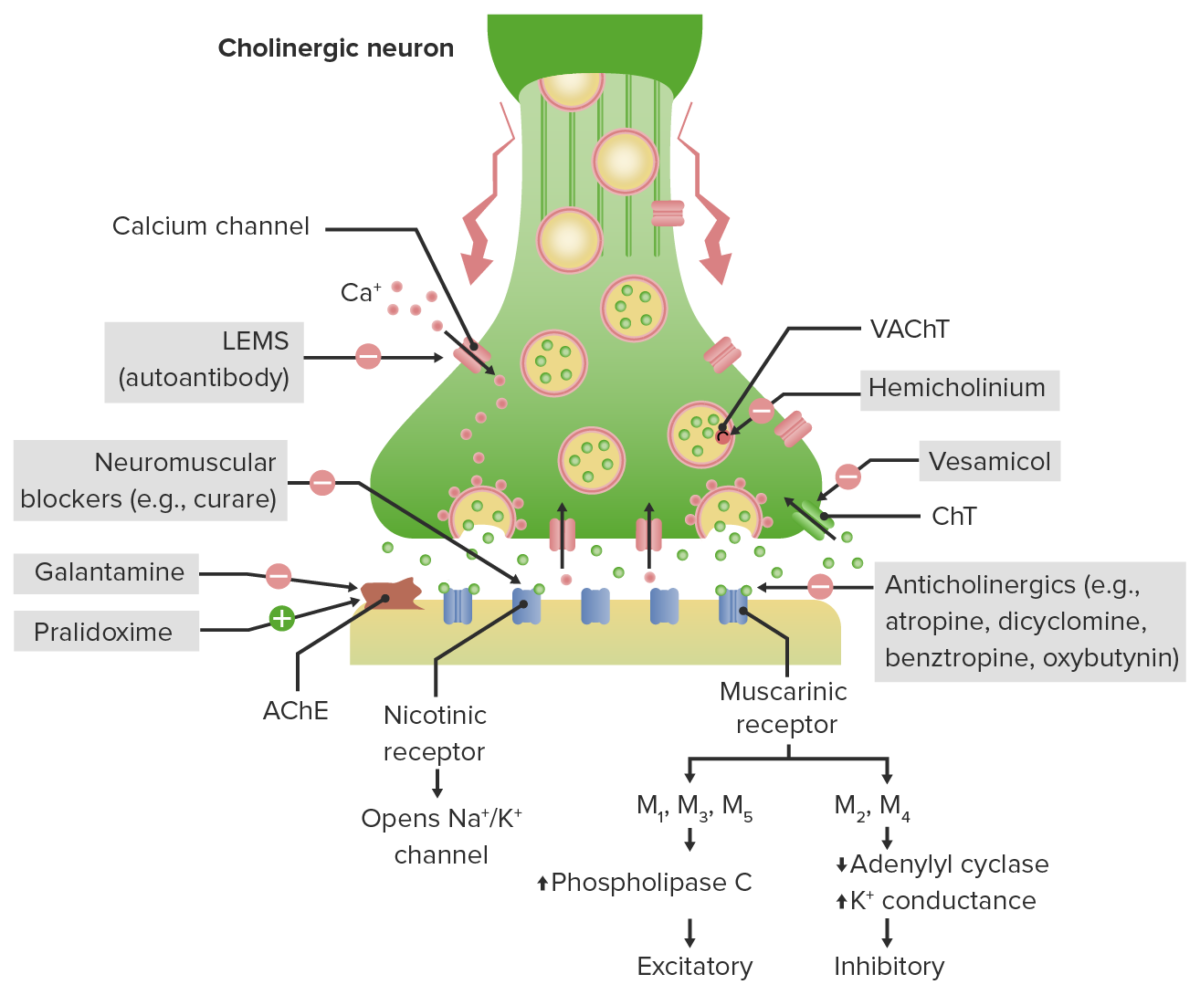
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Atropine is the prototypical anticholinergic drug owing to its antagonism of acetylcholine (ACh) receptors. Overview Mechanism of action and physiologic effects Pharmacokinetics The pharmacokinetic properties of anticholinergic drugs are diverse, as they are available in many forms for different medical uses, such as IV atropine for severe bradycardia, oral tablets for GI […]
Antiestrogens
Classification Several main classes of antiestrogens are to be considered. Prototypical drugs in each class are noted with an asterisk (*). Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators and Selective Estrogen Receptor Downregulators Mechanism of action of SERMs Tamoxifen, raloxifene, ospemifene, bazedoxifene, and clomiphene citrate: Mechanism of action of SERDs Fulvestrant: Physiologic effects SERMs act as estrogen agonists […]
Lipid Control Drugs
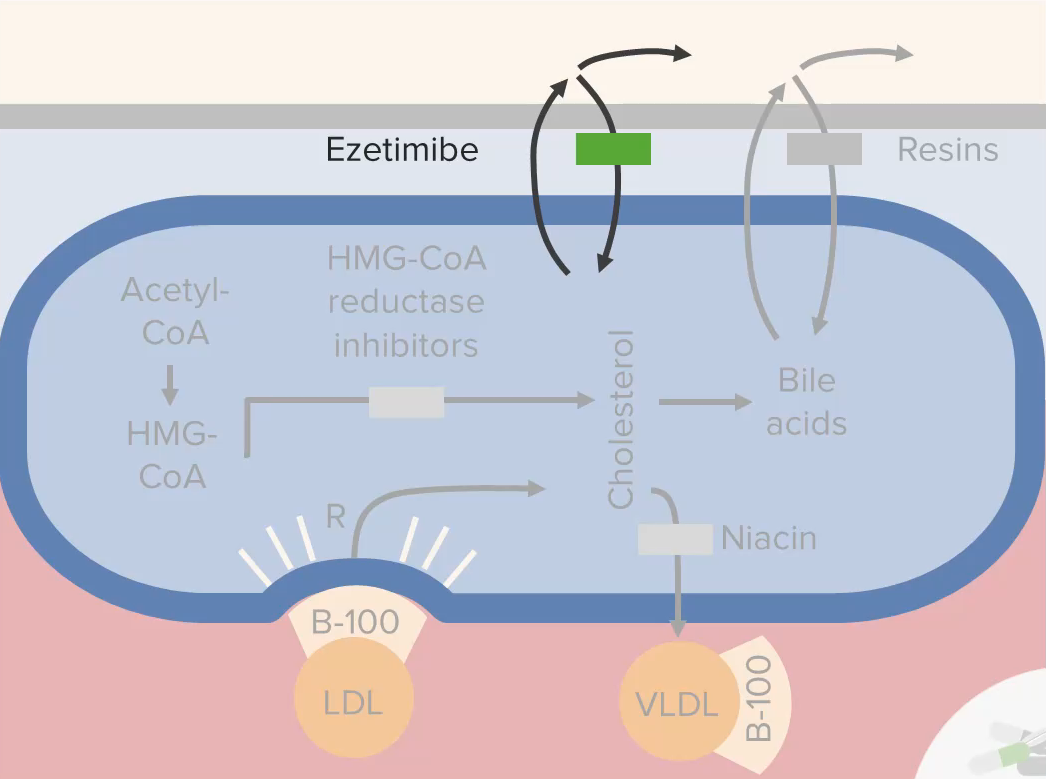
Overview Definition Lipid control agents are a group of medications (other than statins), which manage levels of LDL, HDL, and triglycerides through a variety of mechanisms. Dyslipidemia Lipid control agents PCSK9 Inhibitors Medications in the class Pharmacodynamics Mechanism of action: Physiologic effect: Pharmacokinetics Indications Adverse effects Drug interactions No clinically significant interactions exist. Fibrates Medications […]
Androgens and Antiandrogens
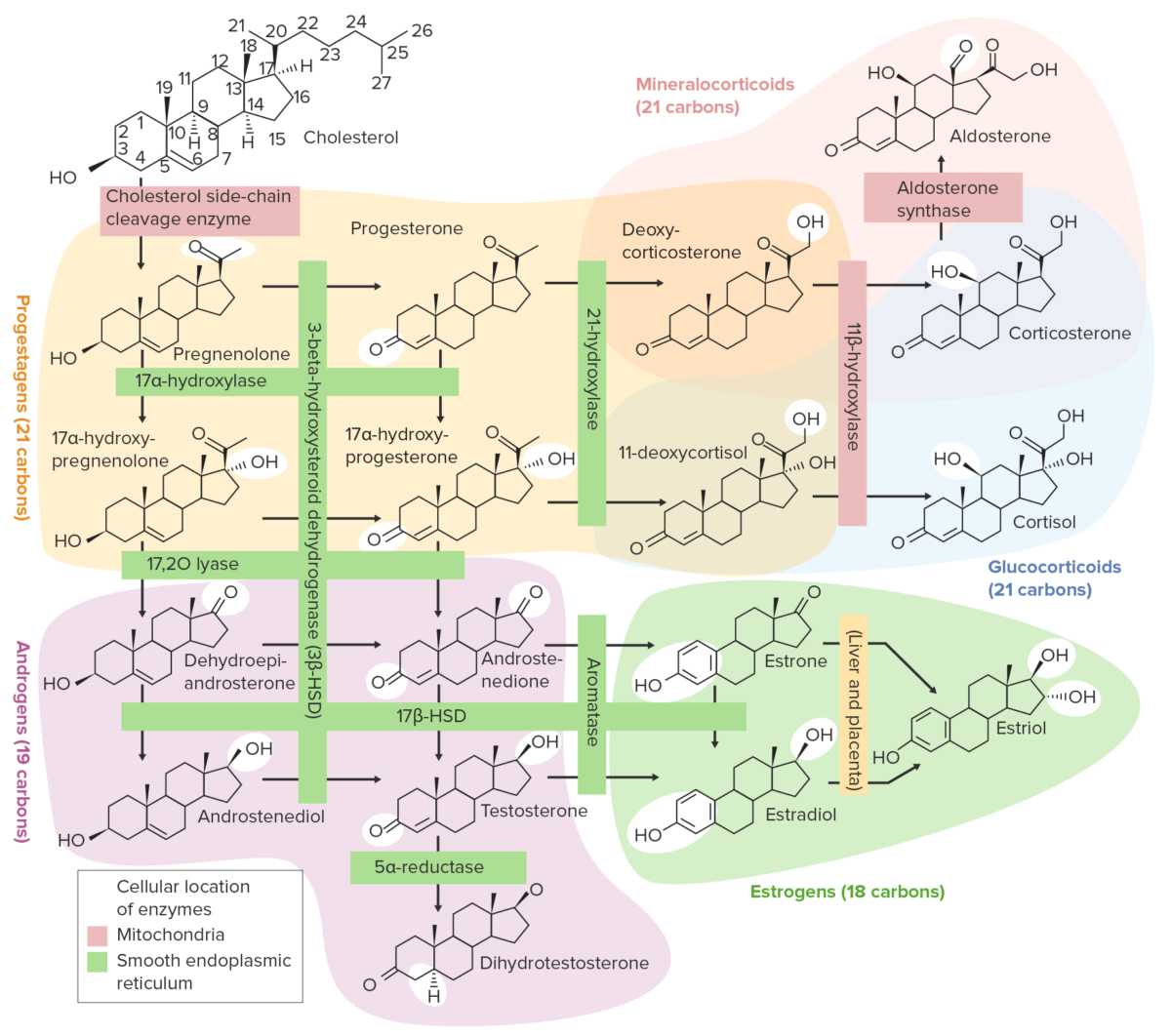
Androgens Definition Androgens are hormones, which lead to the development and maintenance of male sex characteristics. Endogenous androgens Androgens are produced naturally in the gonads (testes and ovaries) and the adrenal glands. The naturally produced androgenic hormones include: Medications in the drug class Pharmacodynamics and mechanism of action Physiologic effects The physiologic effects of endogenously […]
Tricyclic Antidepressants
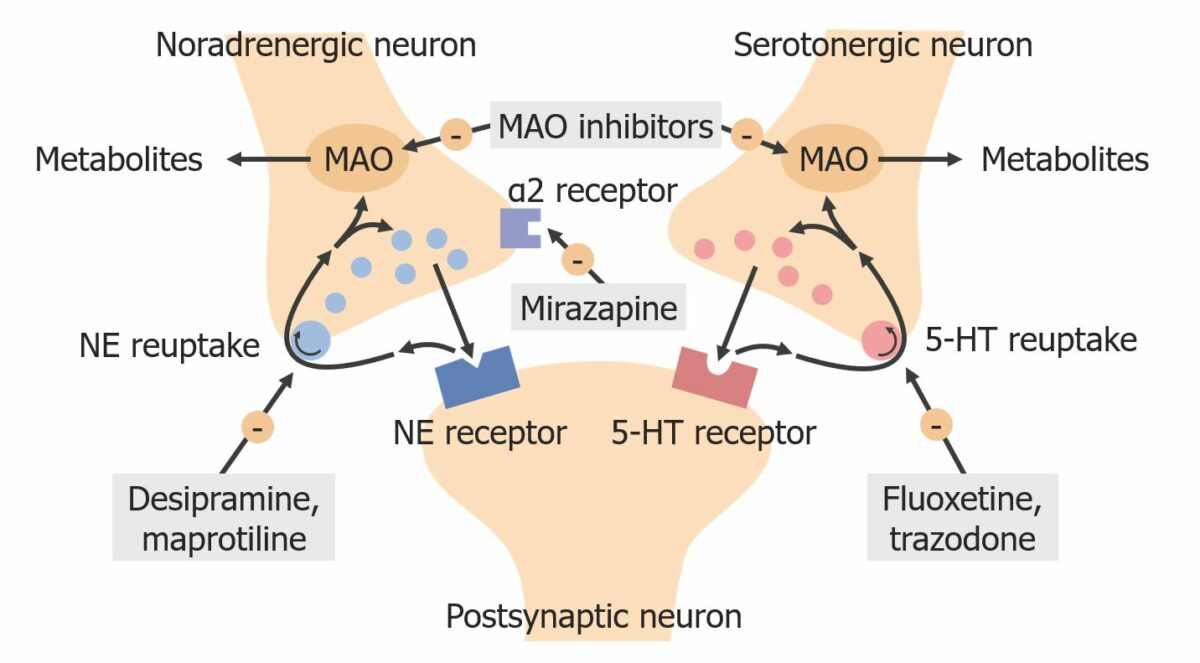
Overview Tricyclics antidepressants (TCAs) Antidepressant medications are named based on the characteristic 3-ring chemical structure. Used mainly for depression, a unipolar mood disorder characterized by persistent low mood, loss of interest, and somatic symptoms for ≥ 2 weeks 2nd-line management for depression after selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) Chemistry Related to phenothiazines structurally Consists of […]
Anesthesiology: History and Basic Concepts
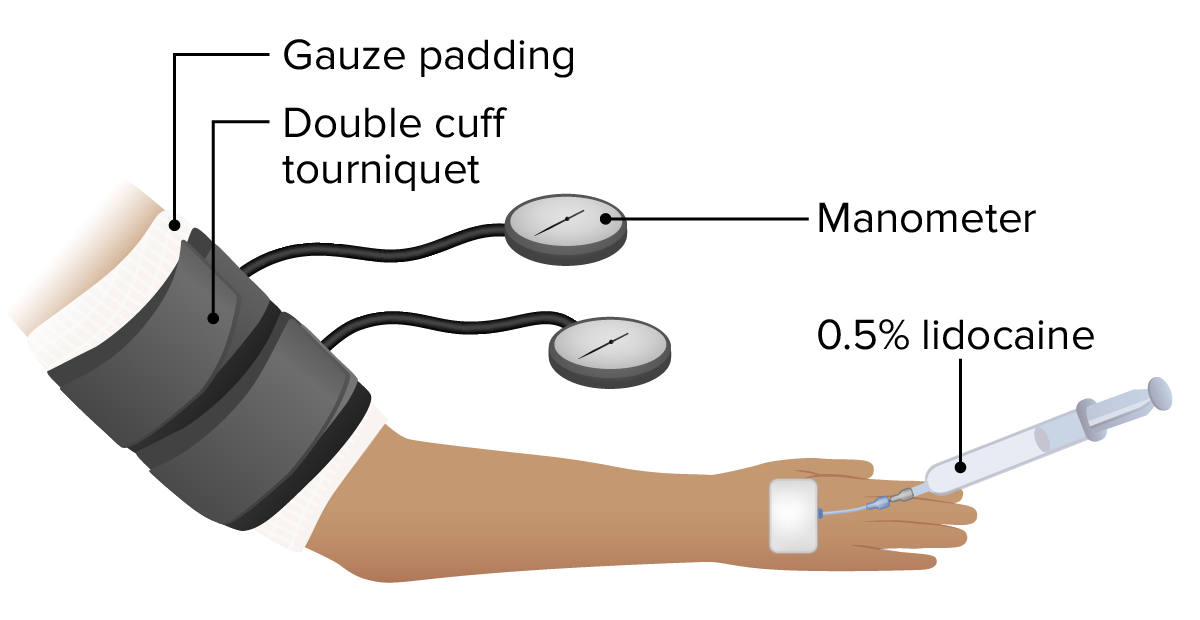
Introduction Definition Anesthesiology is the field of medicine focusing on interventions that bring about a state of anesthesia, which is characterized by a reversible loss of consciousness, as well as analgesia, amnesia, and muscle relaxation. State of anesthesia Certified personnel who perform and manage anesthesia Settings where anesthesia is performed History Historical landmarks in the […]
Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs
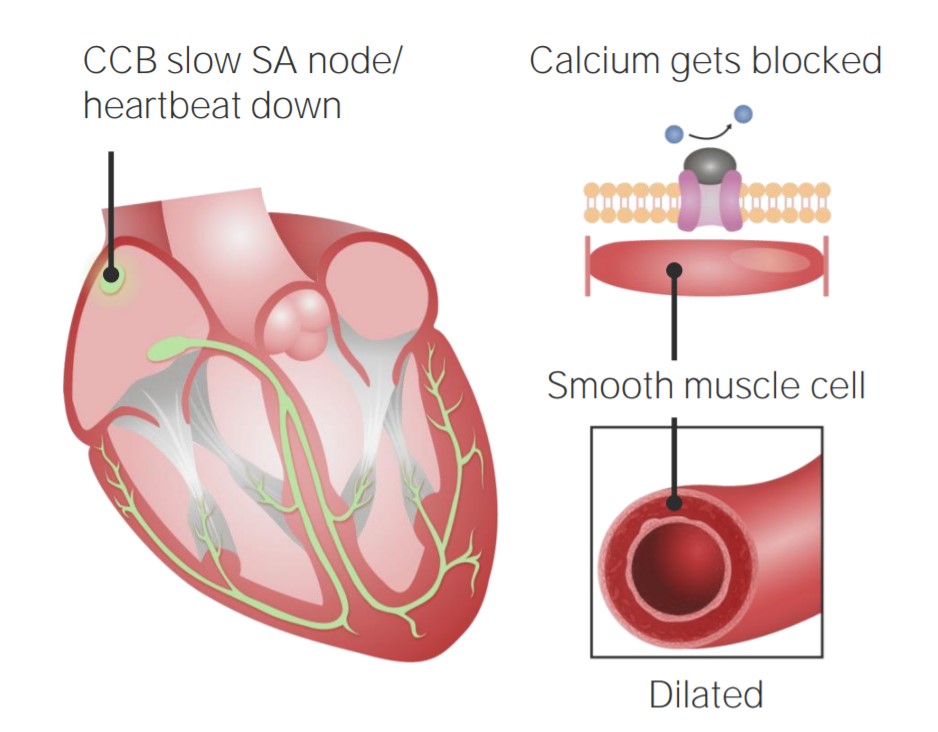
Overview Pulmonary hypertension (PH) Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is defined as an elevated pulmonary arterial pressure. General therapeutic options Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) Inhibitors Chemistry Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Indications Adverse drug effects Precautions Contraindications Drug interactions Soluble Guanylate Cyclase (sGC) Stimulator (Riociguat) Chemistry Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Indications Adverse drug effects Contraindications Drug interactions Prostacyclin Receptor Analogues […]
Second-Generation Antipsychotics
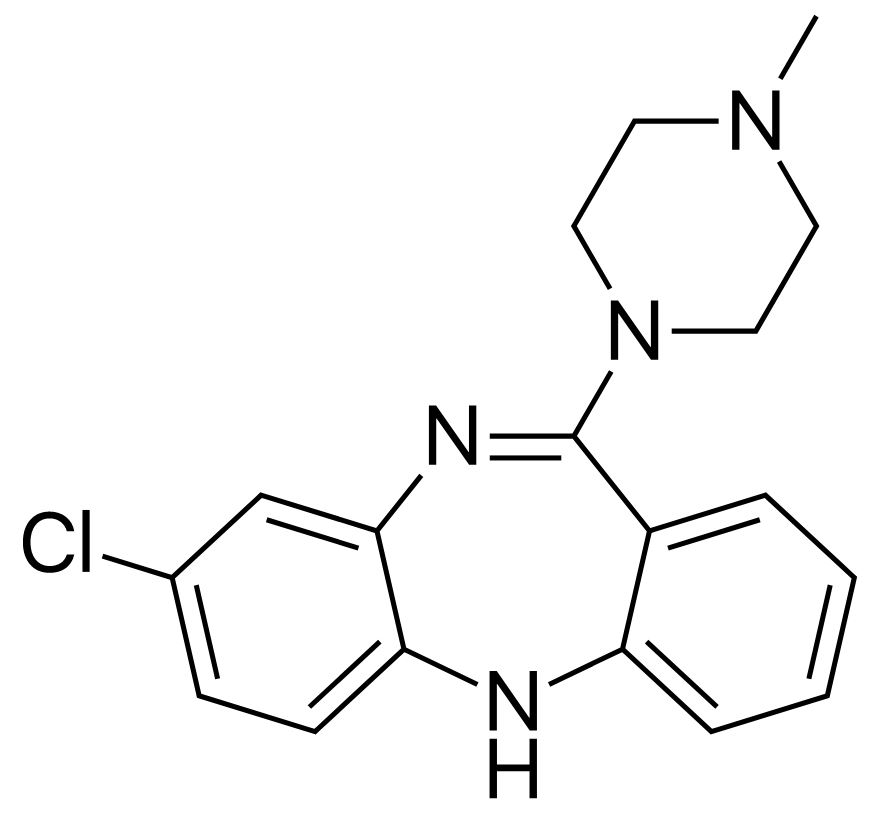
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemical structure Medications in this class Mechanism of action Physiologic effects Pharmacokinetics The 2nd-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) differ significantly from one another in pharmacokinetics. These agents are available as oral tablets/capsules (asenapine is a sublingual tablet or transdermal patch), and some are also available as IM injections. Most SGAs are metabolized by the […]
Immunosuppressants

Overview Definition Immunosuppressants are a class of drugs that decrease the activity of the immune system in conditions such as autoimmune diseases, organ transplantation, and malignancies. Immune system Classification Immunosuppressants can be classified into various categories of drugs with different targets in the immune system and varying mechanisms of action: Biologic Agents Definition Biologic agents […]