Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS
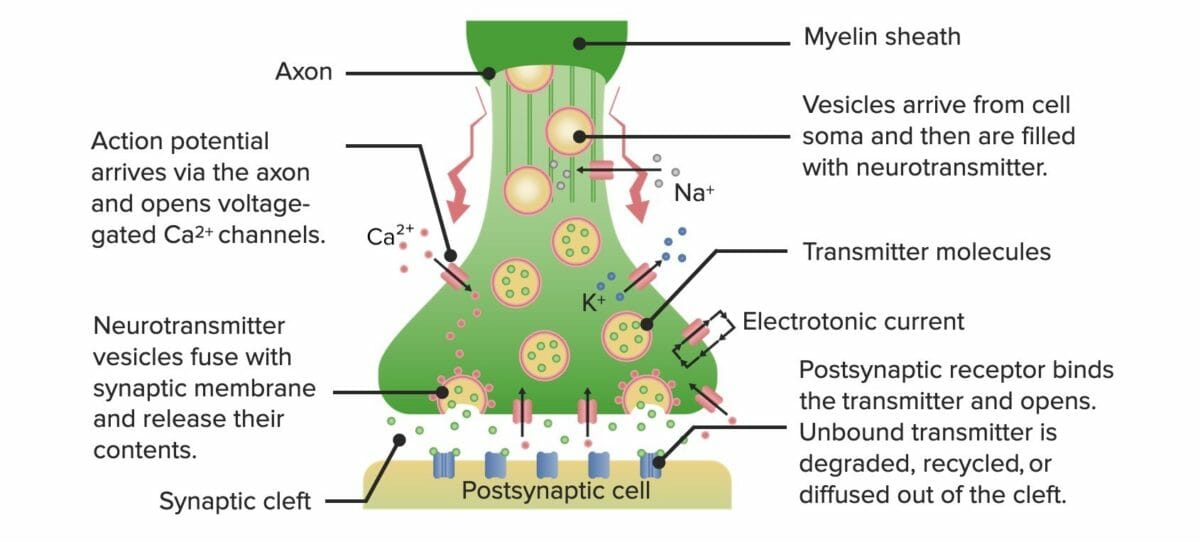
Neurotransmission Synapses and neurotransmission Overview of Neurotransmitters More than 500 unique neurotransmitters have been identified in humans. Characteristics Effects Classes High-yield CNS Neurotransmitters 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)/serotonin Catecholamines Table: Dopaminergic projection pathways Pathway Neuron origin Neuron projection location Functions Mesolimbic Ventral tegmental area Amygdala Cingulate gyrus Frontal cortex Hippocampus Nucleus accumbens Olfactory bulb Emotion Impulsivity Memory and […]
Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins
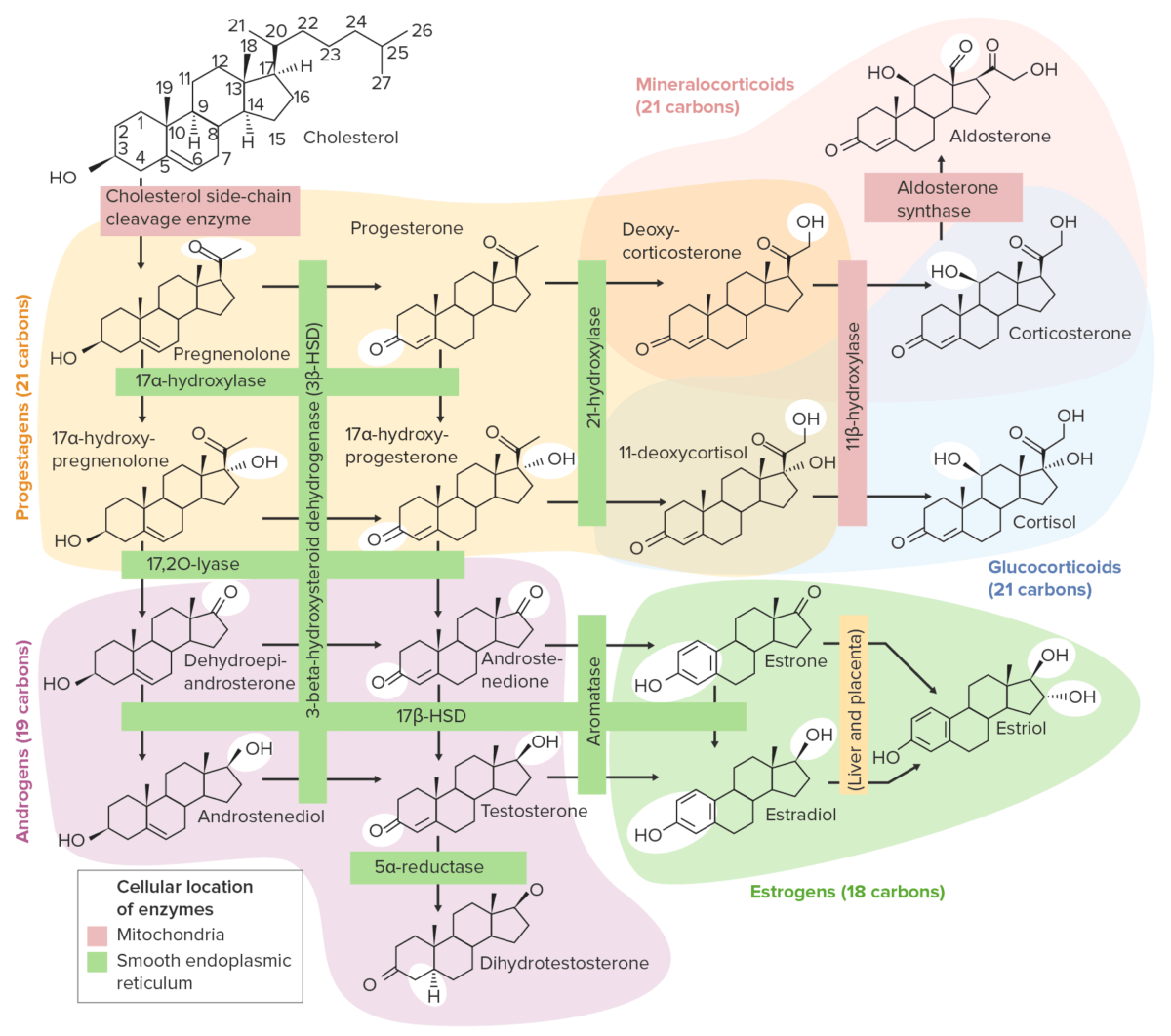
Overview Definitions Classification Estrogens In the body, estradiol is oxidized to estrone, and both estradiol and estrone can be converted to estriol. Estrone is a biologically active estrogen found in compounded medications and some pharmaceutical preparations used to treat menopausal symptoms. Estrone is prepared from the urine of pregnant mares (conjugated equine estrogen (CEE)). Phytoestrogens […]
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
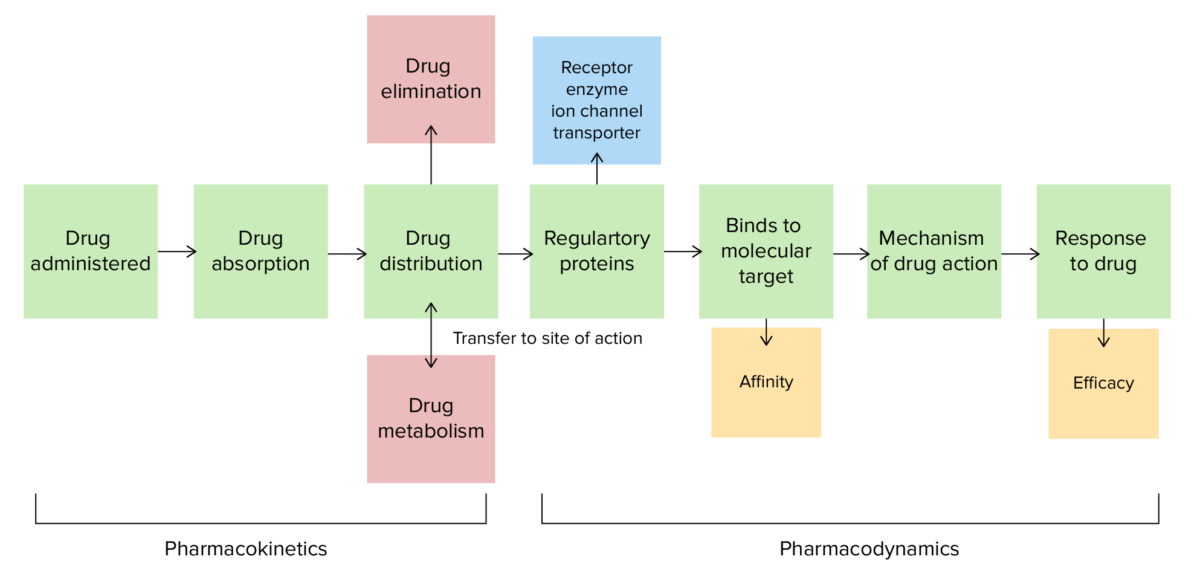
Overview Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics are fields of study that focus on the interplay between medications and the body. Pharmacokinetics is the study of how the human body interacts with a drug: Pharmacodynamics is the study of the effects of a drug and its organ-specific mechanism of action, including effects on the cellular level: Pharmacokinetics: Absorption […]
Heart Failure and Angina Medication
Heart Failure Heart failure (HF) A clinical syndrome characterized by the inability of the cardiac output to meet the metabolic demands of the body: Decreased cardiac output activates the sympathetic nervous system and RAAS: Types: Heart failure classification: General therapy Address the associated conditions or causes: Pharmacologic management depends on the type of heart failure: […]
Multidrug-resistant Organisms and Nosocomial Infections
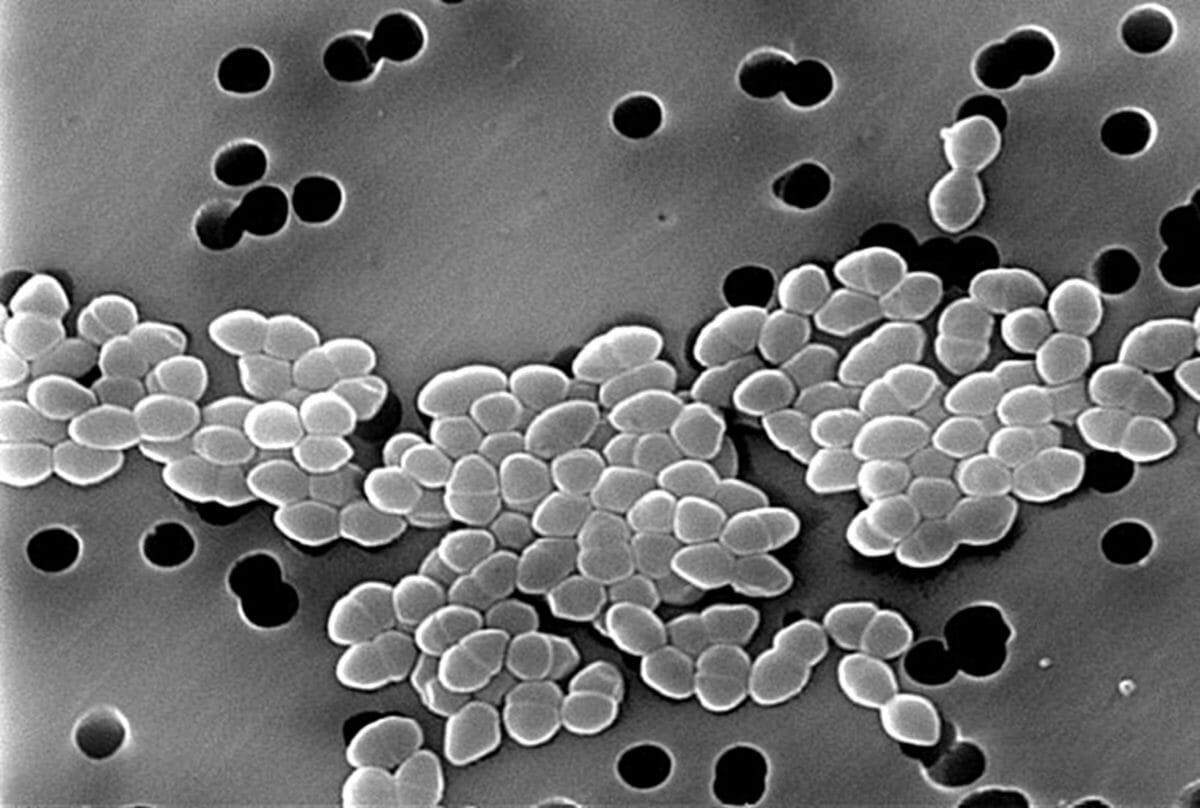
Overview Multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) Hospital-acquired infection (HAI) Other considerations Excluding nosocomial transmission of SARS-CoV-2 during the pandemic, non–bacterial HAIs are less common than bacterial HAIs. Epidemiology Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) MRSA Infections and antibiotics Prevention Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci (VRE) VRE Infections and antibiotics Prevention Bacteria that Produce Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (ESBL) ESBL Infections and antibiotics […]
Dosage Calculation
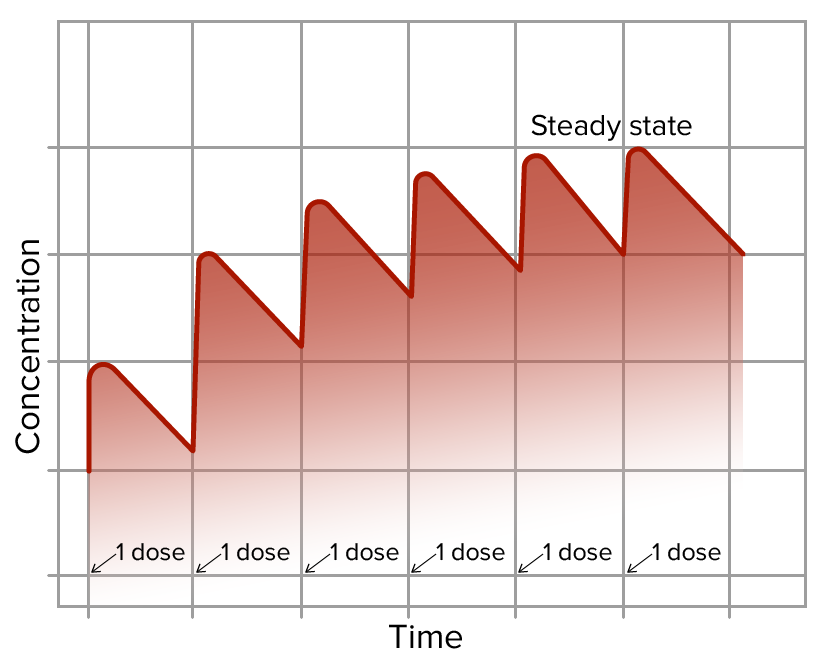
Overview It is important for healthcare professionals including doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and pharmacy technicians to know which medications to prescribe and at what dose to prescribe them. Therapeutic Window Definition Therapeutic window is the dosage range within which the drug is effective (i.e., the dose at which the drug produces the desired effect) without causing […]
Spasmolytics
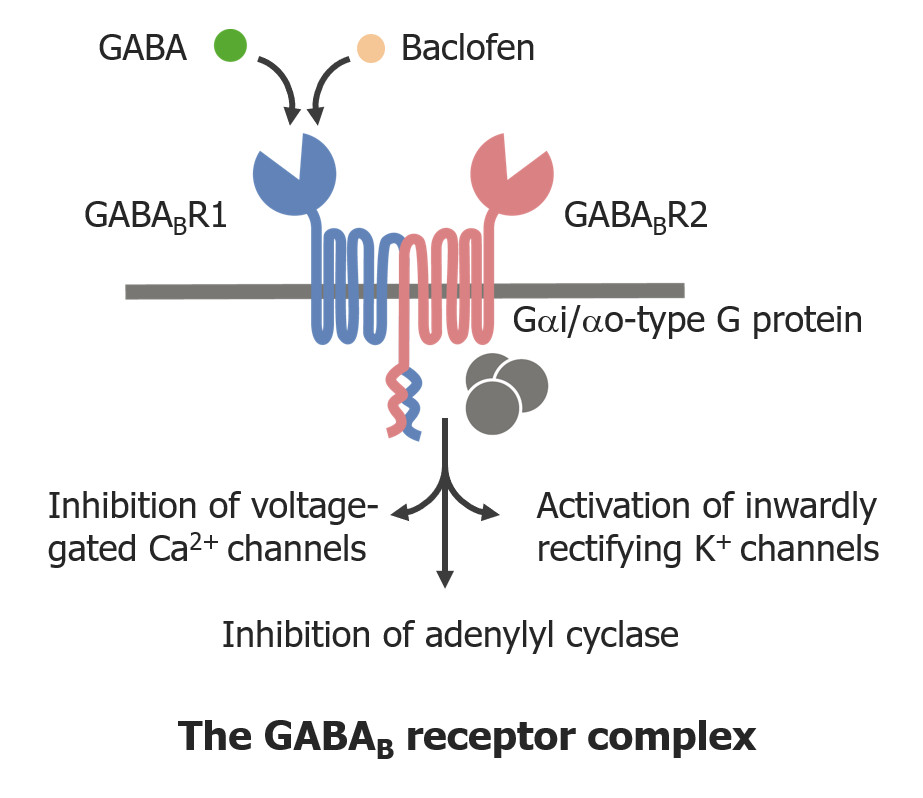
Overview Physiology review Excitation: Excitation-contraction coupling: Function and classification Spasmolytics can be divided based on where and how they exert their effects: CNS Depressants Medications in this group Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Indications Adverse effects Contraindications and precautions Drug interactions Agonists of GABA receptors Medications in this group Mechanism of action Baclofen: Diazepam: Pharmacokinetics Pharmacokinetics […]
Neuromuscular Blockers
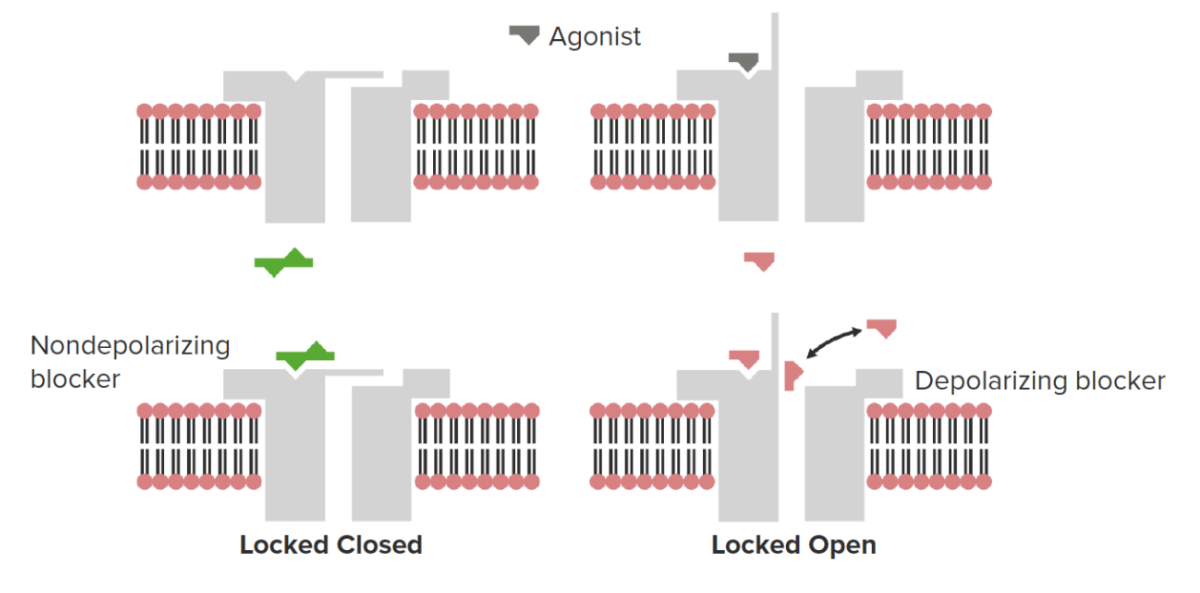
Classification and Mechanism of Action Classification Neuromuscular blockers can be classified based on their mechanism of action. Mechanism of action Normal physiology: Depolarizing neuromuscular blockers: Nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockers: Pharmacokinetics Table: Pharmacokinetics of neuromuscular blocking agents Medication Onset of action (min) Duration of action (min) Metabolism Excretion Succinylcholine < 1 4–6 Plasma pseudocholinesterase Urine Atracurium 2–3 […]
Mineralocorticoids
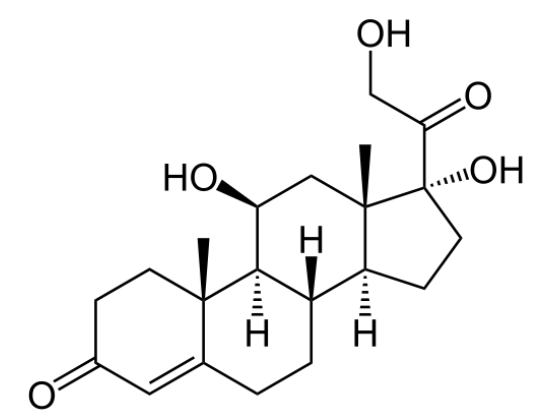
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemical structure Fludrocortisone is the primary drug in this class. Mechanism of action Physiologic effects Pharmacokinetics Absorption Distribution Metabolism and excretion Indications Although fludrocortisone has glucocorticoid activity, it is primarily used for its mineralocorticoid activity (particularly in conditions with inadequate aldosterone production). Adverse Effects and Contraindications Adverse effects There are many side […]
Glucocorticoids
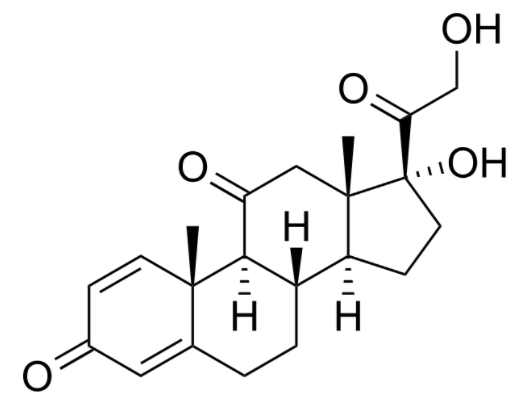
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemical structure Glucocorticoids are synthetic analogs of cortisol and cortisone. Alterations may include: Fluorination (dexamethasone, betamethasone) Methylation (methylprednisolone) Physiology Endogenous glucocorticoids are: Derived from cholesterol (which is synthesized from acetyl-CoA) Secreted from the zona fasciculata Effects: respond to immediate stressors ↑ Immediate available energy through: Fat and protein catabolism → ↑ blood […]