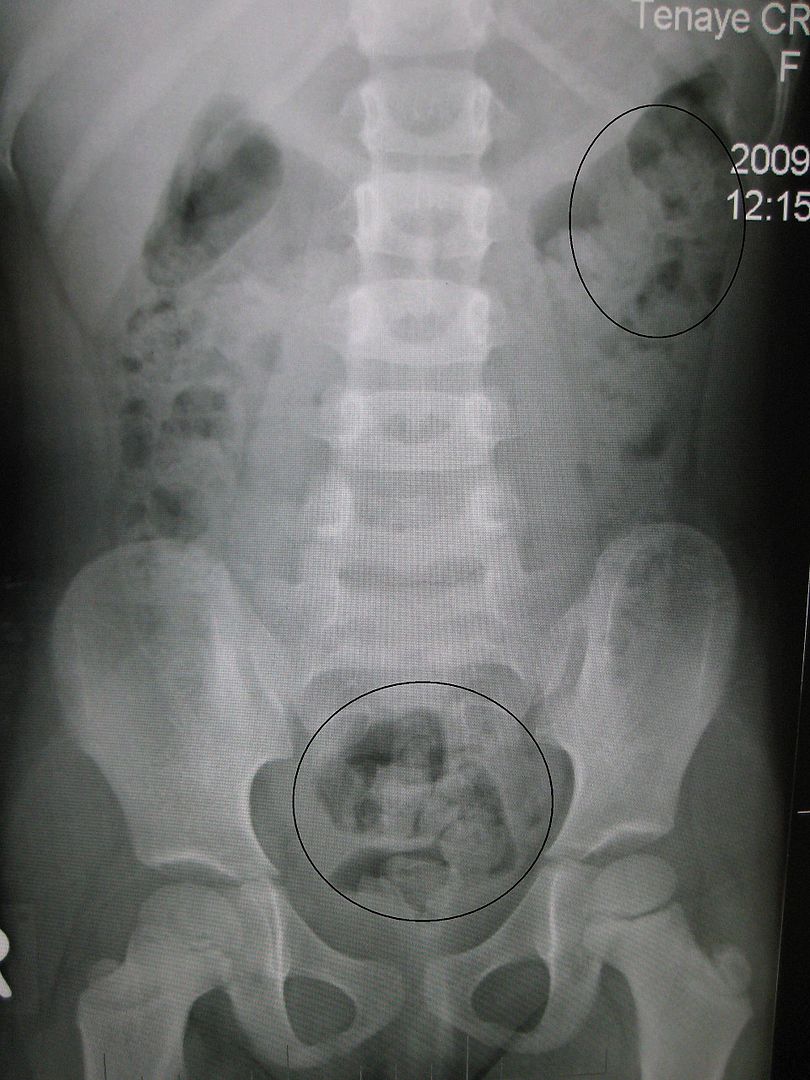
Congenital Duodenal Obstruction
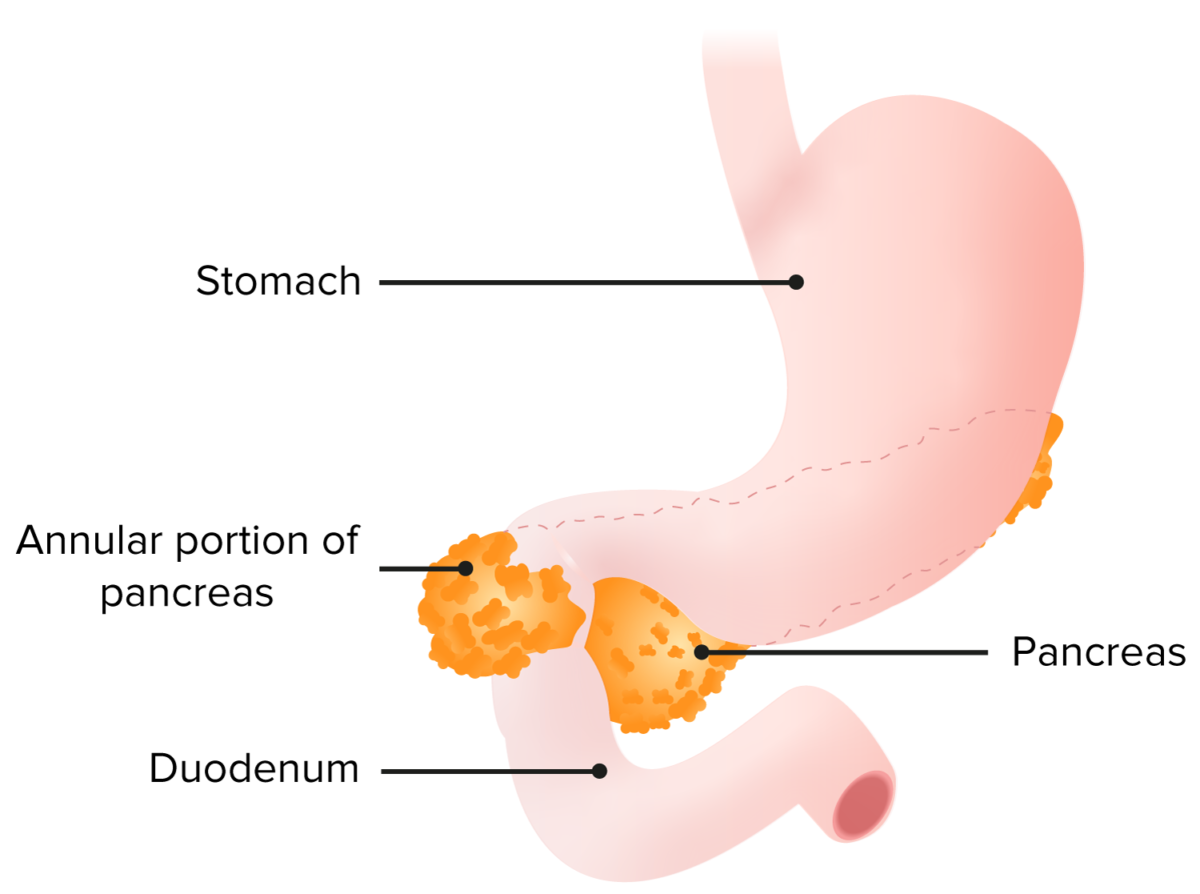
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Clinical Presentation Signs and symptoms of intestinal obstruction: Associated abnormalities: Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis History Physical exam Imaging Management Medical therapy Surgical management References
Pediatric Constipation
Overview Definition Table: Rome IV pediatric functional constipation criteria Infants and toddlers (≤4 years developmental age) Children (>4 years developmental age) At least 2 of the following findings for over 1 month: At least 2 of the following findings for over 1 month, occurring at least once per week: 2 or fewer bowel movements per […]
Esophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal Fistula
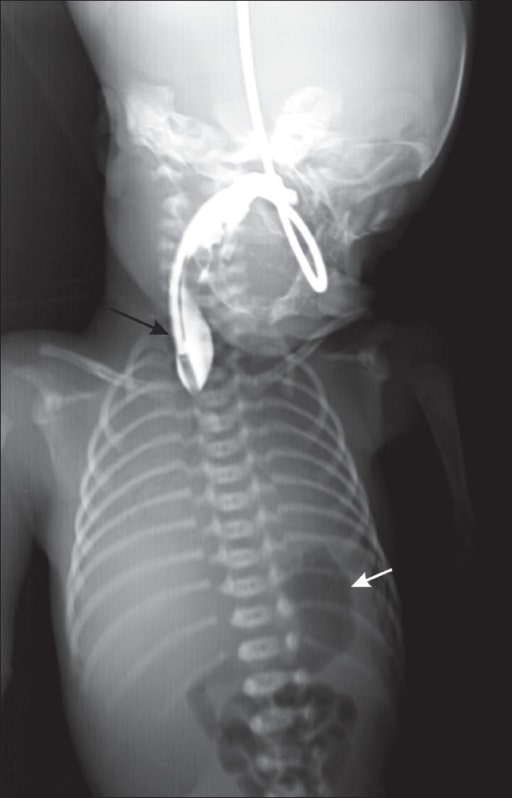
Overview Definitions Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) and esophageal atresia (EA) are congenital malformations of the esophagus and lower respiratory tract. Epidemiology Etiology Classification of EA and TEF Types Description Incidence Type A EA without TEF Approximately 8% of cases Type B EA with TEF to the proximal esophageal segment Approximately 1% of cases Type C EA […]
Congenital Renal Abnormalities
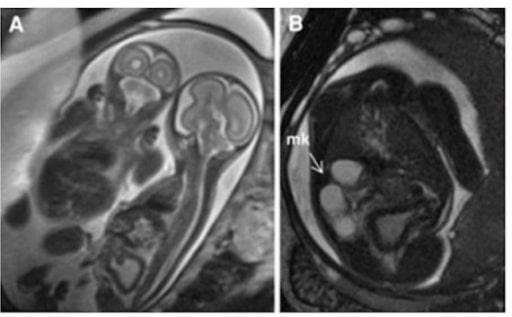
Renal Embryology The kidney develops in the pelvis and migrates cranially. Three separate renal systems form in sequence, giving rise to the kidney, in association with the urinary tract and urogenital system: Disorders of the Renal Parenchyma Introduction Renal embryologic disorders affecting the size, the shape, or the structure of kidney parenchyma (renal dysgenesis): Renal […]
Fluid Replacement Therapy in Children
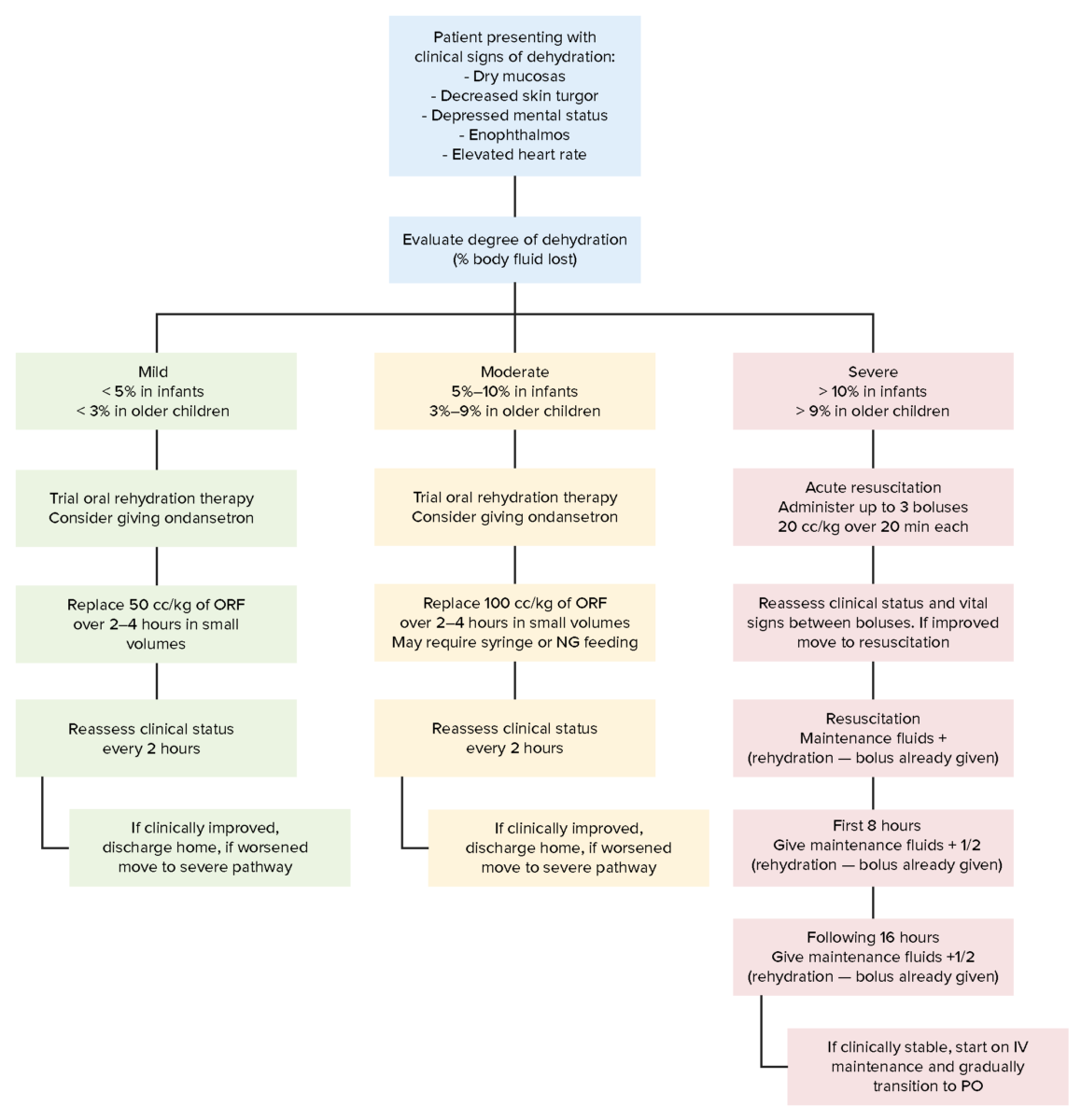
Overview Definition Dehydration is a decrease in total body water, both intracellular and extracellular. Epidemiology Dehydration in children worldwide is primarily caused by diarrhea: Etiology Diagnosis In most cases, a good history and physical exam are sufficient to diagnose dehydration and its etiology. Laboratory testing is reserved for severe cases and to monitor rehydration. History […]
Acute Bronchiolitis
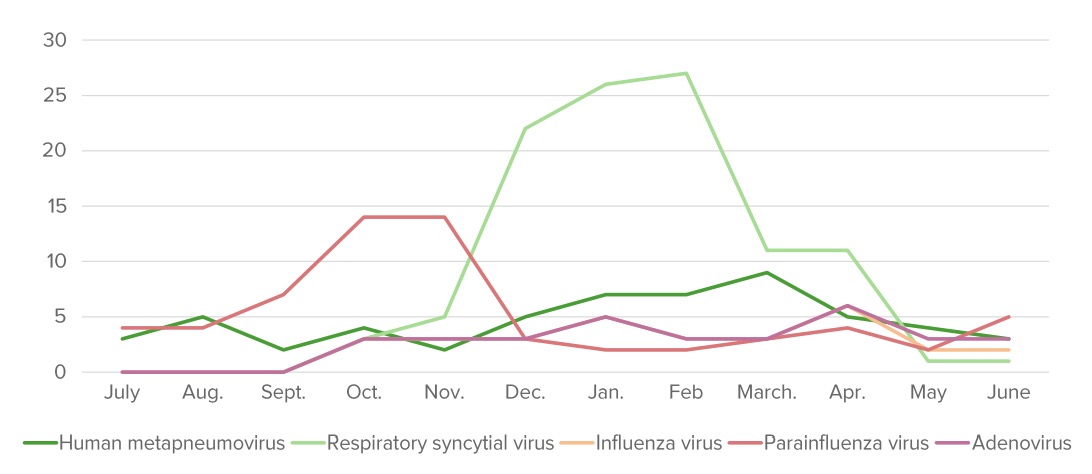
Overview Definition Acute bronchiolitis is a clinical constellation of respiratory symptoms (increased work of breathing, wheezing, and crackles) caused by acute inflammation of the small airways (small bronchi and bronchioles), typically secondary to viral infections. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathophysiology Pathologic changes are noted within 24 hours of contact with a pathogen: Clinical […]
Blount’s Disease
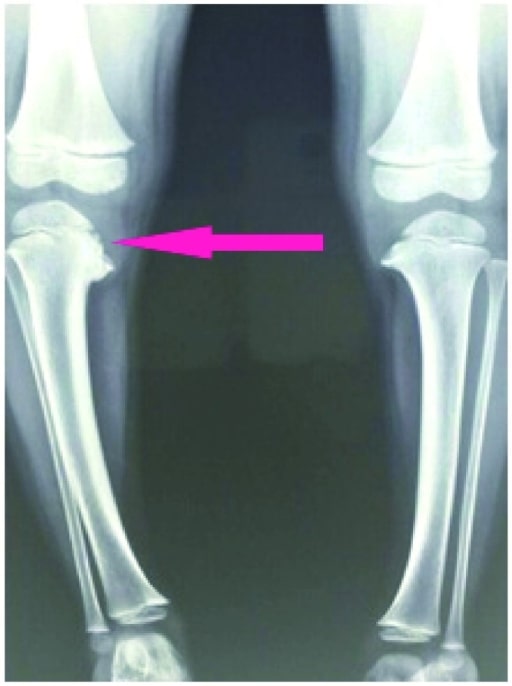
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Blount’s disease (BD) is the progressive bowing of the legs produced by abnormal ossification at the medial aspect of the tibial epiphysis. Classification Epidemiology Etiology and Pathophysiology Etiology The exact cause of BD is not known and is believed to be multifactorial or due to a combination of hereditary and developmental […]
Pulmonary Stenosis
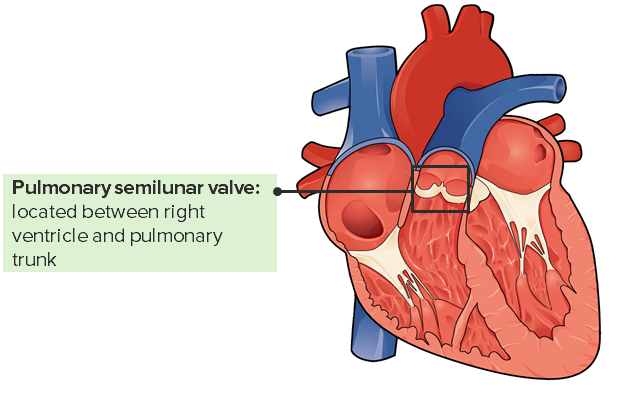
Overview Anatomy Pulmonary (or pulmonic) valve: Table: Overview of pulmonary valve disorders Pulmonary stenosis (PS) Pulmonary regurgitation (PR) Etiology Mostly congenital Mostly acquired Murmur Systolic murmur, left upper sternal border (preceded by a systolic click that decreases with inspiration) Diastolic murmur, left upper sternal border, increases with inspiration S2 Split S2 with soft and delayed […]
Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD)
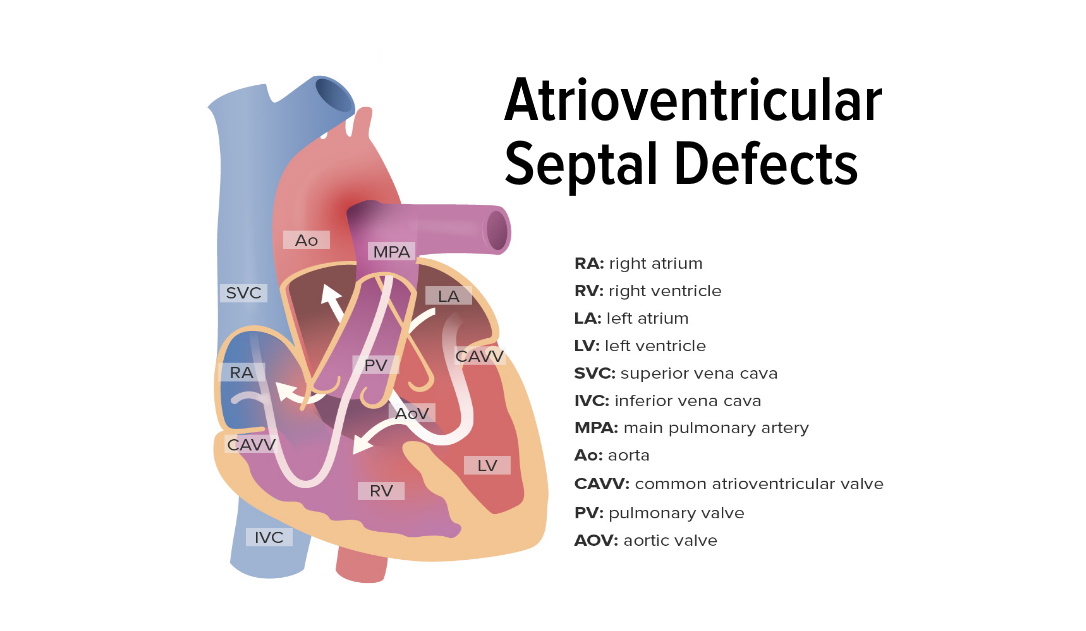
Overview Definitions Classification Classification of AVSD is based on anatomy of defect: Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Symptoms of AVSD (cyanosis, heart failure, and pulmonary hypertension) are due to excessive blood flow in the pulmonary system. Partial AVSD Complete AVSD Clinical Presentation Partial AVSD Complete AVSD Diagnosis Chest X-ray Severe partial or complete atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD): […]
Physical Examination of the Newborn

Introduction Before examining the infant, a thorough chart review should be performed. Maternal history Infant’s birth history Table: APGAR scoring Sign 0 points 1 point 2 points A Appearance Cyanotic or mottled Cyanotic extremities, pink body Pink extremities and body P Pulse Absent < 100/min > 100/min G Grimace No response to stimulation Grimace with […]