Toddler’s Fractures
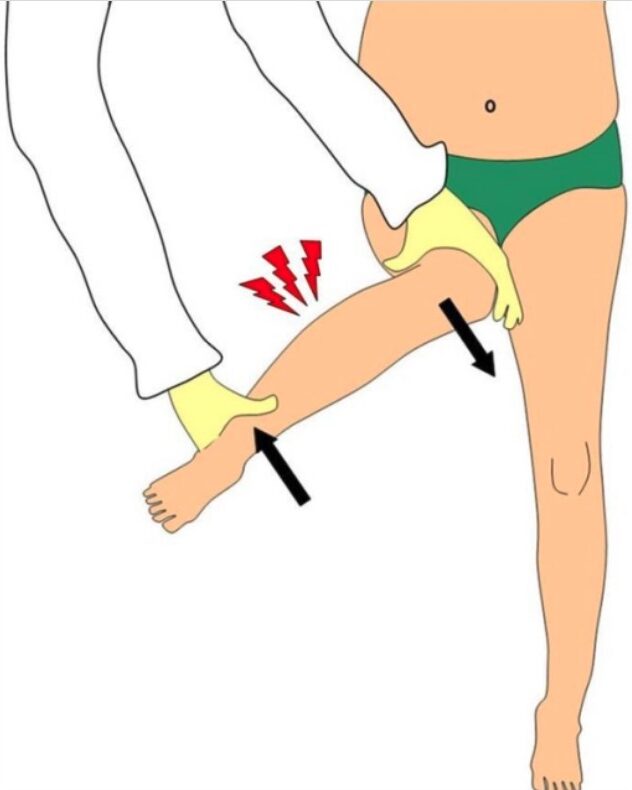
Overview Definition Non-displaced spiral fractures of the distal tibia are often called “toddler’s fractures,” as they are commonly seen in children who are just starting to walk. Epidemiology Etiology Diagnosis and Management Clinical presentation Diagnosis of toddler’s fracture may be challenging due to lack of documented trauma and the inability of the child to localize […]
Greenstick Fracture
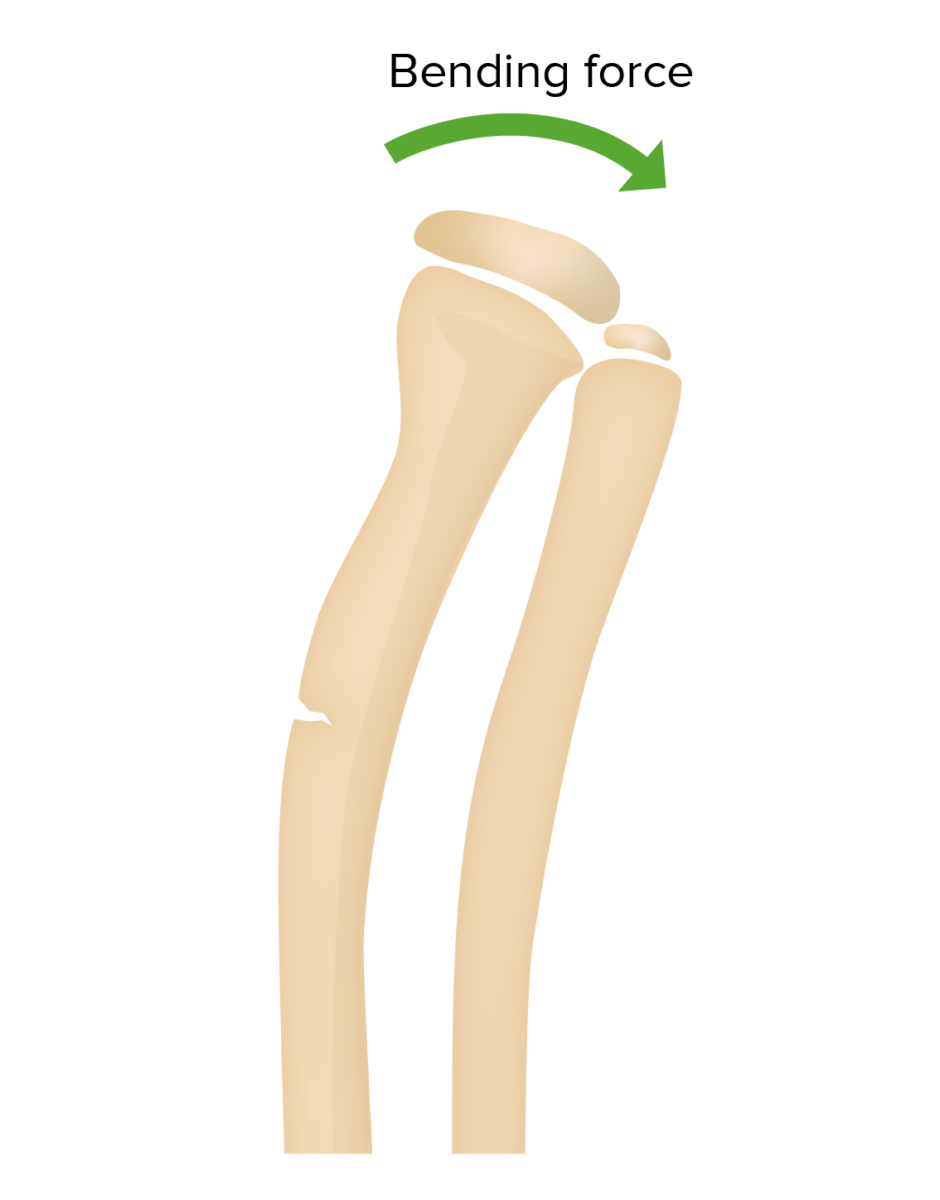
Overview Definition A greenstick fracture is a partial thickness fracture, which involves a complete fracture of the cortex and periosteum on only 1 side of the bone. The fracture is termed “greenstick” as it resembles the break in a live, green twig where 1 side of the stick remains intact. Epidemiology Etiology Location: Causes: Pathophysiology […]
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
Overview Definition The ductus arteriosus (DA) is a fetal blood vessel connecting the left pulmonary artery to the aorta, bypassing the pulmonary circulation. Failure of the vessel to close and involute within 72 hours of birth results in a condition called patent ductus arteriosus (PDA). Epidemiology Embryology and Pathophysiology Embryology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation The severity […]
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS)
Overview Definition Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) is characterized by the underdevelopment of the left side of the heart. The components of HLHS include: Epidemiology Variants There are 3 types of HLHS based on the morphology of the cardiac valves: Etiology Pathophysiology Normal cardiac physiology and development In HLHS Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Management Emergent management […]
Apophyseal Avulsion Fracture
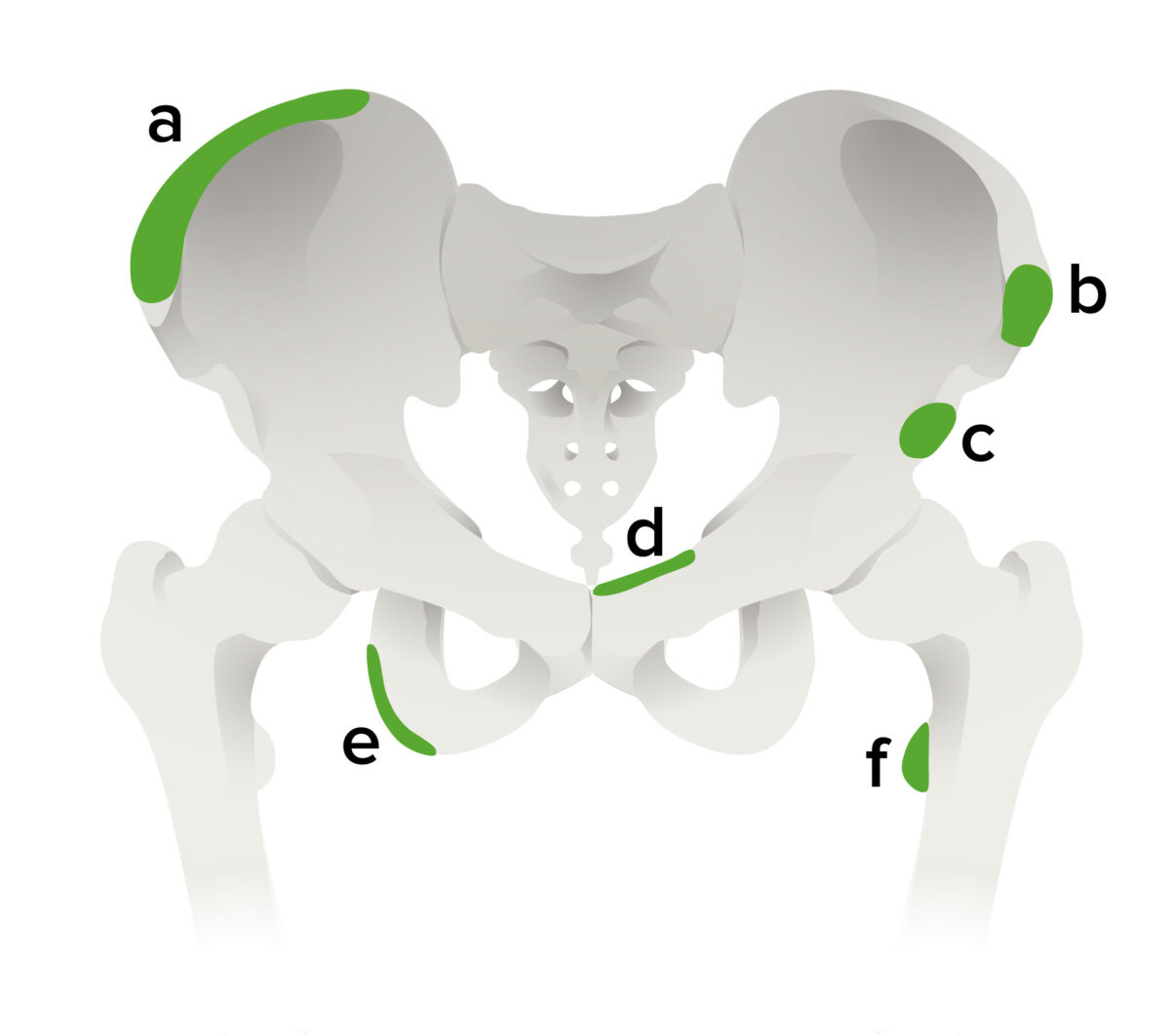
Overview Definition An avulsion fracture occurs when part of an apophysis is ripped off by the ligament due to a sudden forceful eccentric or concentric contraction of the muscle attached to it. Epidemiology Anatomy Apophyses exist on many bones and are the insertion site of a number of ligaments. Avulsion fractures can occur at any […]
Erythema Infectiosum
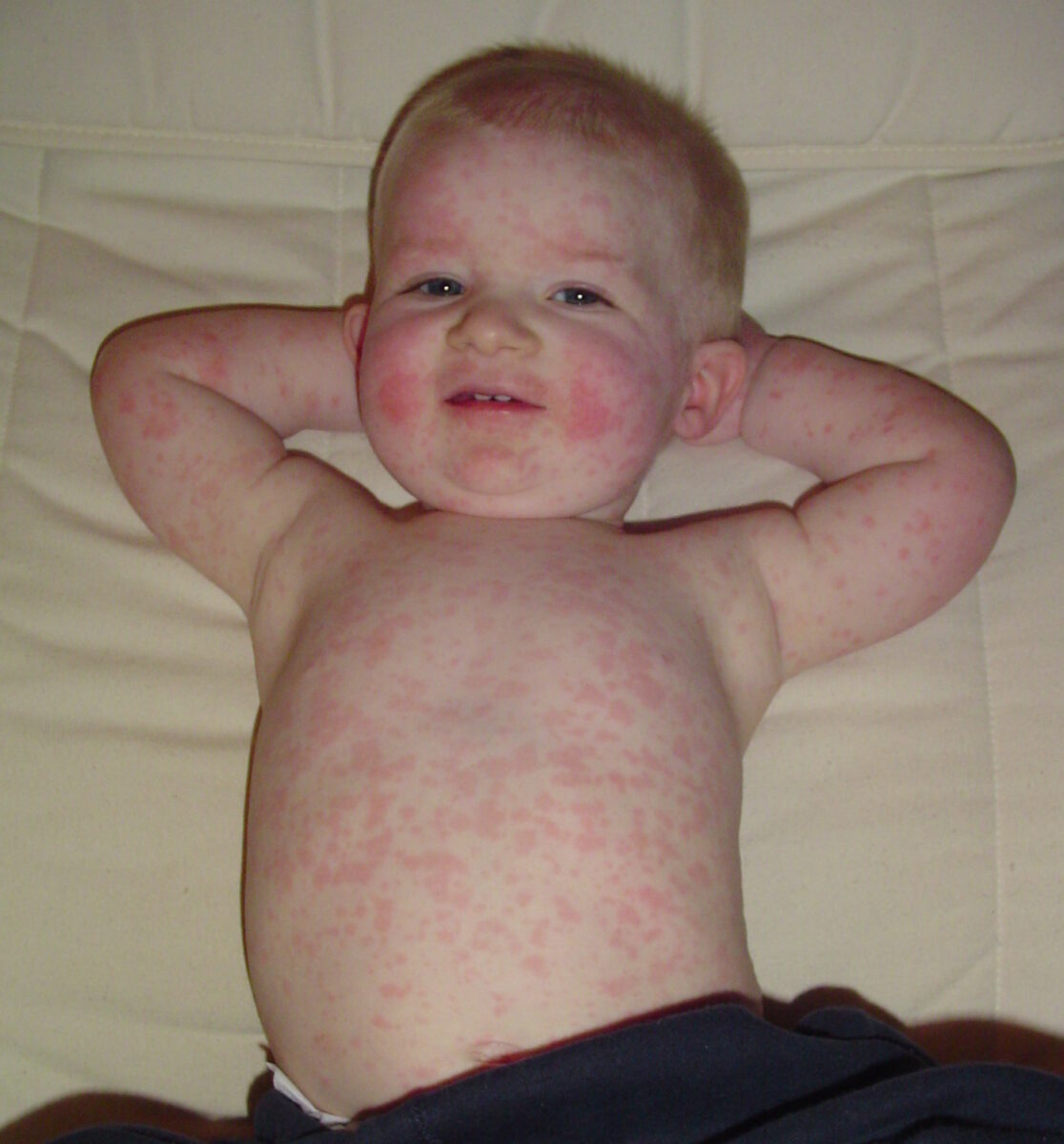
Overview Pathophysiology Mode of transmission Incubation The incubation period is 4–21 days. Pathogenesis Clinical Presentation Initial prodromal symptoms (viremia) Later symptoms (viremia resolved) Complications Diagnosis and Management Diagnostic approach Treatment Prevention Differential Diagnosis Table: Comparison of common childhood rashes Number Other names for the disease Etiology Description 1st disease Measles Rubeola 14-day measles Morbilli Measles […]
Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease
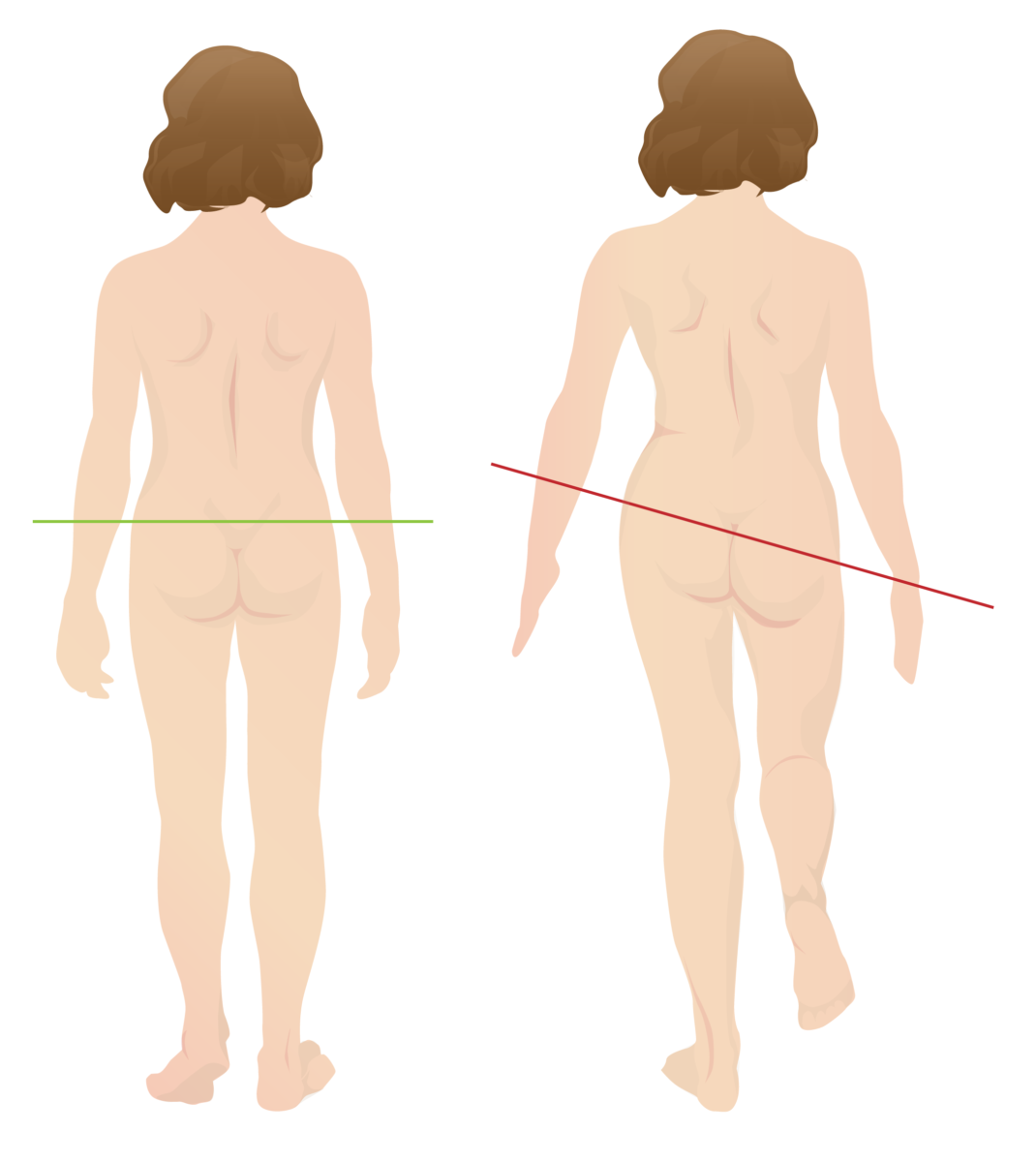
Overview Definition Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease (LCPD), also called coxa plana, is a disorder of the hip in which blood supply to the proximal femoral epiphysis is temporarily interrupted, resulting in avascular necrosis and permanent deformity of the femoral head and acetabulum. Epidemiology Etiology Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease is a multifactorial disease caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, […]
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis
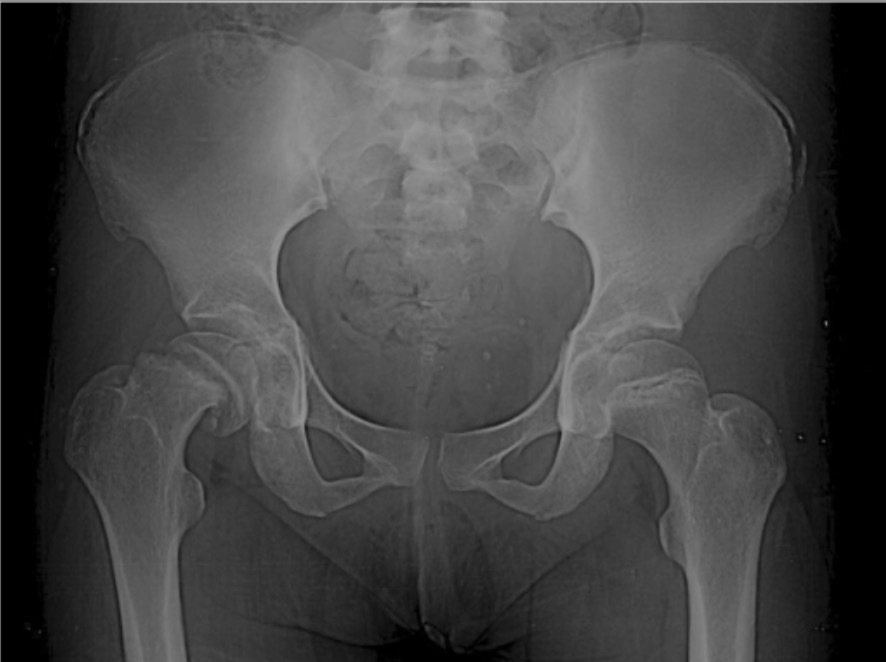
Overview Definition Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE) is a hip disorder common in adolescence that features the displacement of the capital epiphysis of the femoral head through the growth plate (physis) in relationship to the femoral neck. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE) is considered a Salter-Harris type 1 fracture, because SCFE is a transverse fracture […]
Foot Deformities
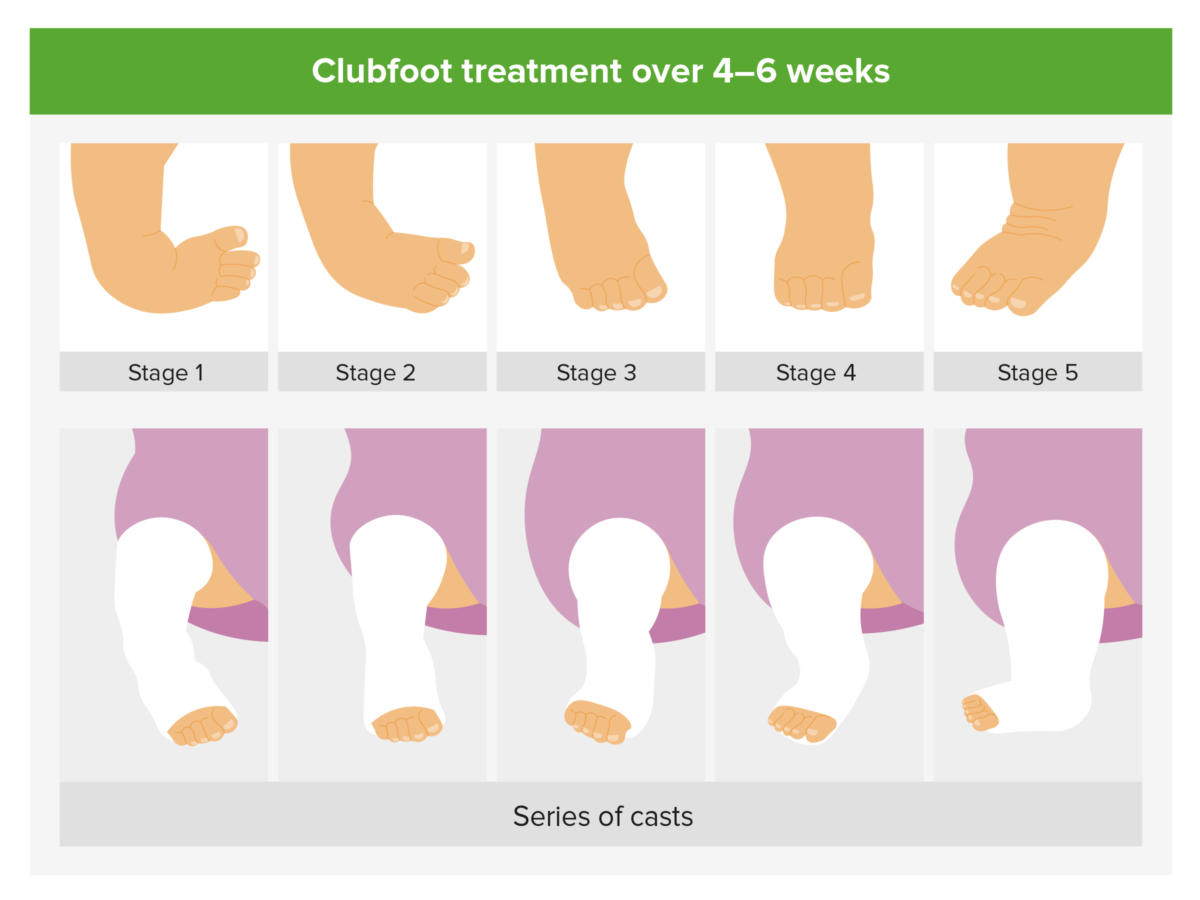
Clubfoot (Talipes Equinovarus) Definition Clubfoot, also called talipes equinovarus, is a complex condition with a plantar flexed foot (equinus), adductus of the forefoot, and an inversion deformity of the heel (varus). Epidemiology Etiology Etiology is debated, as the majority of infants with clubfoot have no identifiable syndromic, genetic, or extrinsic cause. Classification There are multiple […]
Ebstein’s Anomaly
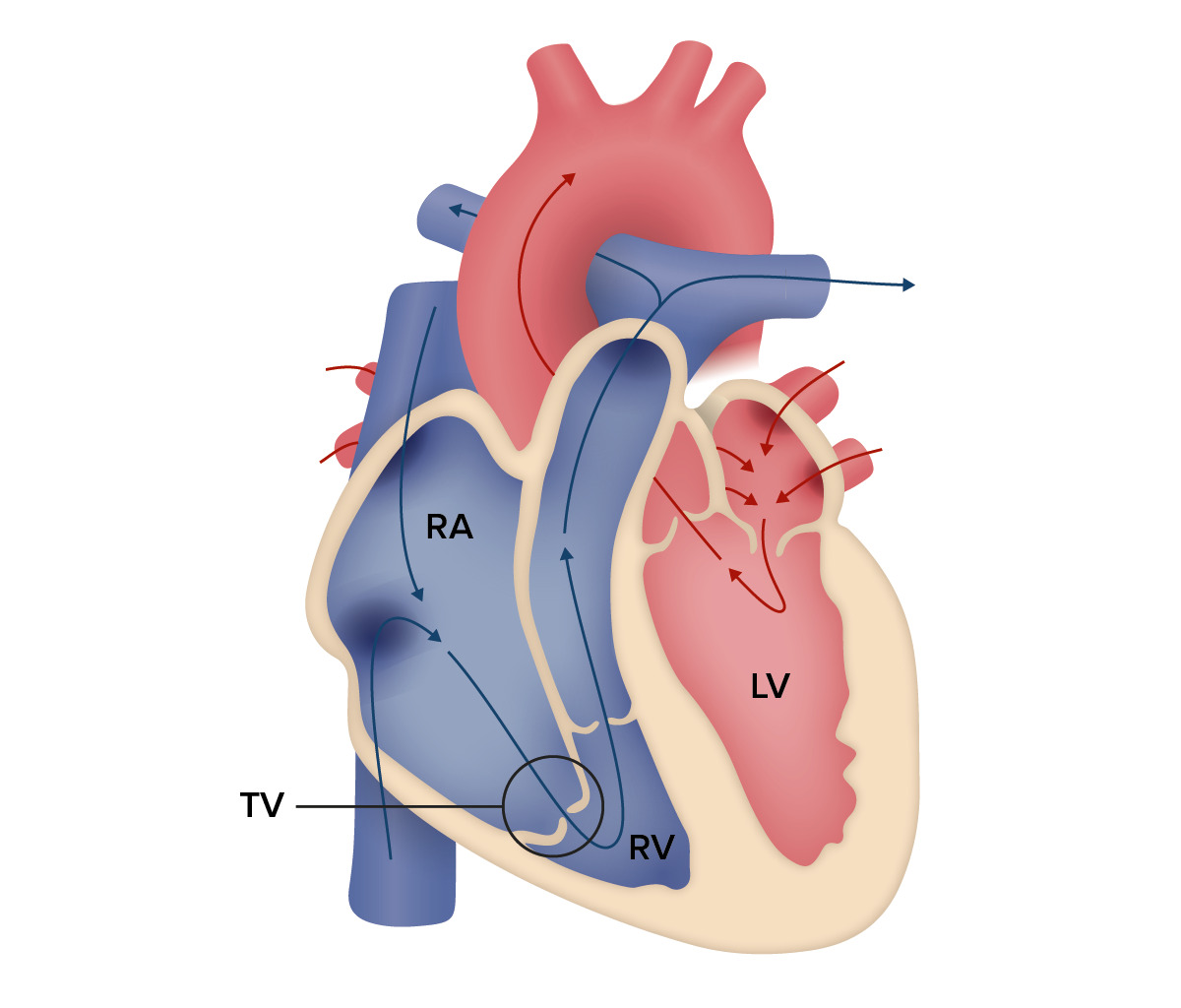
Overview Definition Ebstein’s anomaly (EA) is a cyanotic congenital heart disease (CHD) characterized by the downward displacement of the septal and posterior leaflets of the tricuspid valve (TV) into the right ventricle (RV). Morphology Epidemiology Etiology Failure of delamination (separation) of the TV from the myocardial wall due to: Pathophysiology The basis of cyanosis and […]