Minimal Change Disease
Overview Definition Minimal change disease (MCD) is a primary glomerular disorder of unclear etiology that causes nephrotic syndrome. The term “minimal” refers to the minimal structural changes of the glomeruli when observed under light microscopy. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Management Management Classification based on response to corticosteroids Complications Differential Diagnosis References
Primitive Reflexes
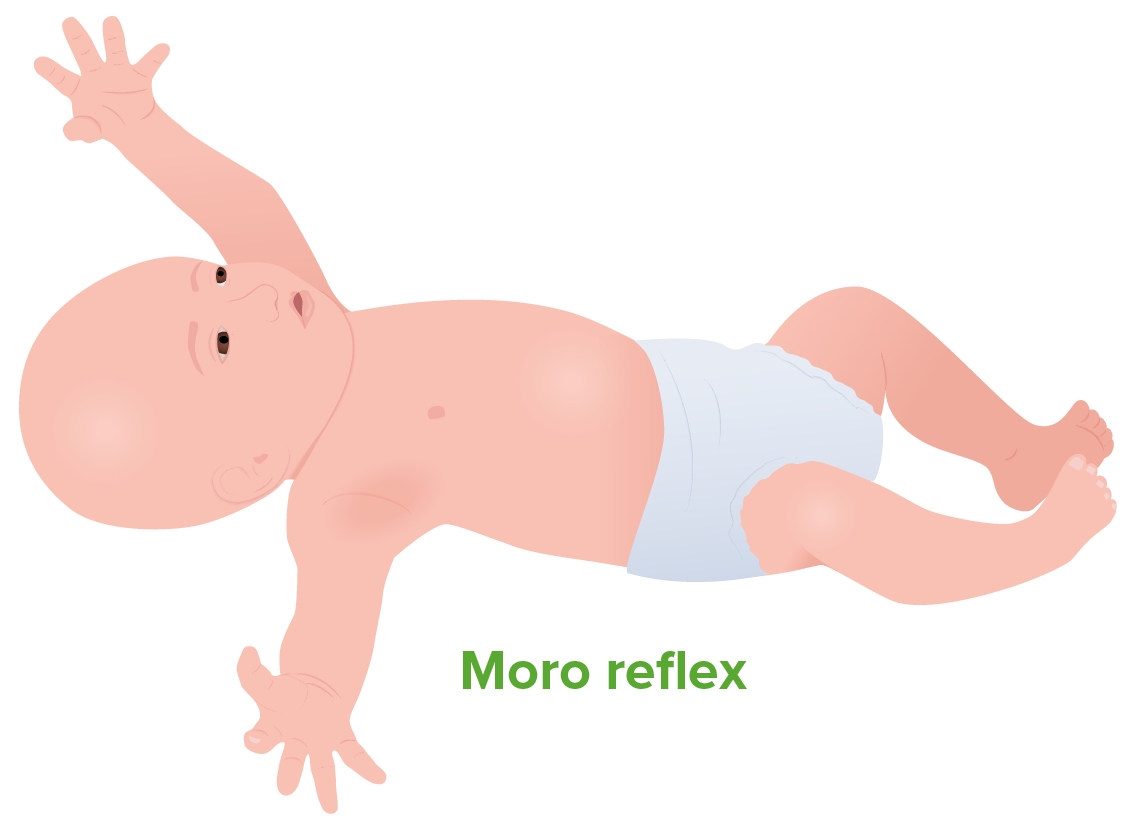
Moro Reflex Rooting Reflex Suck-Swallow Reflex Palmar Grasp Reflex Plantar Reflex (Babinski Sign) Stepping Reflex Tonic Neck Reflex Galant Reflex Summary Table: Summary of primitive reflexes Reflex Stimulus Reaction Disappears Moro Pull up → drop Spreads arms → pulls them back 3–6 months Rooting Stroke cheek/mouth. Orients mouth toward the stimulus 4 months Palmar grasp […]
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder
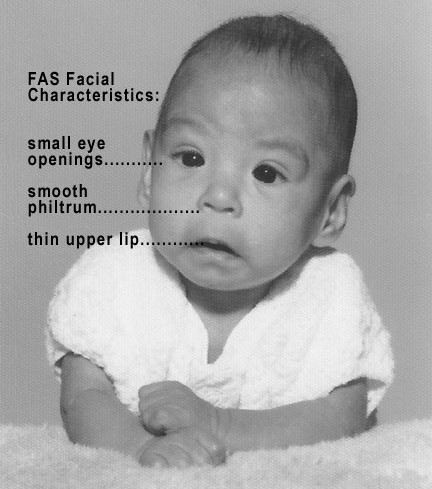
Overview Definition Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD) Consists of the postnatal physical, developmental, cognitive, and psychiatric deficits noted in a patient who has been exposed to alcohol while in utero. Epidemiology Etiology Classification Being an umbrella term, FASD has multiple conditions nested within it: Pathophysiology Alcohol is a teratogen that has irreversible effects: Factors that […]
Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Overview Definition Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) is a condition caused by a lack of pulmonary surfactant, most commonly seen in preterm infants born at < 28 weeks of gestation. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Normal fetal lung development Surfactant Respiration at birth and RDS Clinical Presentation Signs and symptoms Course of RDS Diagnosis Management Prevention of […]
Seizures in Children
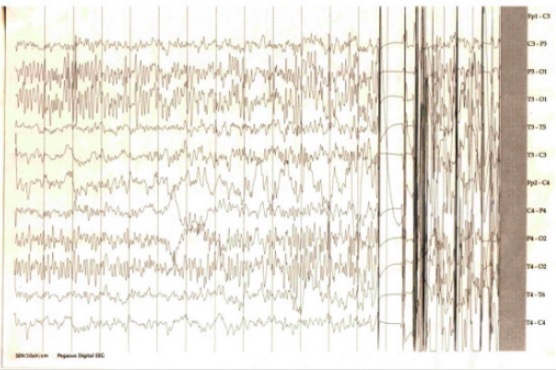
Overview Definition A seizure is an abnormal, excessive, and hypersynchronous firing of neurons in the brain. Epidemiology Classification Separating seizures into different types guides testing, treatment, and prognosis. The classification system was revised in 2017 by the International League Against Epilepsy and is now based on 3 key features: where the seizure begins in the brain, level […]
Failure to Thrive
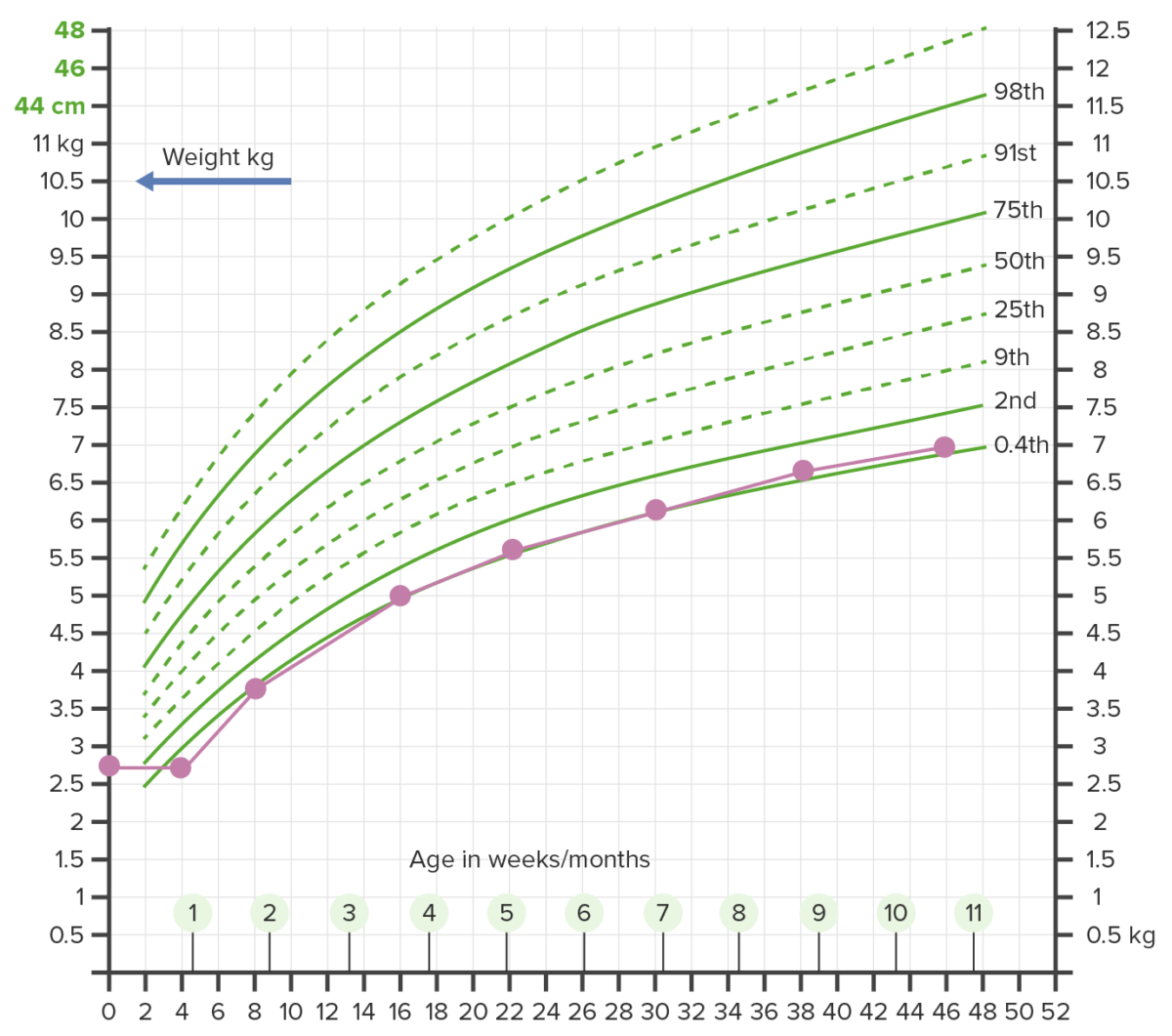
Overview Definition Failure to thrive (FTT) describes suboptimal weight gain and growth in children. Failure to thrive is measured as a drop below the 5th percentile for age and sex, or a drop in weight that crosses 2 major percentile lines on standardized growth charts in a 6-month period. Multiple definitions exist and are considered […]
Pediatric Vomiting

Definition and Etiology Definition Vomiting (emesis) refers to the forceful oral expulsion of gastric contents. Etiology Clinical Presentation History A complete history should be elicited to narrow the differential diagnosis of vomiting in a child. Physical examination Table: Degree of dehydration in children Mild Moderate Severe Weight loss < 5% in infants < 3% in […]
Pulmonary Hypoplasia
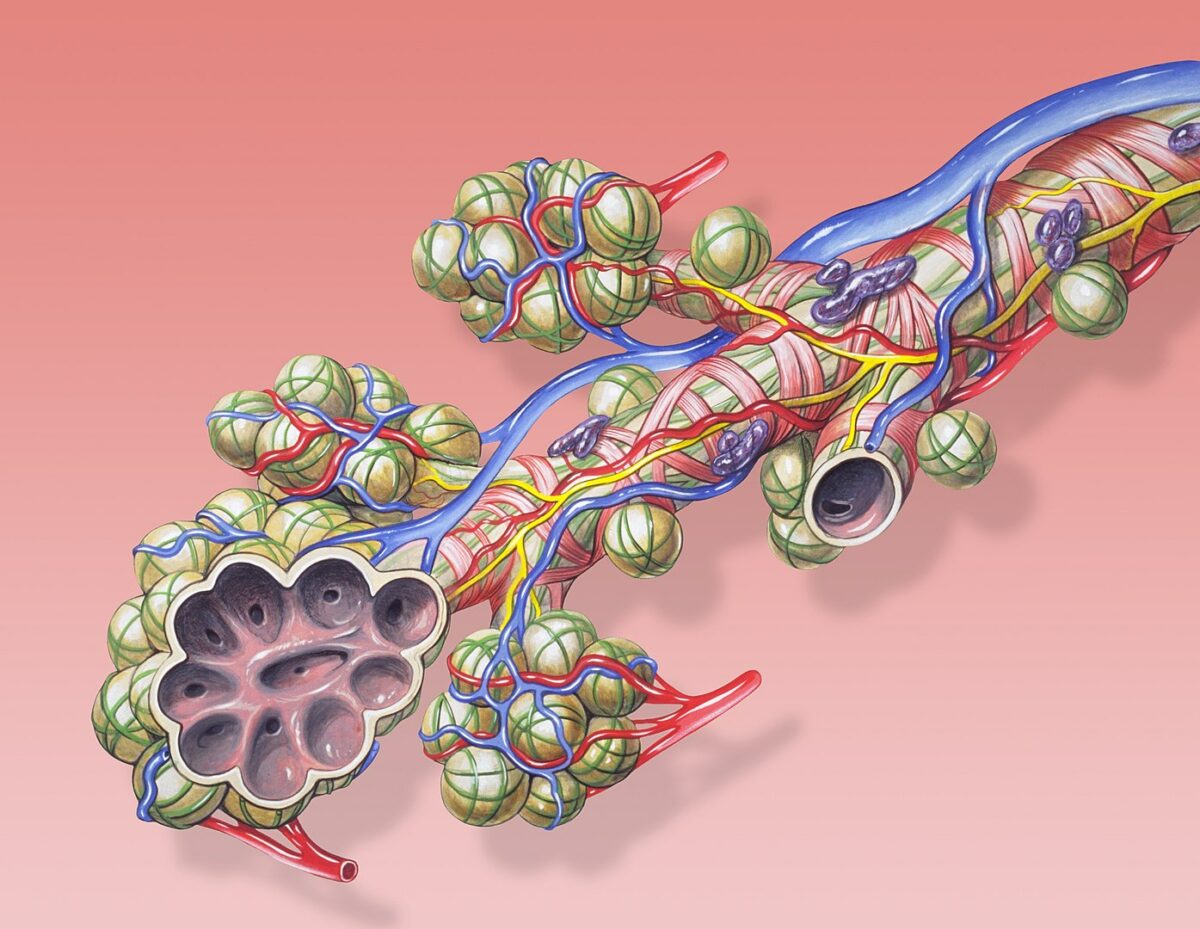
Overview Definition Pulmonary hypoplasia is the insufficient or defective development of one or both lungs, resulting in underdeveloped or undeveloped pulmonary parenchyma with decreased alveoli and airway branches. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Fetal lung development Abnormal fetal lung development Multiple aspects of the impairment of fetal lung growth can lead to hypoplasia. Clinical Presentation Antenatal Postnatal […]
Brief Resolved Unexplained Event
Overview Definition A brief resolved unexplained event (BRUE) is defined as a sudden and unexplained change in an infant’s breathing, appearance, or behavior that was brief (< 1 minute, average 20–30 sec) and is fully resolved. Change in terminology An “apparent life-threatening event” (ALTE) is no longer current but was defined as: BRUE specifies “there […]
Nephrotic Syndrome in Children
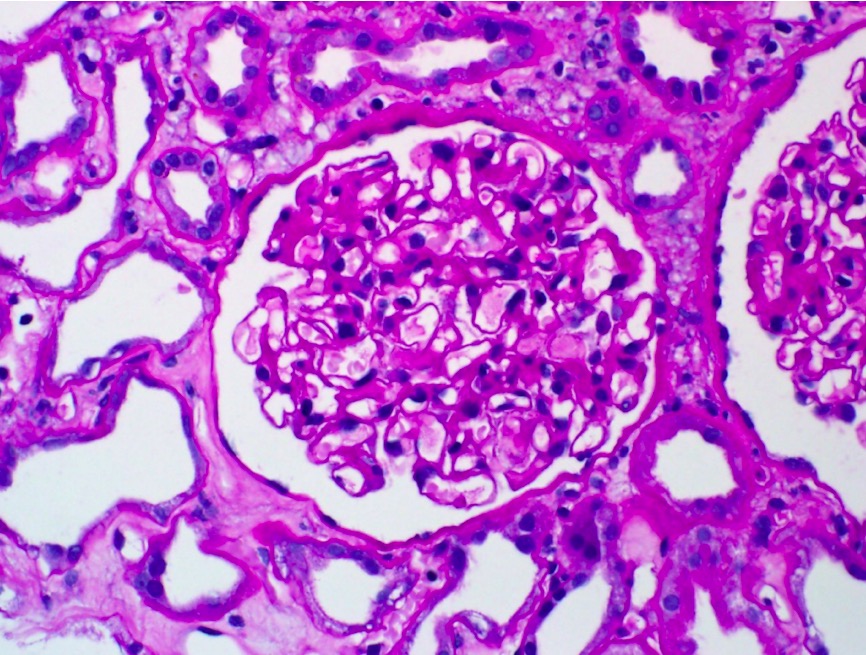
Overview Definition Nephrotic syndrome is a renal disorder characterized by increased permeability of the glomerular filtration barriers significantly leading to severe proteinuria. Classic features include: Epidemiology Classification Different general classification systems can overlap: Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome is further classified on the basis of steroid responsiveness: Etiology Congenital/infantile: Primary (90% idiopathic): Secondary: Pathophysiology The structure of […]