Febrile Infant

Overview Definition of fever Etiology Systematic approach in determining the cause of fever When to admit to inpatient care Young Infants Overview Diagnosis and management Table: Criteria for the management of the febrile baby (28 days–56 days old) Rochester, NY Philadelphia, PA Boston, MA Ultrasonography, urine culture, CBC, blood culture Yes Yes Yes Spinal tap […]
Thoracic Trauma in Children
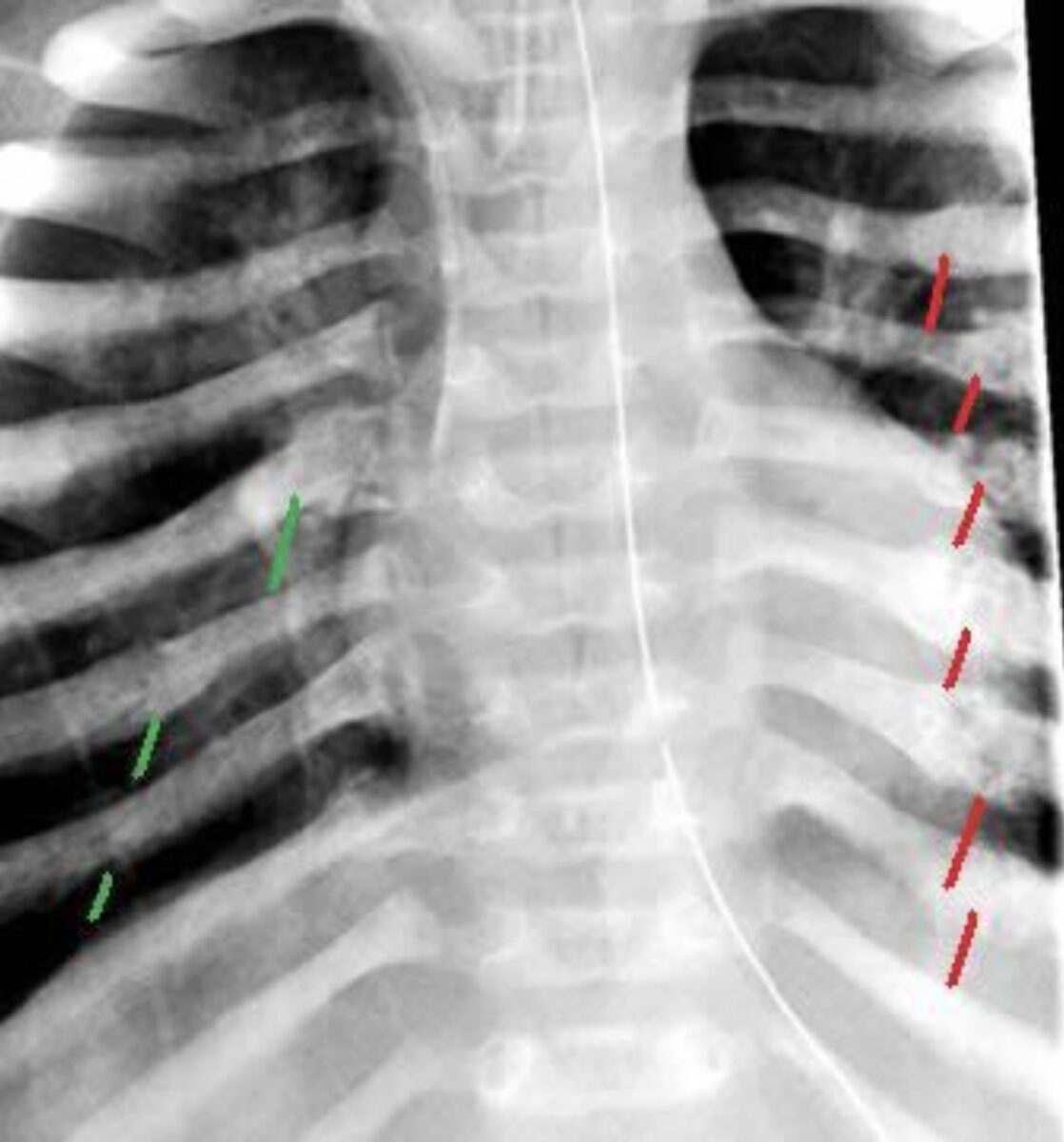
Overview Classification Epidemiology Pathophysiology and anatomy The thoracic region of a child is more compliant compared to that of adults: Common Thoracic Injuries Table: Common thoracic injuries in children Pneumothorax Common (33% of cases) Tension pneumothorax: sudden compromise in right heart filling Hemothorax Less common Described as a chest “white-out” in X-ray Hemothorax can contain […]
Meningitis in Children
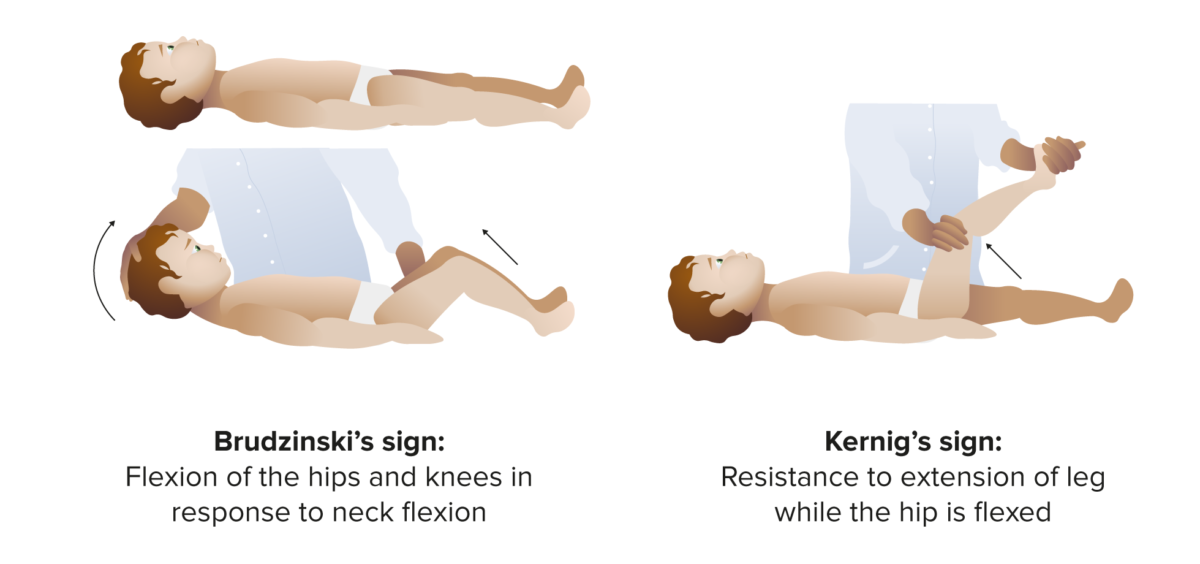
Overview Definition Meningitis is inflammation of the membranes, or meninges, surrounding the spinal cord and brain. Epidemiology Risk factors Etiology Table: Common causal agents of meningitis in children Bacteria Viruses Fungi Newborns: Group B Streptococcus Escherichia coli Listeria monocytogenes Infants > 1 month and children: S. pneumoniae Neisseria meningitidis H. influenzae type b Mycobacterium tuberculosis […]
Sepsis in Children
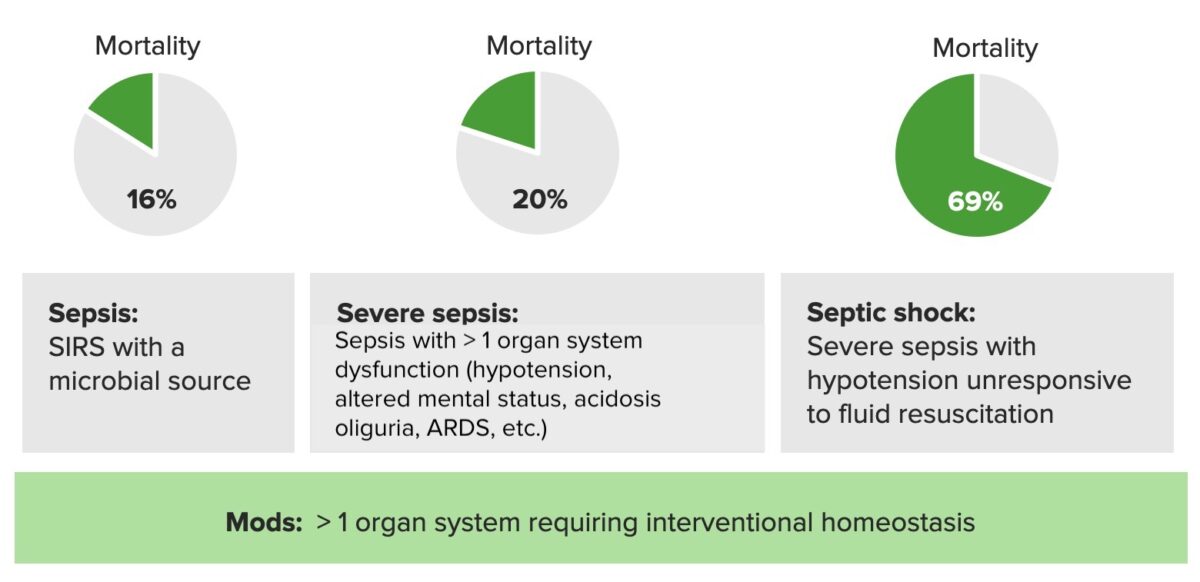
Overview Definition Systematic inflammatory response syndrome criteria Sepsis: Severe sepsis: Septic shock is severe sepsis that is unresponsive to fluid resuscitation. Other sepsis-scoring criteria Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Risk factors Etiology Pathophysiology The host’s ability to resist direct damage by the pathogen and immune system response determines if an infection can be controlled or will […]
Pediatric Diarrhea
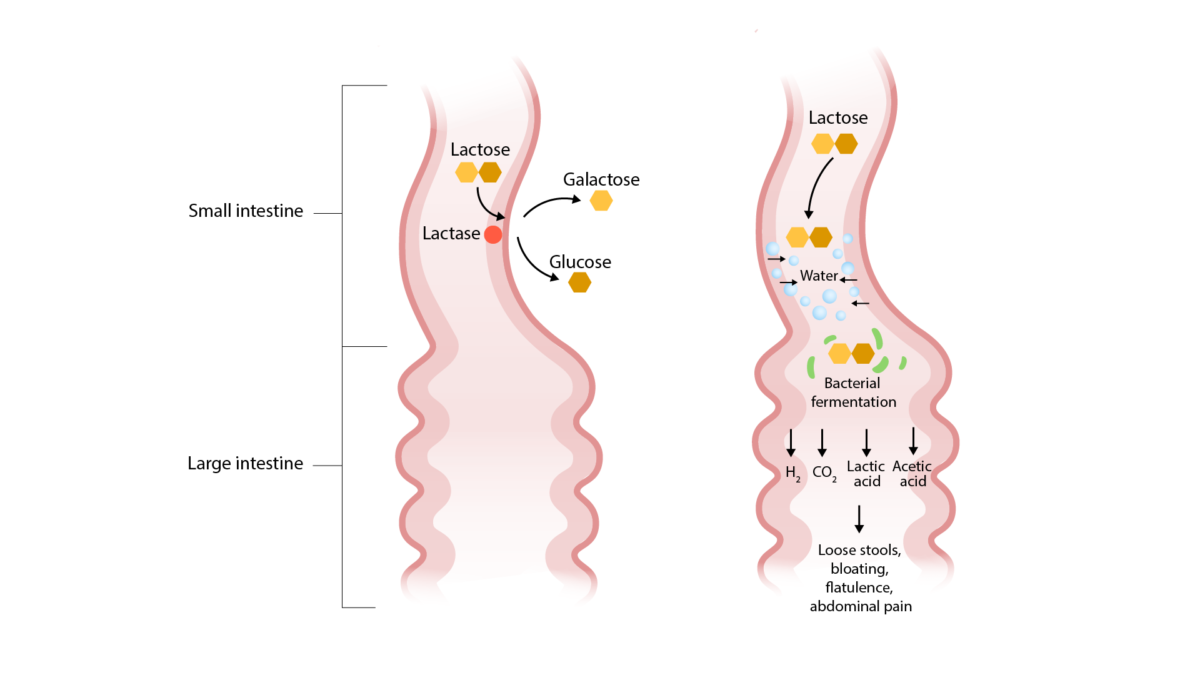
Overview Definition Diarrhea is defined as excess stool output that is often loose or watery. Quantification of stool output varies: Classification Epidemiology Etiology Acute Infants and young children: Older children: Chronic Infants and young children: Older children: Classifications Secretory Osmotic Increased motility Decreased motility Decreased surface area Mucosal invasion Clinical Presentation History Physical examination Table: […]
Child Abuse
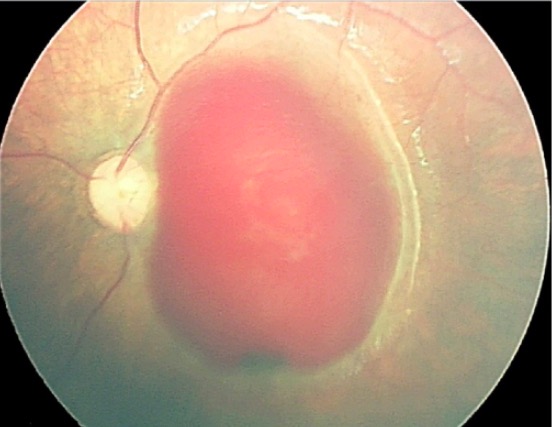
Overview Definition Child abuse refers to an act or failure to act that results in actual or potential harm to a minor’s health, development, or dignity by the parent or caregiver responsible for the child’s welfare. In the majority of the United States, a minor is defined as a child below 18 years of age, […]
Cerebral Palsy
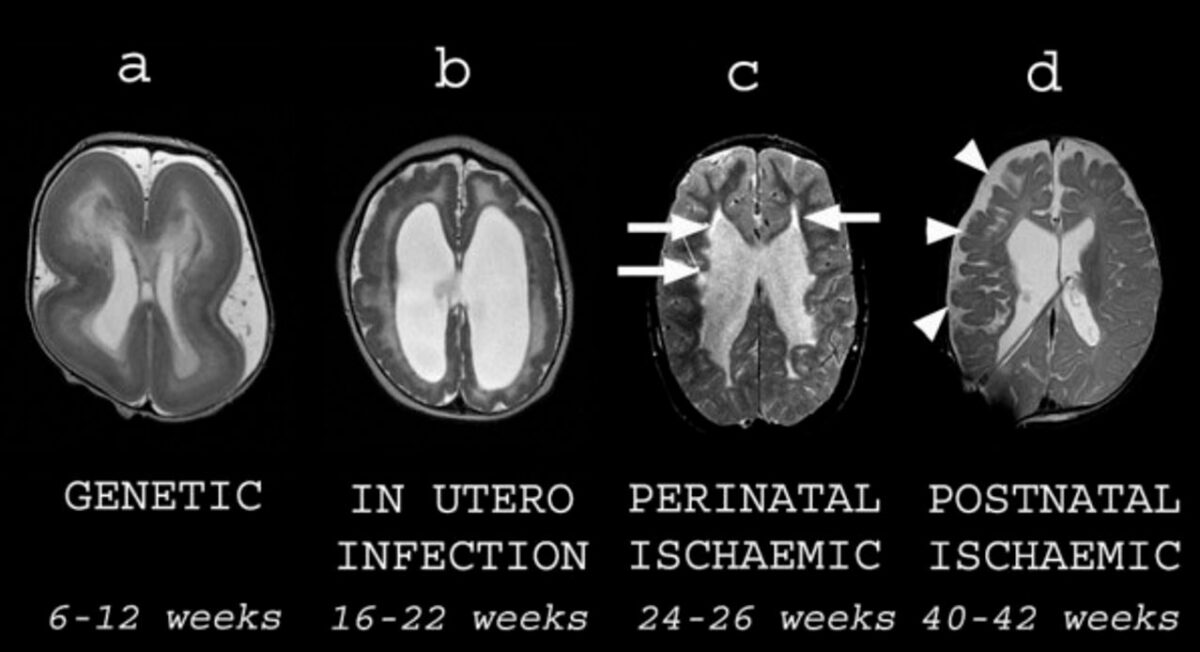
Overview Definition Cerebral palsy (CP) is a syndrome of permanent motor impairment (posture and movement) that results from nonprogressive lesions to the developing brain. Epidemiology Etiology Classification Pathophysiology The ultimate cause of CP is injury to a child’s CNS during its embryological or perinatal development. The pathophysiology of this insult varies based on its etiology. […]
Short Stature in Children
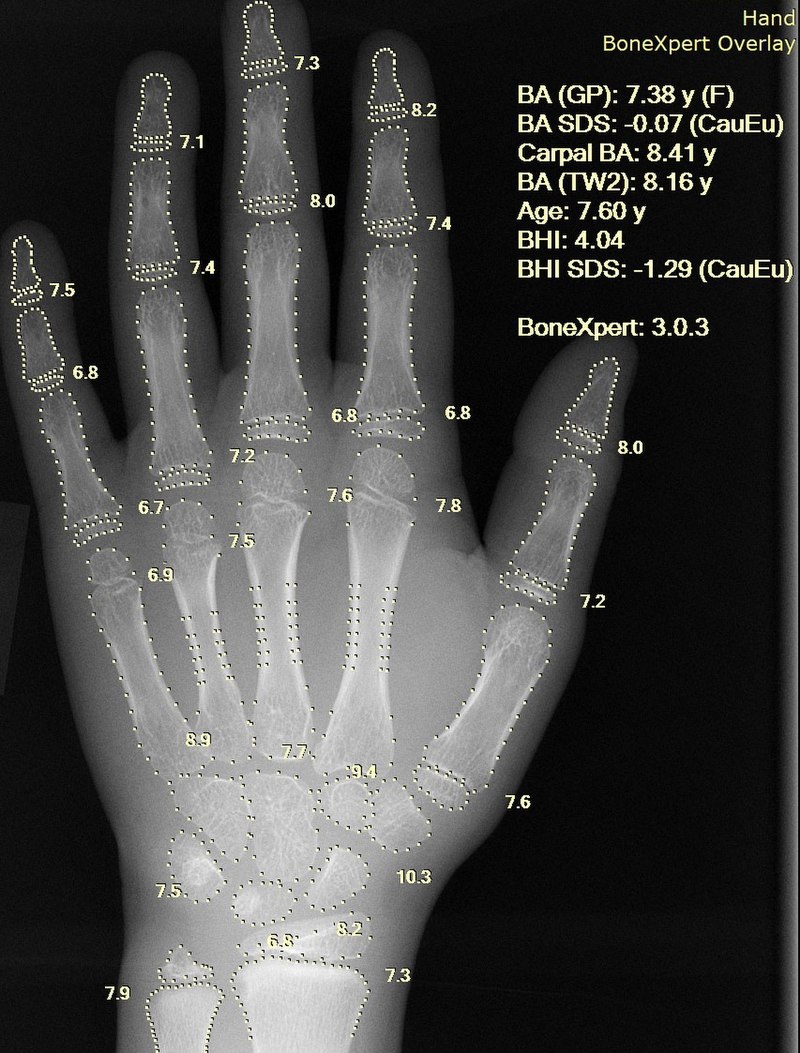
Overview Definition Children are diagnosed with short stature if their measured height is 2 standard deviations below the mean for age and sex. “Short stature” is an umbrella term, describing the result of processes that may be either idiopathic or pathological. Classification Idiopathic: normal variants of patterns of growth that often result in achieving full […]
Pneumonia in Children
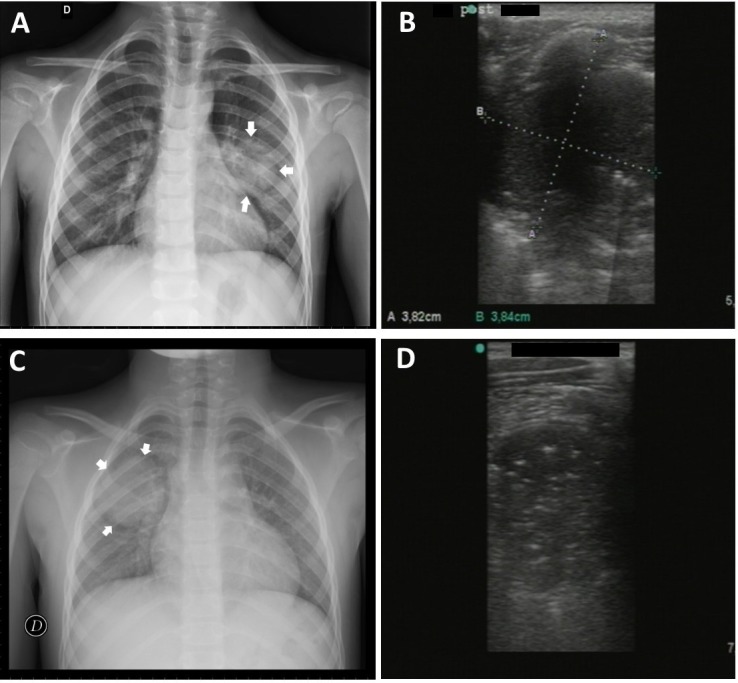
Overview Epidemiology Classification Etiology and Pathophysiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Clinical presentation Clinical presentation varies by age of patient and by course of the illness. By age: By clinical course: Criteria for respiratory distress in children with pneumonia Diagnosis Diagnosis made based on history and exam and can be confirmed or refined with imaging. Imaging […]
Developmental Milestones and Normal Growth

Overview Developmental milestones are a set of benchmarks in gross motor, fine motor, language, cognition, social/emotional, and behavior patterns expected by a certain age. Assessment of developmental disorders must take into account gestational age at birth; e.g., a premature baby should be expected to reach their milestones appropriately for their chronological age. Pediatricians assess developmental […]