Erythema Infectiosum (Clinical)
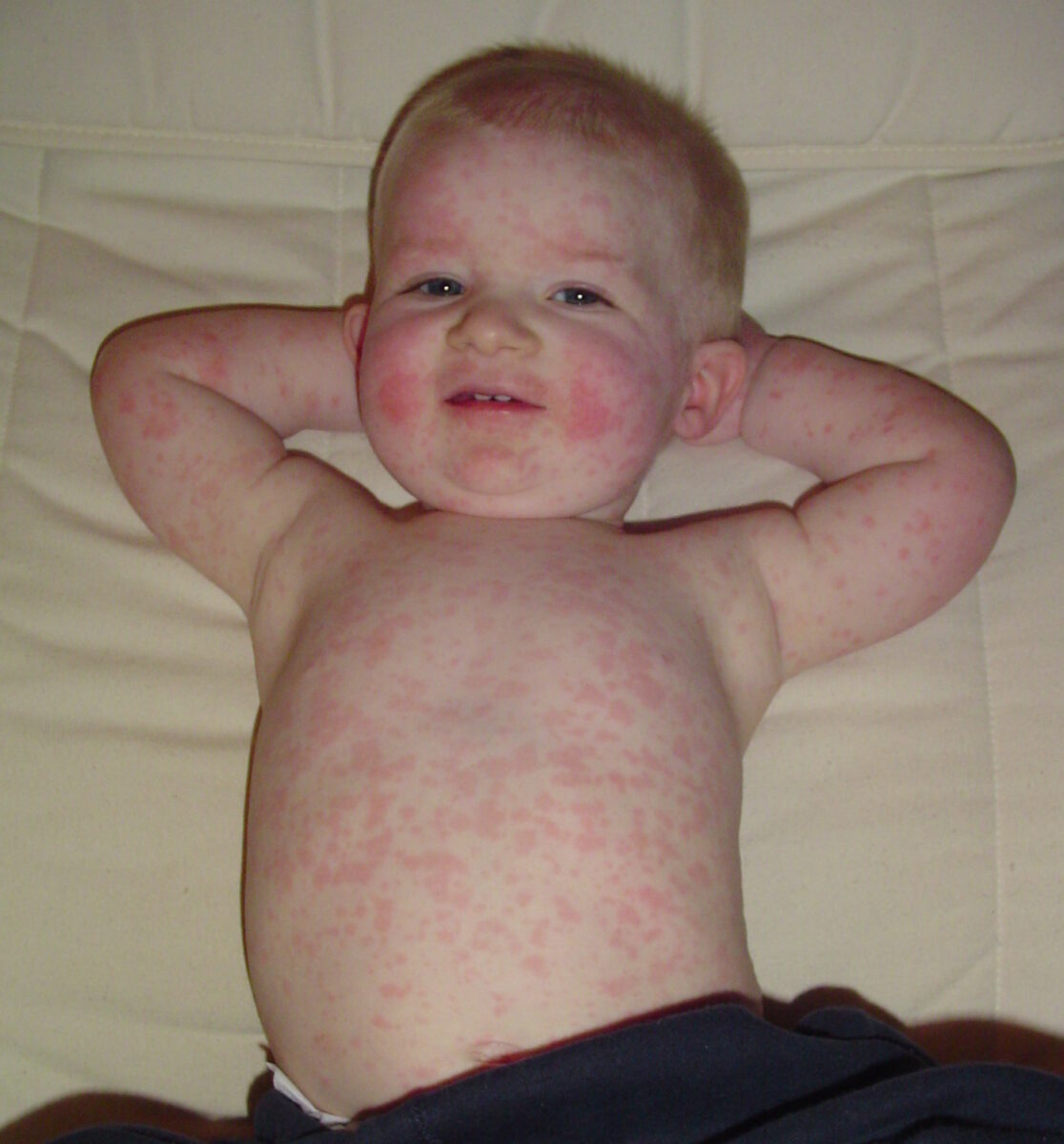
Overview Definition Erythema infectiosum is an illness caused by parvovirus B19, which presents with fever and a characteristic rash. Epidemiology[1–3] Pathophysiology Mode of transmission[3,4,15] Incubation[3,14,15] The incubation period is 4–21 days. Pathogenesis[3,7] Clinical Presentation Initial prodromal symptoms (viremia)[3,5,14,15] Later symptoms (viremia resolved)[3,5,14,15] Complications[4–6,8,13,14] Diagnosis and Management Diagnostic approach[4,10,13–15] Treatment Erythema infectiosum is generally a self-limited […]
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (Clinical)
Overview Definition Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is a disease of the capillaries (microangiopathy) that causes the formation of blood clots, anemia caused by the destruction of RBC in these clotted capillaries (hemolytic anemia), acute kidney injury, and low platelets (thrombocytopenia). Epidemiology[1–4] Etiology Etiology is classified as acquired (infectious versus noninfectious) or hereditary.[2,5,6,13] Pathophysiology The pathophysiology […]
Acute Bronchiolitis (Clinical)
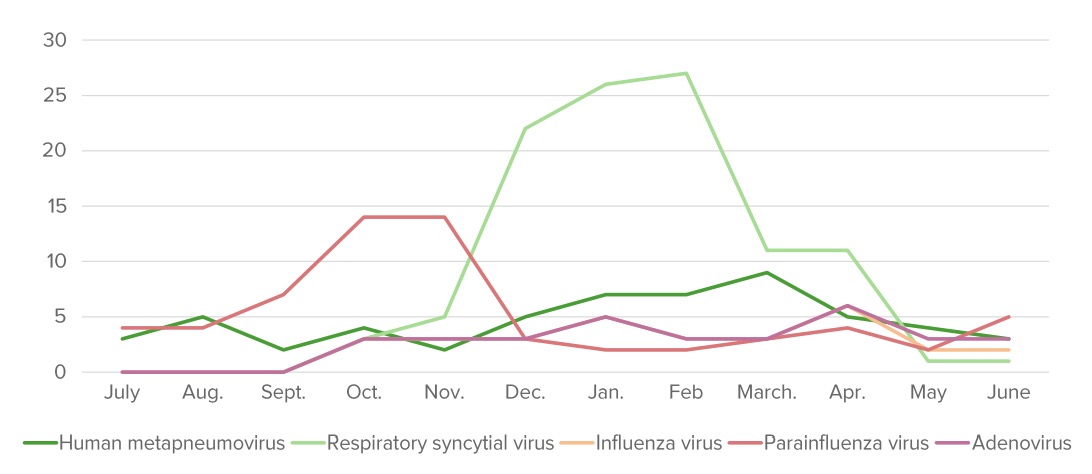
Overview Definition Acute bronchiolitis is a clinical constellation of respiratory symptoms (increased work of breathing, wheezing, and crackles) caused by acute inflammation of the small airways (small bronchi and bronchioles), typically secondary to viral infections. Epidemiology[2,3,6] Etiology[5,6] Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathophysiology[3,6,10] Pathologic changes are noted within 24 hours of contact with a pathogen: Clinical […]
Scarlet Fever (Clinical)
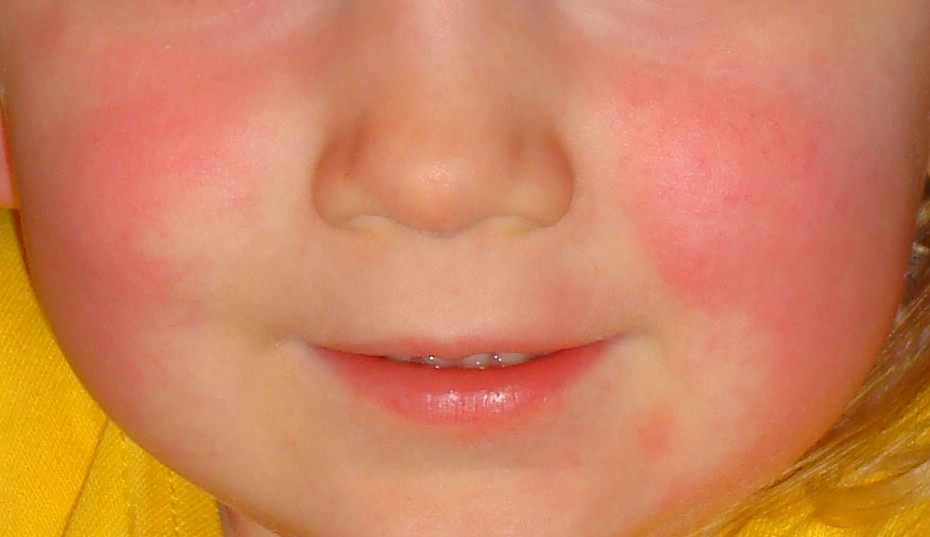
Overview Definition Scarlet fever (also called “scarlatina”) is a diffuse erythematous eruption or rash that occurs as a result of complications of infections with Streptococcus pyogenes. Epidemiology[2] Etiology[1,2] Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Symptoms[5–7] Signs[5–7] Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis[5,7] Choosing who to test and who treat[10–12] Selecting which patients to treat with antibiotics can be complex: Approach […]
Pertussis/Whooping Cough (Clinical)

Overview Epidemiology[1,2,12] Etiology[1,2,7,9,12] Risk factors[9,12] Individuals at risk for contracting pertussis and/or severe disease include: Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation First stage: catarrhal[4,7,9,12] Second stage: paroxysmal[2,4,7,9,12] Third stage: convalescent[4,7,9,12] Diagnosis Diagnosis is strongly suspected with clinical history but requires laboratory confirmation.[4,9,12,13] History: Laboratory tests: Management and Prevention Antimicrobial therapy Whom to treat:[9,12] Postexposure prophylaxis:[7,9,13] Options:[6,7,9,12] Cough management[5] […]
Chronic Apophyseal Injury
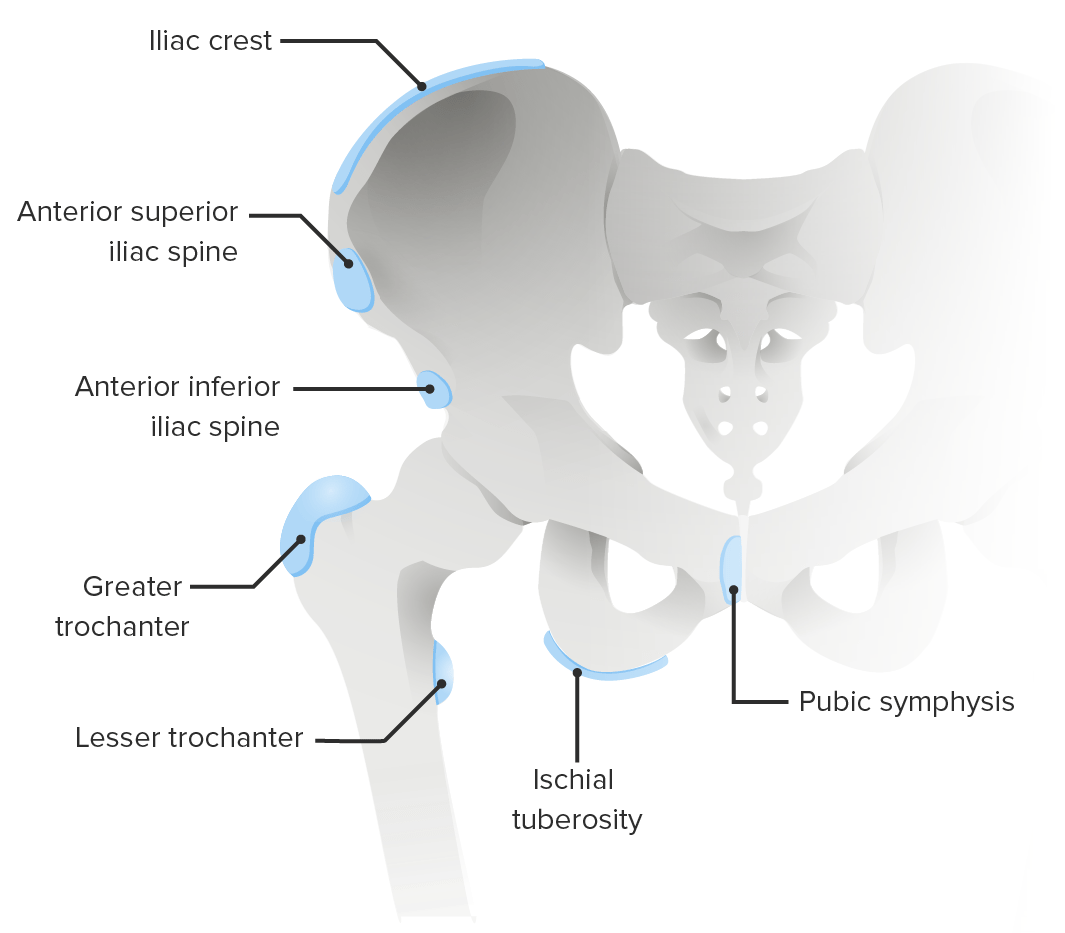
Overview Etiology The apophysis, a secondary ossification center, may be susceptible to repetitive or acute physical loading, which may lead to injury. Table: Risk factors for common types of chronic apophyseal injury Disease Risk factor Osgood-Schlatter disease (tibial tubercle apophysitis) Sports that involve running and jumping leading to repetitive tension or traction on the tibial […]
Congenital TORCH Infections
Overview TORCH A group of specific congenital infections acquired either in utero or during delivery: Toxoplasmosis Others (syphilis, varicella zoster virus (VZV), parvovirus B19, and HIV) Rubella CMV Herpes simplex Prenatal screening is important in identification. Epidemiology Toxoplasmosis 1 billion individuals affected worldwide The frequency in population depends on the incidence in women of childbearing […]
Cholestasis in Neonates and Young Infants
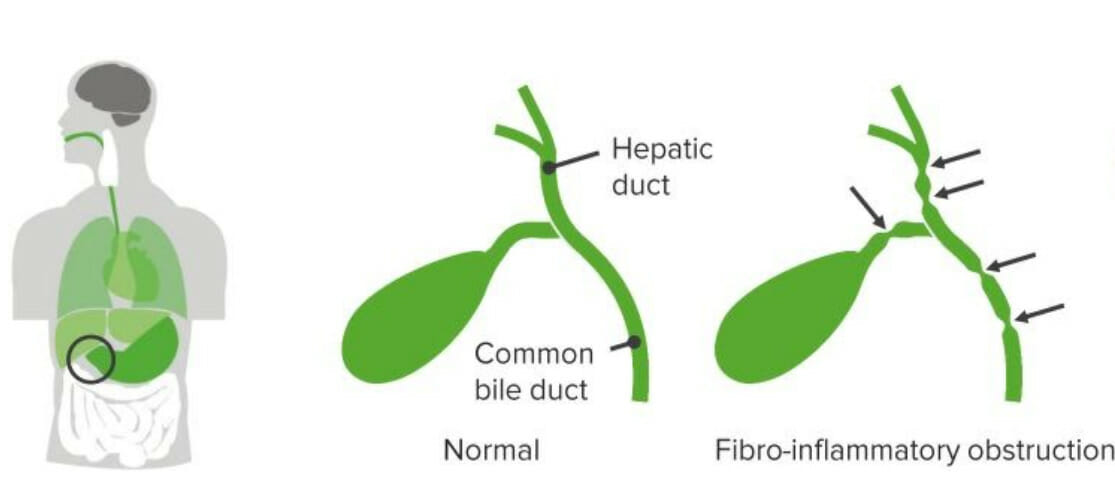
Overview Definition Cholestasis in neonates and young infants is conjugated hyperbilirubinemia in the 1st 3 months of life due to impaired bile excretion. Etiology Biliary tract malformations involving the gallbladder and bile duct are grouped into cystic and noncystic obliterative cholangiopathies, the most common of which is biliary atresia. Less common causes include the genetic […]
Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis (ADEM)
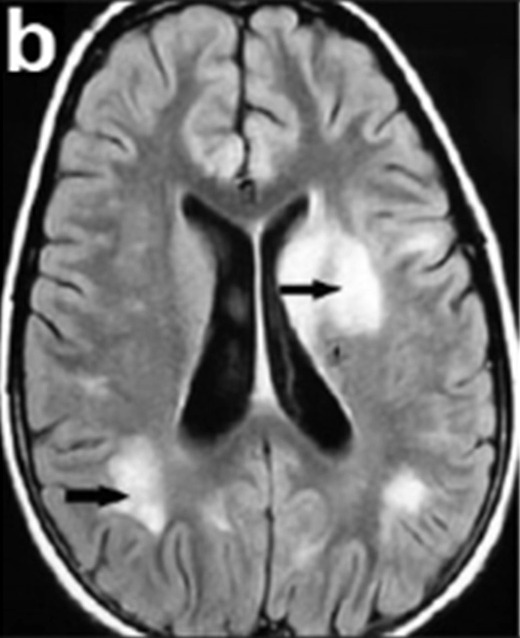
Overview Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM) is an acute neurologic deficit caused by an autoimmune attack on the brain and spinal cord that leads to multifocal demyelination. Pediatric ADEM All of the following criteria must be met for a diagnosis of pediatric ADEM: A polyfocal neurological event with a suspected demyelinating and inflammatory cause Unexplained encephalopathy […]
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Overview Juvenile idiopathic arthritis, formerly known as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, is the most common chronic rheumatological disease in the pediatric population. While there are multiple subgroups with distinct pathogeneses, the key feature is arthritis. Definition Juvenile idiopathic arthritis is a term used to describe a group of inflammatory conditions of the joints affecting children younger […]