Moraxella
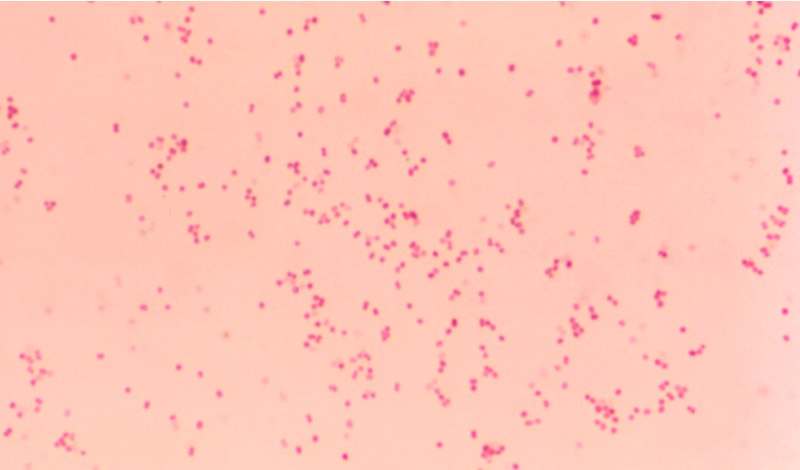
Classification Characteristics Features: M. catarrhalis and M. lacunata are the most clinically relevant species within this genus. Pathogenesis Transmission Pathogenic features Associated Diseases M. catarrhalis M. lacunata M. lacunata is a common cause of chronic angular blepharoconjunctivitis in humans. Diagnosis Treatment References
Taenia/Taeniasis
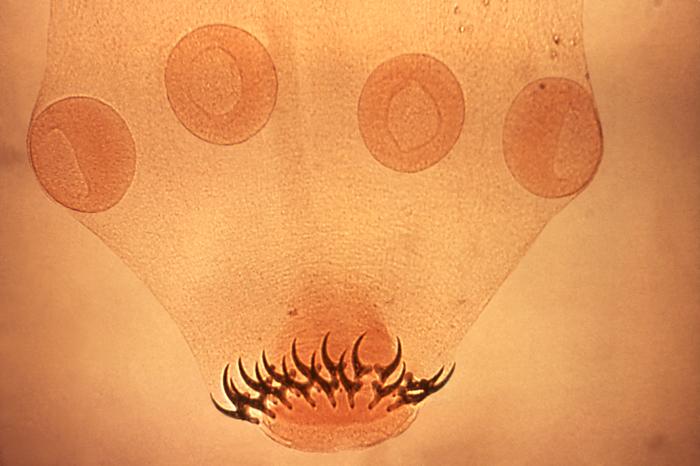
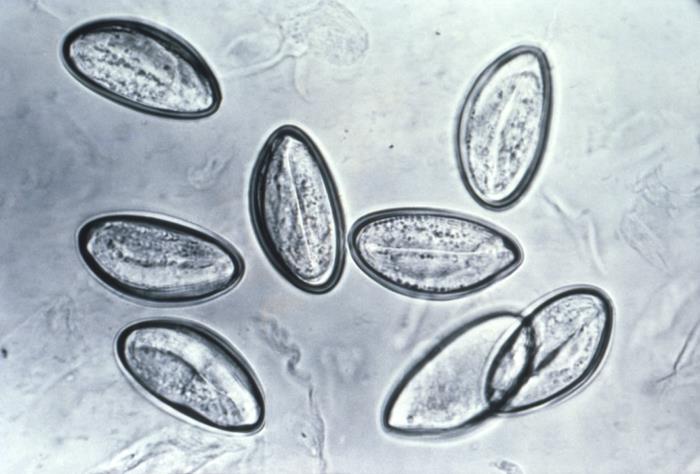
General Characteristics and Epidemiology General features of Taenia Taenia is a genus of parasitic cestodes (tapeworms). Eggs: Adults: Clinically relevant species Taenia tapeworms cause the following diseases: Epidemiology Geographic distribution of species: Taeniasis: Cysticercosis: Pathogenesis Hosts Risk factors for hosts Transmission Life cycle and pathophysiology Taeniasis: Cysticercosis: Clinical Presentation Taeniasis Most patients (particularly adults) are […]
Enterobius/Enterobiasis
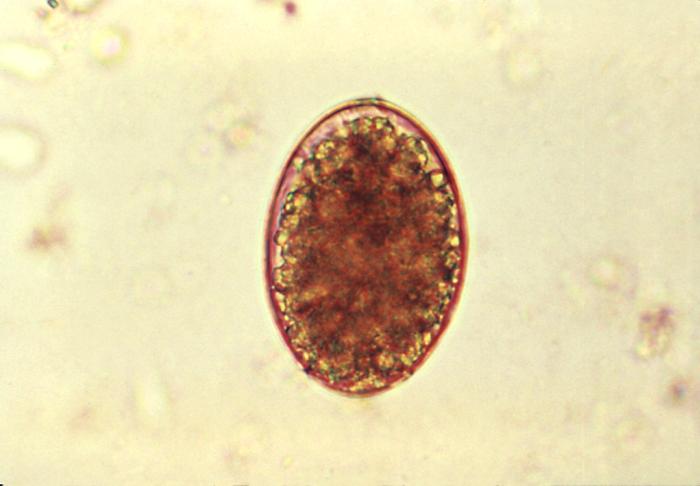
General Characteristics and Epidemiology Basic features of Enterobius Clinically relevant species Enterobius vermicularis, or pinworm, causes enterobiasis. Epidemiology Enterobiasis is the most common helminth infection in the United States and Western Europe. Pathogenesis Reservoir Humans are the primary hosts of E. vermicularis. Transmission Host risk factors Life cycle The entire life cycle of E. vermicularis […]
Dibothriocephalus/Diphyllobothriasis
General Characteristics and Epidemiology General features Diphyllobothriasis, or Dibothriocephalus infection, is caused by a parasitic infection from cestodes (tapeworms) in the genera Dibothriocephalus and Adenocephalus. Clinically relevant species Epidemiology Pathogenesis Hosts Definitive hosts: Intermediate hosts: Transmission Diphyllobothriasis is transmitted through the consumption of raw or undercooked fish. Life cycle Clinical Presentation General signs and symptoms […]
Echinococcus/Echinococcosis
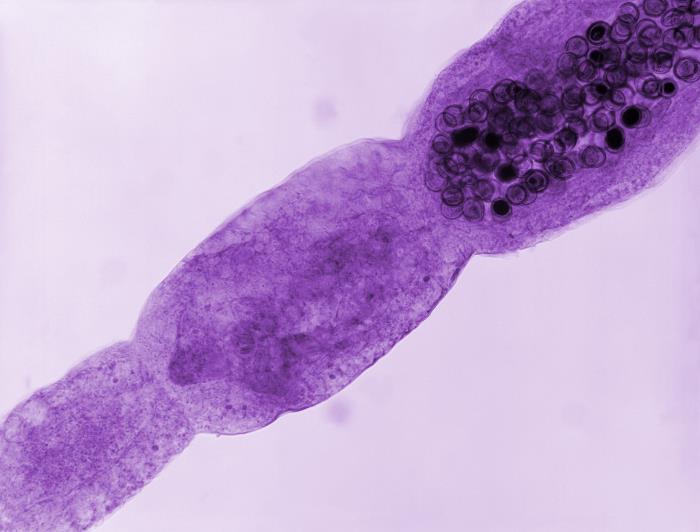
General Characteristics and Epidemiology General features of Echinococcosis Echinococcosis is a parasitic disease caused by Echinococcus tapeworms. Features include: Eggs: Adults: Clinically relevant species Epidemiology E. granulosus: E. multilocularis: E. vogeli and E. oligarthrus: Pathogenesis Hosts E. granulosus: E. multilocularis: Transmission Transmission occurs through ingestion of eggs, usually from food or water contaminated with animal […]
Toxocariasis
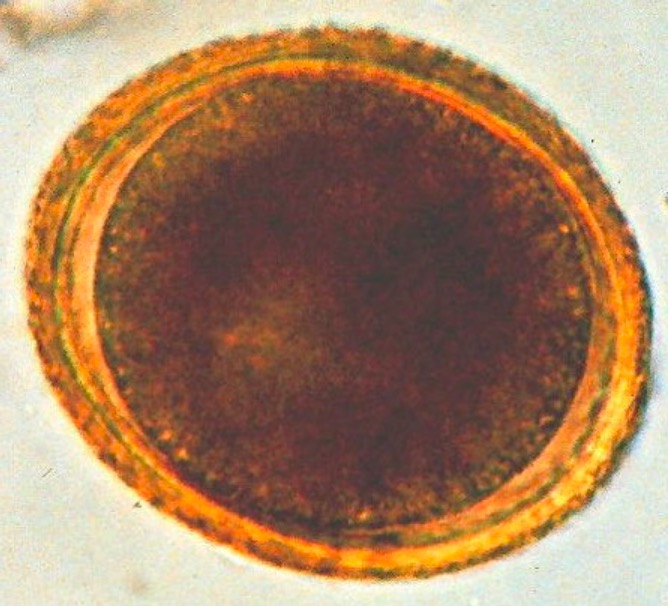
General Characteristics and Epidemiology Basic features of Toxocara Clinically relevant species Toxocariasis is caused by the following species: Epidemiology Pathogenesis Reservoir Transmission Transmission occurs through: Host risk factors Life cycle and pathophysiology In animals: In humans: Clinical Presentation Most Toxocara infections are asymptomatic and have a benign course. The 2 major forms of toxocariasis are […]
Coxiella/Q Fever
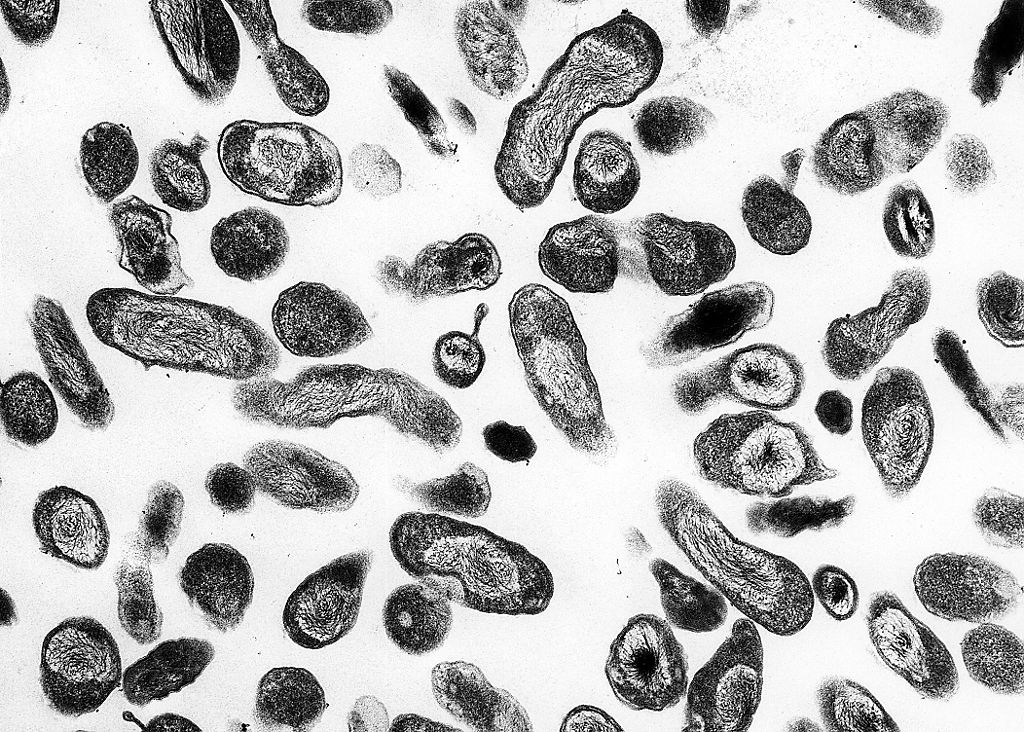
General Characteristics of Coxiella General features of Coxiella Clinically relevant species Coxiella burnetii causes Q fever. Epidemiology and Pathogenesis Epidemiology Reservoir Routes of transmission Host risk factors Virulence factors Antigenic phase variation: Morphological variants: Escape from intracellular killing: Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Patients may present with a wide range of symptoms, and vary in severity from […]
Trichinella/Trichinellosis
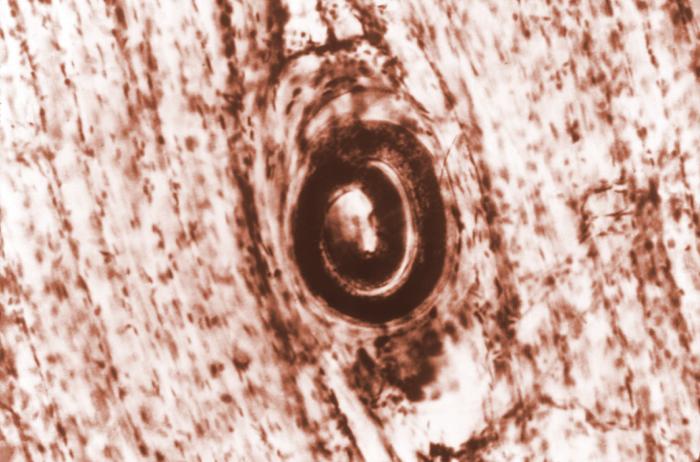
General Characteristics Basic features of Trichinella Clinically relevant species Epidemiology Pathophysiology Reservoirs and transmission Pathogenesis Clinical Presentation Complications Diagnosis Diagnostic tests Additional tests Management Treatment Prognosis Differential Diagnosis References
Hookworm Infections
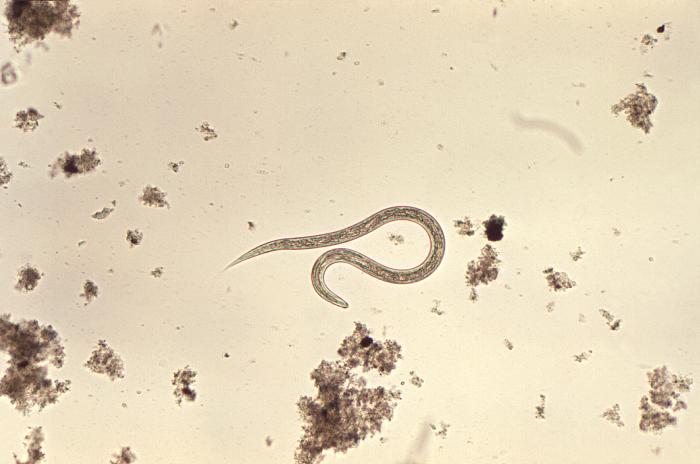
Overview General characteristics Epidemiology Host risk factors Pathogenesis Reservoirs and transmission Life cycle Disease process Clinical Presentation Dermal penetration Pulmonary stage Gastrointestinal stage Nutritional impairment Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Management Medical management: Prevention: Differential Diagnosis References
Plasmodium/Malaria
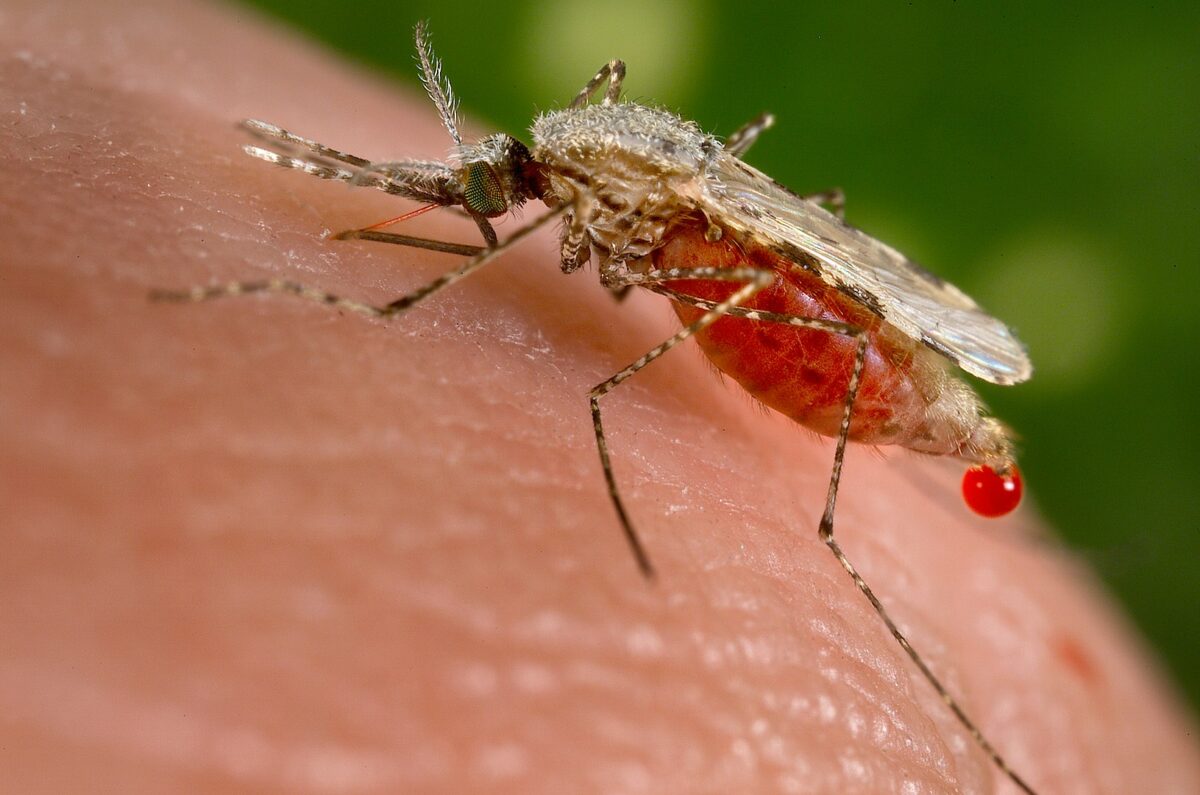
Overview Definition Malaria is a parasitic disease caused by unicellular parasites of the Plasmodium genus and transmitted by mosquitoes of the Anopheles genus. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Transmission Plasmodium life cycle Plasmodium is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes, which are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Uncomplicated malaria Severe malaria Diagnosis History and […]