Pneumocystis jirovecii/Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PCP)
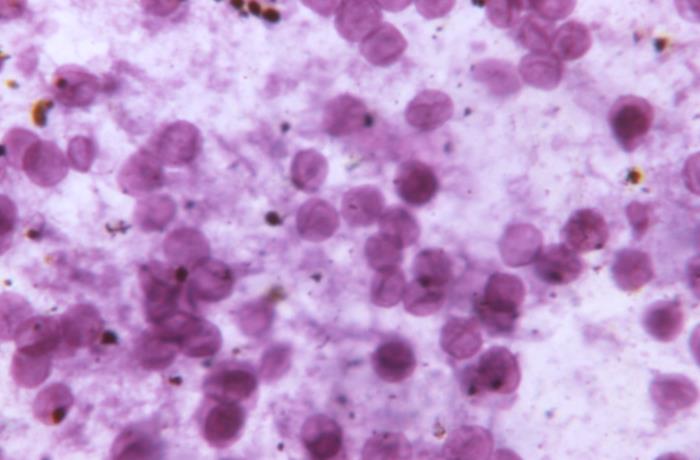
General Characteristics Basic features of Pneumocystis Pneumocystis is a yeast-like fungus. Clinically relevant species P. jirovecii (formerly known as P. carinii) causes pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP). Epidemiology and Pathogenesis Epidemiology Reservoir The reservoir for P. jirovecii is unknown, but immunocompetent humans may play a role. Transmission P. jirovecii spreads through airborne transmission. Host risk factors Pneumocystis […]
Dermatophytes/Tinea Infections
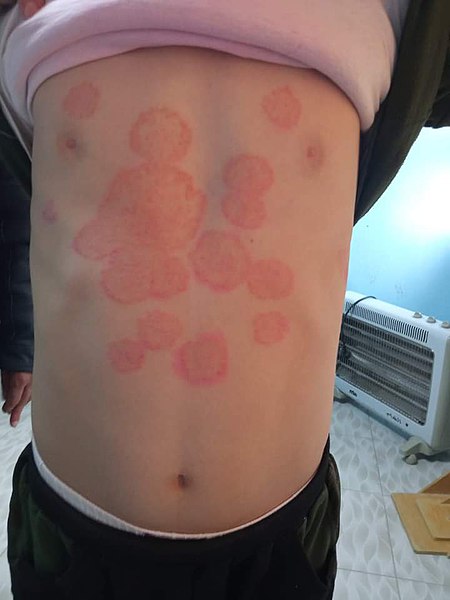
Overview General characteristics of dermatophytes Dermatophytes are filamentous fungi that belong to the genera Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton. Dermatophytes have septate hyphae with chains of conidia. Classification of tinea infections Tinea infections are classified and named by the body region affected. Tinea pedis: “Athlete’s foot” Infection of the interdigital webs of the feet Tinea corporis: […]
Rubella Virus
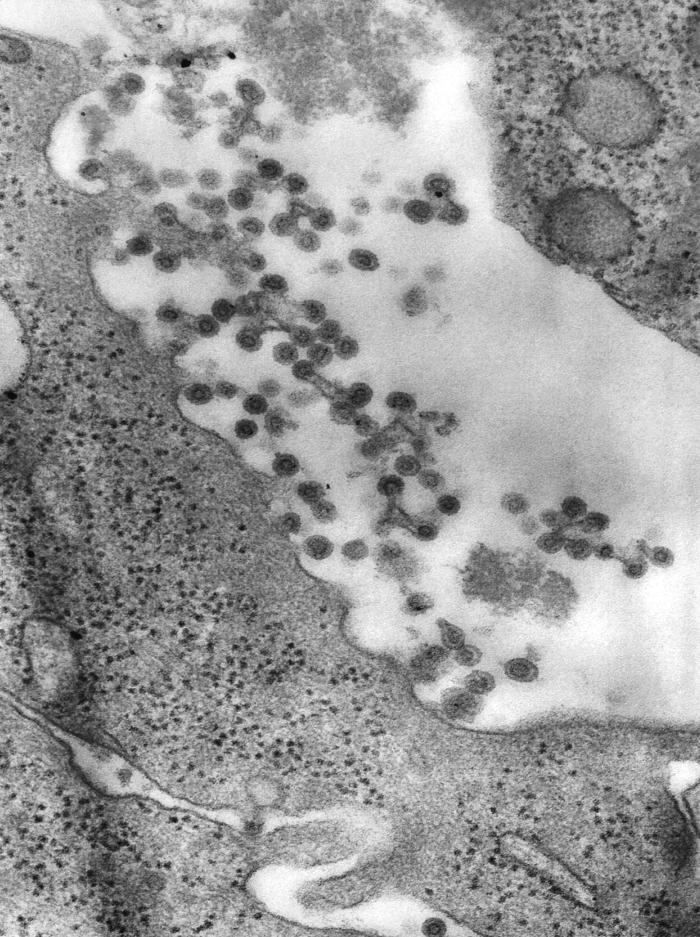
Classification General Characteristics Serotypes, lineages, and strains: Rubella virion Structure: Rubella genome Epidemiology and Pathogenesis Epidemiology Transmission Pathogenesis Prenatal: Postnatal: Postnatal primary infections with rubella undergo a sequential pathogenic process: Clinical Presentation Congenital rubella Postnatal rubella Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention Diagnosis Diagnosis is made clinically and confirmed with serum virus detection and serologic studies. Management […]
Parainfluenza Virus
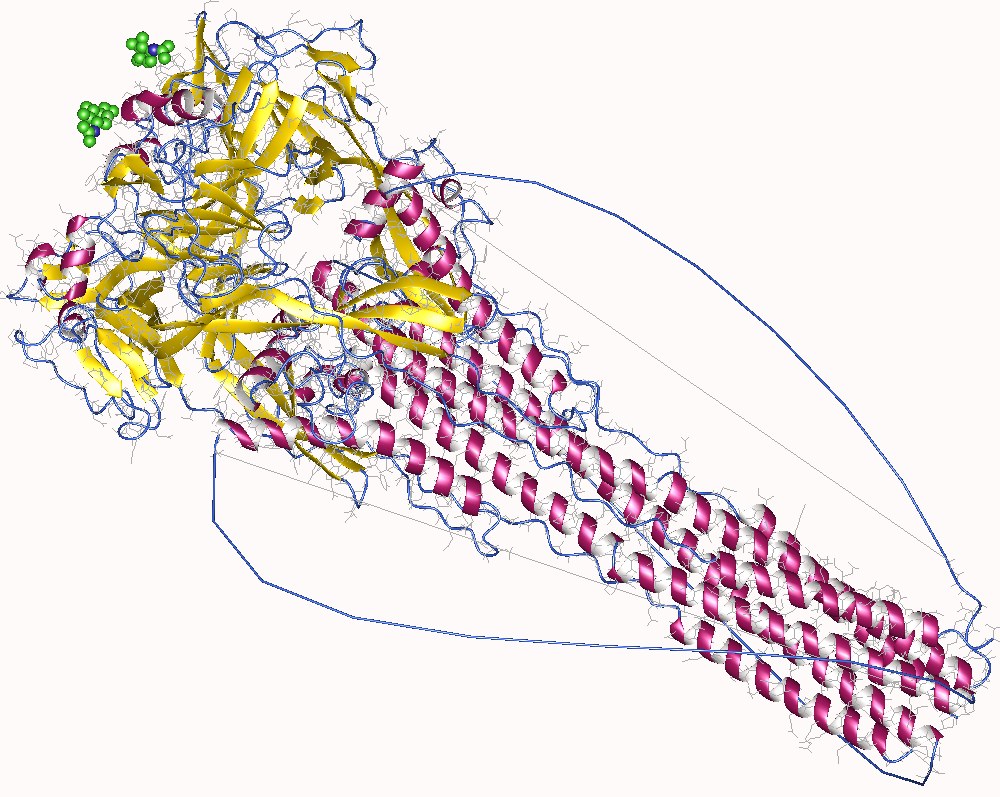
Classification General Characteristics Structure Clinically relevant species Pathogenesis Transmission Virulence factors HPIVs have 6 main proteins: Replication cycle Pathophysiology HPIVs cause inflammation of the airway through the up-regulation of inflammatory cytokines, including: Virus-specific IgE antibodies mediate the release of histamine in the respiratory tract, contributing to the symptoms and pathogenesis of croup. Risk factors Diseases […]
St. Louis Encephalitis Virus

Classification General Characteristics and Epidemiology Basic features of St. Louis encephalitis virus (SLEV) Taxonomy: Family: Flaviviridae Genus: Flavivirus RNA virus Single-stranded Positive-sense Linear Spherical Icosahedral symmetry Enveloped Size: Approximately 50 nm Positive-sense ssRNA core Associated disease St. Louis encephalitis virus causes St. Louis encephalitis (SLE). Epidemiology Incidence: 0.003–0.752 cases per 100,000 people in the United […]
Tick-borne Encephalitis Virus
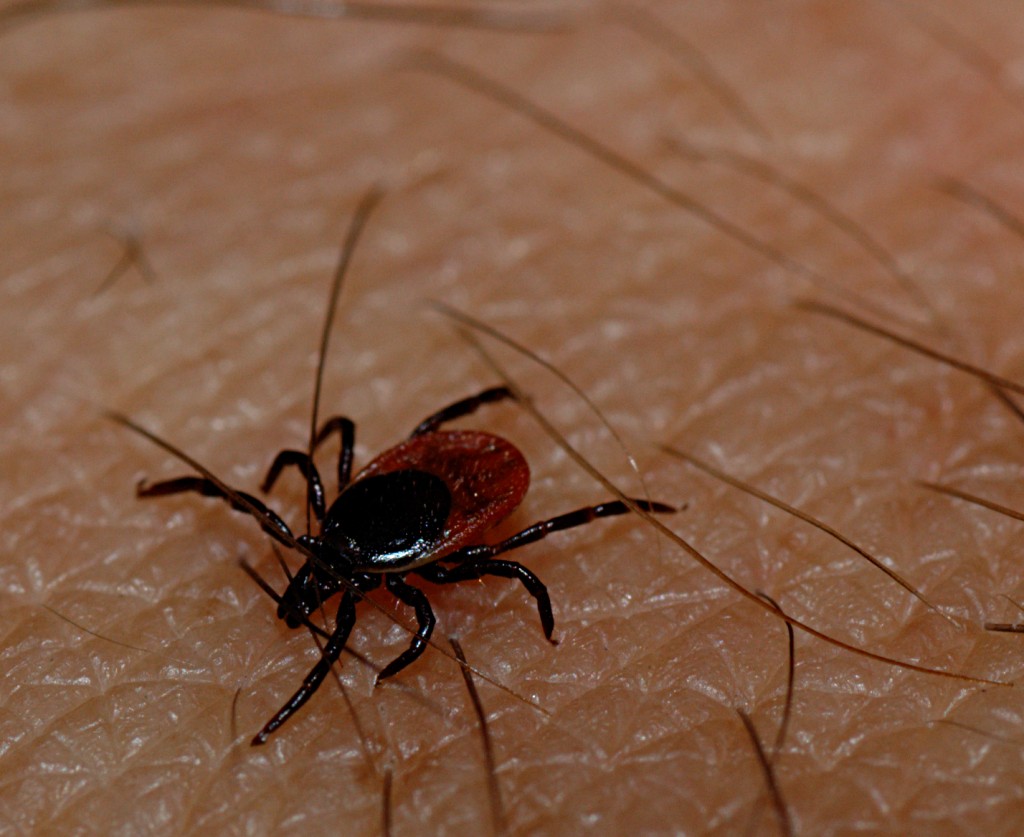

Classification General Characteristics and Epidemiology Basic features of tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) Taxonomy: Family: Flaviviridae Genus: Flavivirus RNA virus Single-stranded Positive-sense Linear Spherical Icosahedral symmetry Enveloped capsid Size: approximately 50 nm Clinically relevant species Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is caused by 3 subtypes of closely related viruses: European (Western) Siberian Russian (Far Eastern) Epidemiology TBE is […]
West Nile Virus
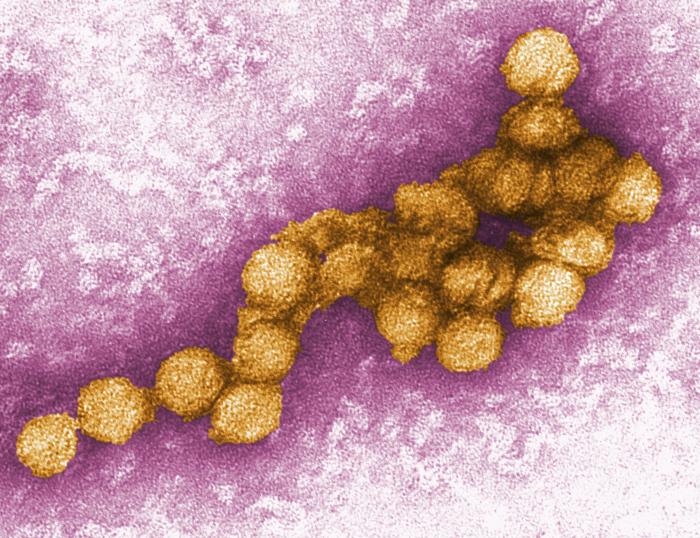
Classification General Characteristics and Epidemiology Basic features of West Nile virus Taxonomy: Flaviviridae family Flavivirus genus RNA virus: Single stranded Positive sense Linear Spherical Icosahedral symmetry Enveloped Size: approximately 50 nm Associated disease Two phylogenetic lineages of West Nile virus cause the following diseases: West Nile fever Neuroinvasive disease: Meningitis Encephalitis Acute flaccid paralysis Epidemiology […]
Yellow Fever Virus
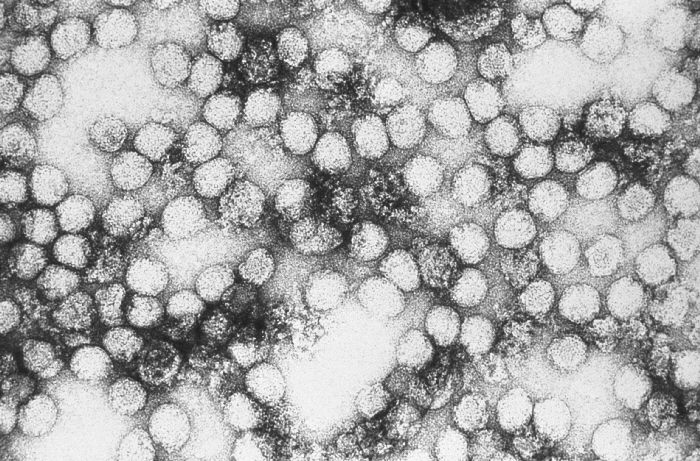
Classification General Characteristics and Epidemiology Basic features of yellow fever virus Taxonomy: Family: Flaviviridae Genus: Flavivirus RNA virus: Single-stranded Positive-sense Linear Spherical Icosahedral symmetry Enveloped Size: 40–60 nm Clinically relevant species Yellow fever virus has only 1 serotype, which causes the disease (yellow fever). Epidemiology Approximately 200,000 infections per year worldwide Approximately 30,000 deaths per […]
Echovirus

Classification General Characteristics and Epidemiology General features of Echovirus Echoviruses (Enteric Cytopathic Human Orphan viruses) represent strains of various species within: Family: Picornaviridae Genus: Enterovirus RNA virus: Linear Single stranded Positive sense Functions as mRNA Diameter: 20–30 nm Icosahedral symmetry Lacks a lipid envelope Acid resistant Clinically relevant species There are approximately 29 recognized Echovirus […]
Entamoeba spp./Amebiasis
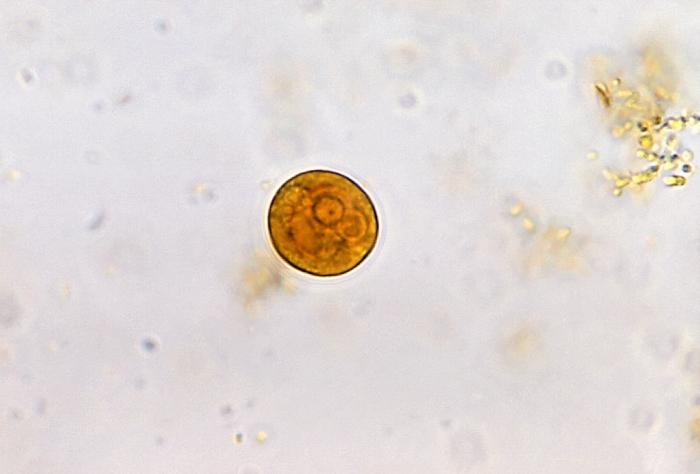
Overview Epidemiology Etiology Causative organism: anaerobic protozoan parasites of the Entamoeba genus Transmission occurs through the ingestion of cysts: Risk factors and high-risk populations: Pathophysiology Life cycle of Entamoeba species (spp.) The life cycle of Entamoeba spp. is dependent on the infection of a host because transition through the life stages occurs within the host’s […]